SpringMVC系列或者是SpringBoot系列中都会有大量的案例,这些案例都需要运行来验证效果,所以急需一款高效的接口测试工具。
可能大家用的比较多的是swagger或者postman,这2个确实不错,不过今天今天给大家推荐一种更简单的接口测试工具。
这款工具就是idea中的自带的: HTTP Client ,这款工具特别好用,主要的优点:
1、若想测试一个接口,只需要几行代码
2、运行特别容易
3、方便切换各种环境
1、创建一个springboot项目
idea中创建一个springboot项目,来个controller,内容如下,模拟了5种常见的情况,基本上包含了我们开发中所有的场景
@RestController
public class IndexController {
//get请求
@RequestMapping("/get")
public String get() {
return "get";
}
//post请求,模拟表单提交
@PostMapping("/post")
public Map<String, String[]> post(HttpServletRequest request) {
return request.getParameterMap();
}
//post请求json数据
@PostMapping("/body")
public List<Integer> body(@RequestBody List<Integer> list) {
return list;
}
//put请求
@PutMapping("/put")
public String put() {
return "put";
}
//模拟多文件上传,顺便带上表单数据
@PostMapping("/upload")
public Map<String, Object> upload(@RequestParam("file1") MultipartFile file1,
@RequestParam("file2") MultipartFile file2,
User user,
HttpServletRequest request) {
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("file1.size", file1.getSize());
result.put("file1.name", file1.getName());
result.put("file2.originalFilename", file1.getOriginalFilename());
result.put("file2.size", file2.getSize());
result.put("file2.name", file2.getName());
result.put("file2.originalFilename", file2.getOriginalFilename());
result.put("params", request.getParameterMap());
result.put("user", user);
return result;
}
