Redis 数据库及相关命令实现
1. 数据库管理命令
数据库管理的命令如下表格所示:redis keys命令详解
| 命令 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| FLUSHDB | 清空当前数据库的所有key |
| FLUSHALL | 清空整个Redis服务器的所有key |
| DBSIZE | 返回当前数据库的key的个数 |
| DELkey[key…] | 删除一个或多个键 |
| EXISTSkey | 检查给定key是否存在 |
| SELECTid | 切换到指定的数据库 |
| RANDOMKEY | 从当前数据库中随机返回(不删除)一个key。 |
| KEYSpattern | 查找所有符合给定模式pattern的key |
| SCANcursor[MATCHpattern][COUNTcount] | 增量式迭代当前数据库键 |
| LASTSAVE | 返回最近一次成功将数据保存到磁盘上的时间,以UNIX时间戳格式表示。 |
| TYPEkey | 返回指定键的对象类型 |
| SHUTDOWN | 停止所有客户端,关闭redis服务器(server) |
| RENAMEkeynewkey | 重命名指定的key,newkey存在时覆盖 |
| RENAMENXkeynewkey | 重命名指定的key,当且仅当newkey不存在时操作 |
| MOVEkeydb | 移动key到指定数据库 |
| EXPIREATkeytimestamp | 为key设置生存时间,EXPIREAT命令接受的时间参数是UNIX时间戳 |
| EXPIREkeyseconds | 以秒为单位设置key的生存时间 |
| PEXPIREkeymilliseconds | 以毫秒为单位设置key的生存时间 |
| PEXPIREATkeymilliseconds-timestamp | 以毫秒为单位设置key的过期unix时间戳 |
| TTLkey | 以秒为单位返回key的剩余生存时间 |
| PTTLkey | 以毫秒为单位返回key的剩余生存时间 |
2. 数据库的实现
2.1数据库的结构
typedef struct redisDb {
// 键值对字典,保存数据库中所有的键值对
dict *dict; /* The keyspace for this DB */
// 过期字典,保存着设置过期的键和键的过期时间
dict *expires; /* Timeout of keys with a timeout set */
// 保存着 所有造成客户端阻塞的键和被阻塞的客户端
dict *blocking_keys; /*Keys with clients waiting for data (BLPOP) */
// 保存着 处于阻塞状态的键,value为NULL
dict *ready_keys; /* Blocked keys that received a PUSH */
// 事物模块,用于保存被WATCH命令所监控的键
dict *watched_keys; /* WATCHED keys for MULTI/EXEC CAS */
// 当内存不足时,Redis会根据LRU算法回收一部分键所占的空间,而该eviction_pool是一个长为16数组,保存可能被回收的键
// eviction_pool中所有键按照idle空转时间,从小到大排序,每次回收空转时间最长的键
struct evictionPoolEntry *eviction_pool; /* Eviction pool of keys */
// 数据库ID
int id; /* Database ID */
// 键的平均过期时间
long long avg_ttl; /* Average TTL, just for stats */
} redisDb;