static class User {
private String userName;
private int age;
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
}
项目结构如下图
启动项目,下面我们来对这几个接口进行测试。
2、测试上面5个接口
下面我们通过HTTP Client工具来对上面几个接口进测试。
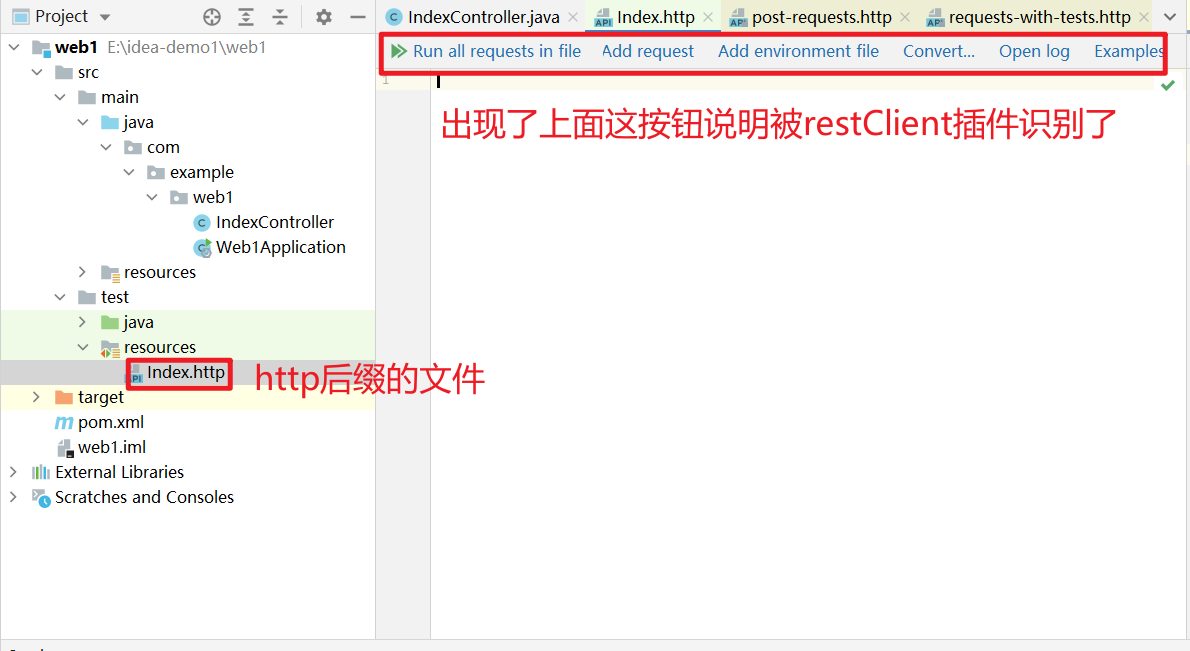
2.1、创建http后缀的文件
文件必须以http为后缀,这种文件会自动被 HTTP Client 插件识别,效果如下
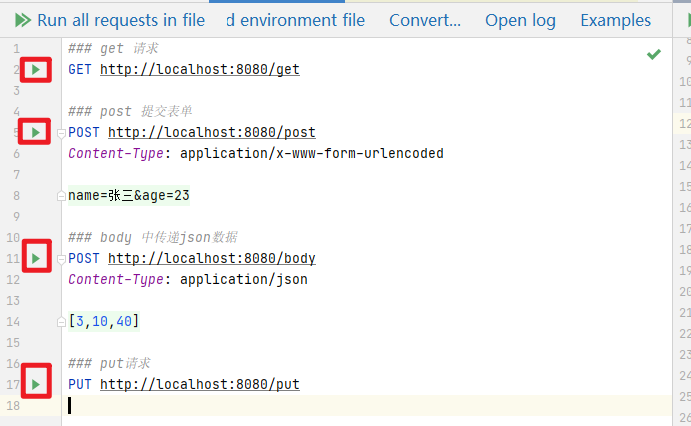
2.2、将下面内容丢到创建好的文件中
### get 请求
GET http://localhost:8080/get
### post 提交表单
POST http://localhost:8080/post
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
name=张三&age=23
### body 中传递json数据
POST http://localhost:8080/body
Content-Type: application/json
[3,10,40]
### put请求
PUT http://localhost:8080/put
### 多文件上传文件接口测试
POST http://localhost:8080/upload
Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=WebAppBoundary
--WebAppBoundary
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="file1"; filename="pic_1.jpeg"
< C:\Users\Think\Desktop\1.jpeg
--WebAppBoundary--
--WebAppBoundary
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="file2"; filename="pic_2.jpeg"
< C:\Users\Think\Desktop\2.jpeg
--WebAppBoundary--
--WebAppBoundary--
Content-Disposition: form-data;name=userName
tom
--WebAppBoundary--
--WebAppBoundary--
Content-Disposition: form-data;name=age
23
--WebAppBoundary--
###
接口格式很简单,如下
请求方式 地址
header部分,key=value格式,每个一行
参数部分(注意这个上面要有个空行)
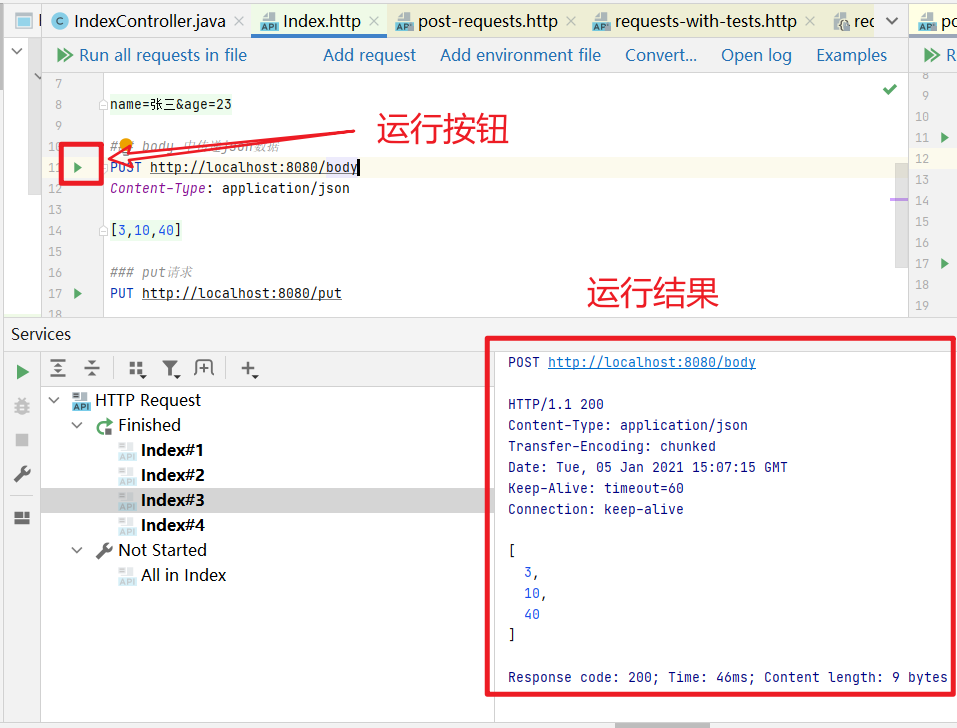
此时文件的效果是下面这样,点击红框中的按钮,即可以运行这个测试用例
2.3、运行接口
3、http文件内容如何写?
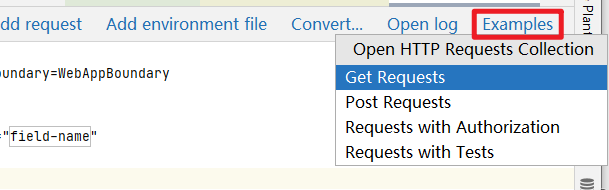
HTTP Client 提供了很多案例,点击 Examples 案例可以看到各种请求案例,这里就不细说了,大家一看就懂。
4、文件上传的写法
多文件上传且携带表单数据,这个比较特别,下面是接口代码
//模拟多文件上传,顺便带上表单数据
@PostMapping("/upload")
public Map<String, Object> upload(@RequestParam("file1") MultipartFile file1,
@RequestParam("file2") MultipartFile file2,
User user,
HttpServletRequest request) {
}
对应的 HTTP Client 的写法如下:
### 多文件上传文件接口测试
POST http://localhost:8080/upload
Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=WebAppBoundary
--WebAppBoundary
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="file1"; filename="pic_1.jpeg"
< C:\Users\Think\Desktop\1.jpeg
--WebAppBoundary--
--WebAppBoundary
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="file2"; filename="pic_2.jpeg"
< C:\Users\Think\Desktop\2.jpeg
--WebAppBoundary--
--WebAppBoundary--
Content-Disposition: form-data;name=userName
tom
--WebAppBoundary--
--WebAppBoundary--
Content-Disposition: form-data;name=age
23
--WebAppBoundary--
###
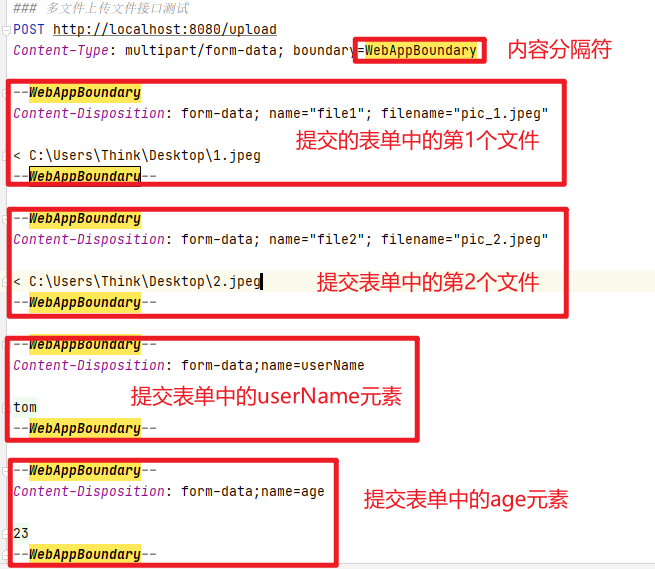
你可以把这个请求想象为页面中的一个表单,表单有4个元素:2个File元素,用来选择需要上传的2个文件,2个输入框,分别用来输入userName和age,用--WebAppBoundary来隔离每个元素,如果有多个元素,都需要用--WebAppBoundary隔离开来,如下:
5、环境切换
我们测试接口的时候,有开发环境、测试环境、UAT环境,生产环境,每个环境的接口信息都不一样,比如接口地址。
HTTP Client 中可以创建环境配置文件,来对不同的环境信息进行配置,操作如下
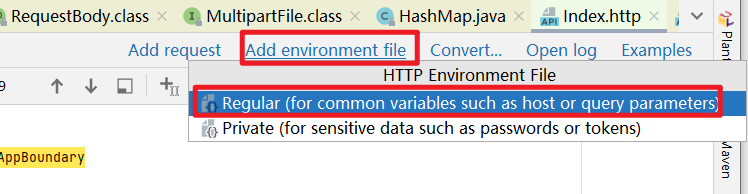
5.1、创建环境配置文件
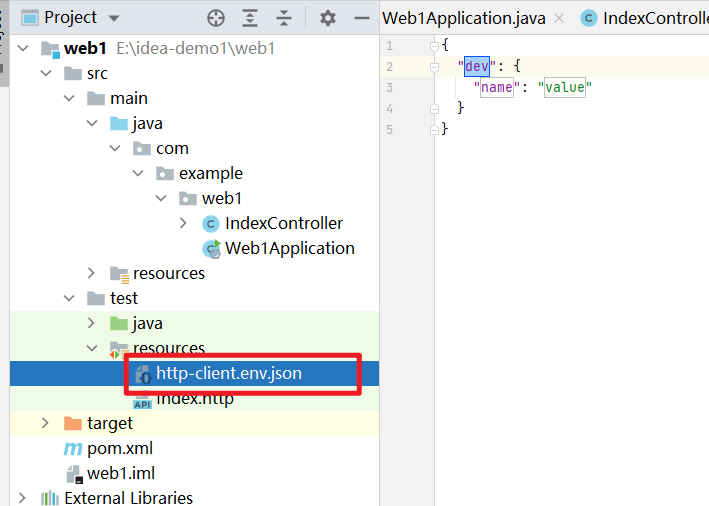
生成了一个环境配置文件,如下
文件内容格式
{
"环境名称": {环境参数json格式},
"环境名称": {环境参数json格式}
}
如
{
"dev": {
"url": "http://localhost:8080",
"name": "张三"
},
"test": {
"url": "http://localhost:9090",
"name": "李四"
}
}
5.2、http文件中引用环境配置信息
通过{{key}}可以引用环境中的信息,运行的时候会被替换,如:
GET {{url}}/get
5.3、运行的时候选择环境
运行的时候会提示你选择环境,此时环境中的配置信息就被用上了

大家赶紧去体验一下。
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