- blocking_keys 和 ready_keys 使用于在列表类型的阻塞命令(BLPOP等),详细内容看:Redis 列表键命令实现
- watched_keys 是用于事物模块。
- eviction_pool 是Redis在内存不足情况下,要回收内存时所使用。
- dict 和 expires 和 id是本篇主要讨论的。
Redis服务器和客户端也都保存有数据库的信息,下面截取出来:
typedef struct client {
redisDb *db; /* Pointer to currently SELECTed DB. */
} client;
struct redisServer {
redisDb *db;
int dbnum; /* Total number of configured DBs */
};
Redis服务器在初始化时,会创建一个长度为dbnum(默认为16)个 redisDb类型数组,客户端登录时,默认的数据库为0号数据库。当执行SELECT index命令后,就会切换数据库。我们用两个客户端,表示如下图:
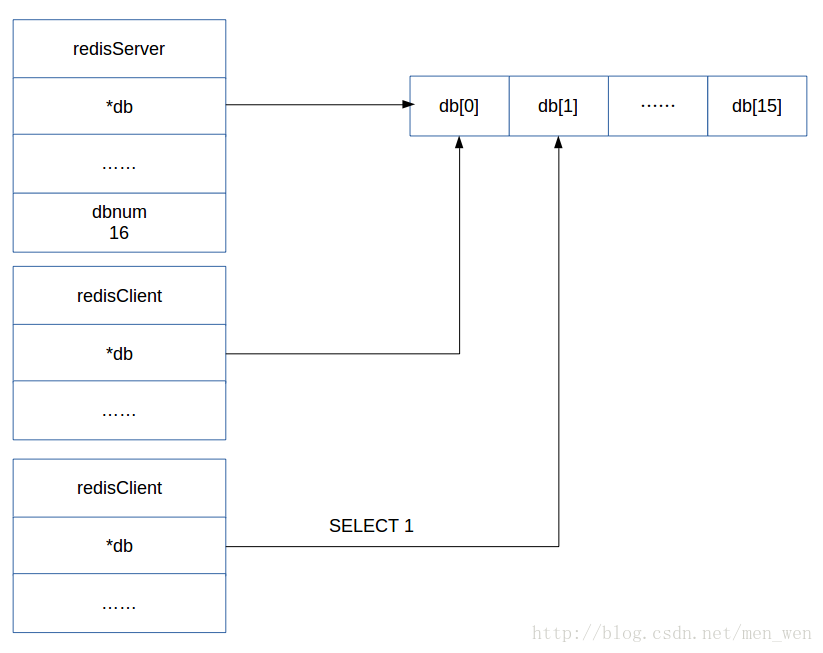
SELECT index命令非常简单,源码如下:
// 切换数据库
int selectDb(client *c, int id) {
// id非法,返回错误
if (id < 0 || id >= server.dbnum)
return C_ERR;
// 设置当前client的数据库
c->db = &server.db[id];
return C_OK;
}
2.2 数据库的键值对字典
Redis是一个key-value数据库服务器,它将所有的键值对都保存在 redisDb 结构中的 dict 字典成员中(Redis 字典结构源码剖析)。
- 键值对字典的键,就是数据库的key,每一个key都是字符串的对象。
- 键值对字典的值,就是数据库的value,每一个value可以是字符串的对象,列表对象,哈希表对象,集合对象和有序集合对象中的任意一种。
数据库对键对象的删除操作,会连带值对象也一并删除,因此再有一些操作中,例如RENAME等命令,中间步骤会使用删除原有键,常常需要对值对象的引用计数加1,保护值对象不被删除,当新的键被设置后,则对值对象的引用计数减1。
我们向一个数据库中添加几个键,并且用图表示出来:
- 红色代表键对象,有 RAW编码的字符串对象,哈希对象。将结构简化表示,重点关注引用计数。
- 蓝色代表值对象,完成结构如图所示。
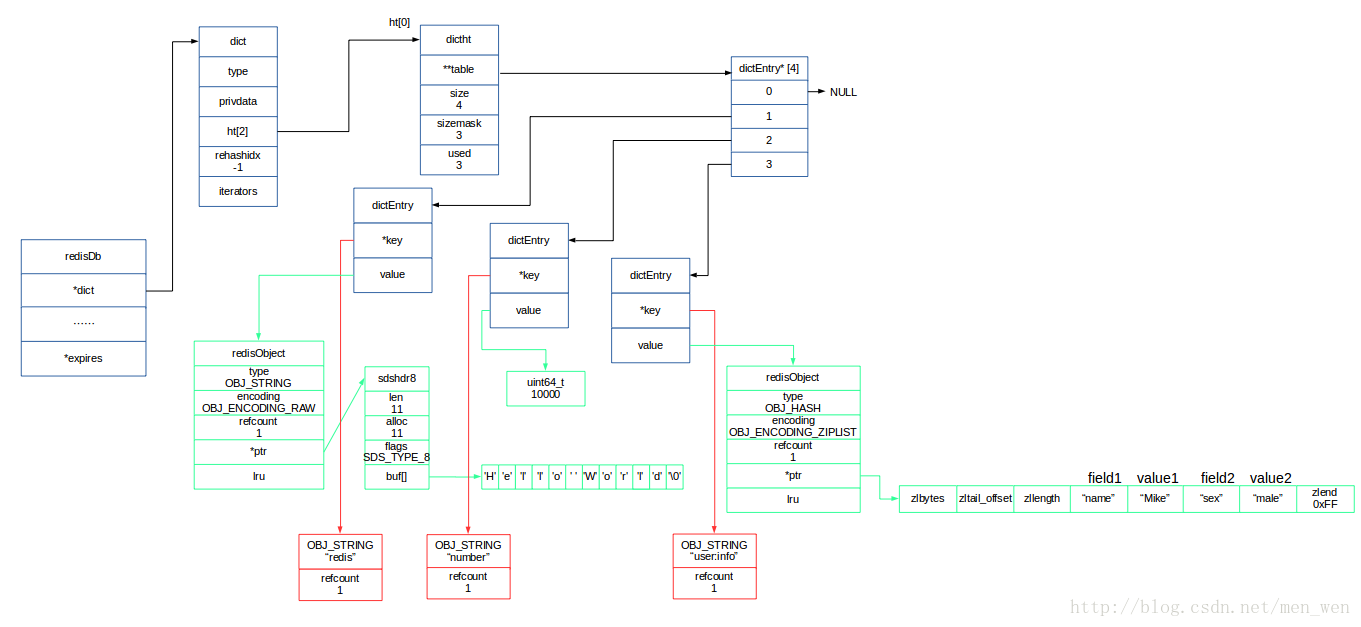
数据库每次根据键名找到值对象时,是分为以 读操作 lookupKeyRead() 或写操作 lookupKeyWrite() 的方式取出的,而这两种有一定的区别,下面展示源码:
- lookupKey()函数
读操作 lookupKeyRead() 或写操作 lookupKeyWrite()都会调用这个底层的函数,这个函数非常简单,就是从键值对字典中先找到键名对应的键对象,然后取出值对象。
// 该函数被lookupKeyRead()和lookupKeyWrite()和lookupKeyReadWithFlags()调用
// 从数据库db中取出key的值对象,如果存在返回该对象,否则返回NULL
// 返回key对象的值对象
robj *lookupKey(redisDb *db, robj *key, int flags) {
// 在数据库中查找key对象,返回保存该key的节点地址
dictEntry *de = dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr);
if (de) { //如果找到
robj *val = dictGetVal(de); //取出键对应的值对象
/* Update the access time for the ageing algorithm.
* Don't do it if we have a saving child, as this will trigger
* a copy on write madness. */
// 更新键的使用时间
if (server.rdb_child_pid == -1 &&
server.aof_child_pid == -1 &&
!(flags & LOOKUP_NOTOUCH))
{
val->lru = LRU_CLOCK();
}
return val; //返回值对象
} else {
return NULL;
}
- lookupKeyRead()函数
lookupKeyRead()函数调用了lookupKeyReadWithFlags()函数,后者其实就判断了一下当前键是否过期,如果没有过期, 更新 misses 和 hits 信息 ,然后就返回值对象。
还有就是两个宏:
- define LOOKUP_NONE 0 //zero,没有特殊意义
- define LOOKUP_NOTOUCH (1<<0) //不修改键的使用时间,如果只是想判断key的值对象的编码类型(TYPE命令)我们不希望改变键的使用时间。
// 以读操作取出key的值对象,会更新是否命中的信息
robj *lookupKeyRead(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
return lookupKeyReadWithFlags(db,key,LOOKUP_NONE);
}
// 以读操作取出key的值对象,没找到返回NULL
// 调用该函数的副作用如下:
// 1.如果一个键的到达过期时间TTL,该键被设置为过期的
// 2.键的使用时间信息被更新
// 3.全局键 hits/misses 状态被更新
// 注意:如果键在逻辑上已经过期但是仍然存在,函数返回NULL
robj *lookupKeyReadWithFlags(redisDb *db, robj *key, int flags) {
robj *val;
// 如果键已经过期且被删除
if (expireIfNeeded(db,key) == 1) {
/* Key expired. If we are in the context of a master, expireIfNeeded()
* returns 0 only when the key does not exist at all, so it's save
* to return NULL ASAP. */
// 键已过期,如果是主节点环境,表示key已经绝对被删除,如果是从节点,
if (server.masterhost == NULL) return NULL;
// 如果我们在从节点环境, expireIfNeeded()函数不会删除过期的键,它返回的仅仅是键是否被删除的逻辑值
// 过期的键由主节点负责,为了保证主从节点数据的一致
if (server.current_client &&
server.current_client != server.master &&
server.current_client->cmd &&
server.current_client->cmd->flags & CMD_READONLY)
{
return NULL;
}
}
// 键没有过期,则返回键的值对象
val = lookupKey(db,key,flags);
// 更新 是否命中 的信息
if (val == NULL)
server.stat_keyspace_misses++;
else
server.stat_keyspace_hits++;
return val;
}
- lookupKeyWrite()函数
lookupKeyWrite() 函数则先判断键是否过期,然后直接调用最底层的 lookupKey() 函数,和 lookupKeyRead()函数 相比, 少了一步更新 misses 和 hits 信息的过程。
// 以写操作取出key的值对象,不更新是否命中的信息
robj *lookupKeyWrite(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
expireIfNeeded(db,key);
return lookupKey(db,key,LOOKUP_NONE);
}
2.3 键的过期时间
redisBb结构中的 expires 字典保存这设置了过期时间的键和过期的时间。通过 EXPIRE 、 PEXPIRE、 EXPIREAT 和 PEXPIREAT四个命令,客户端可以给某个存在的键设置过期时间,当键的过期时间到达时,键就不再可用。
我们先用图展示一下数据库中的过期字典,用刚才的键值对字典中的对象。
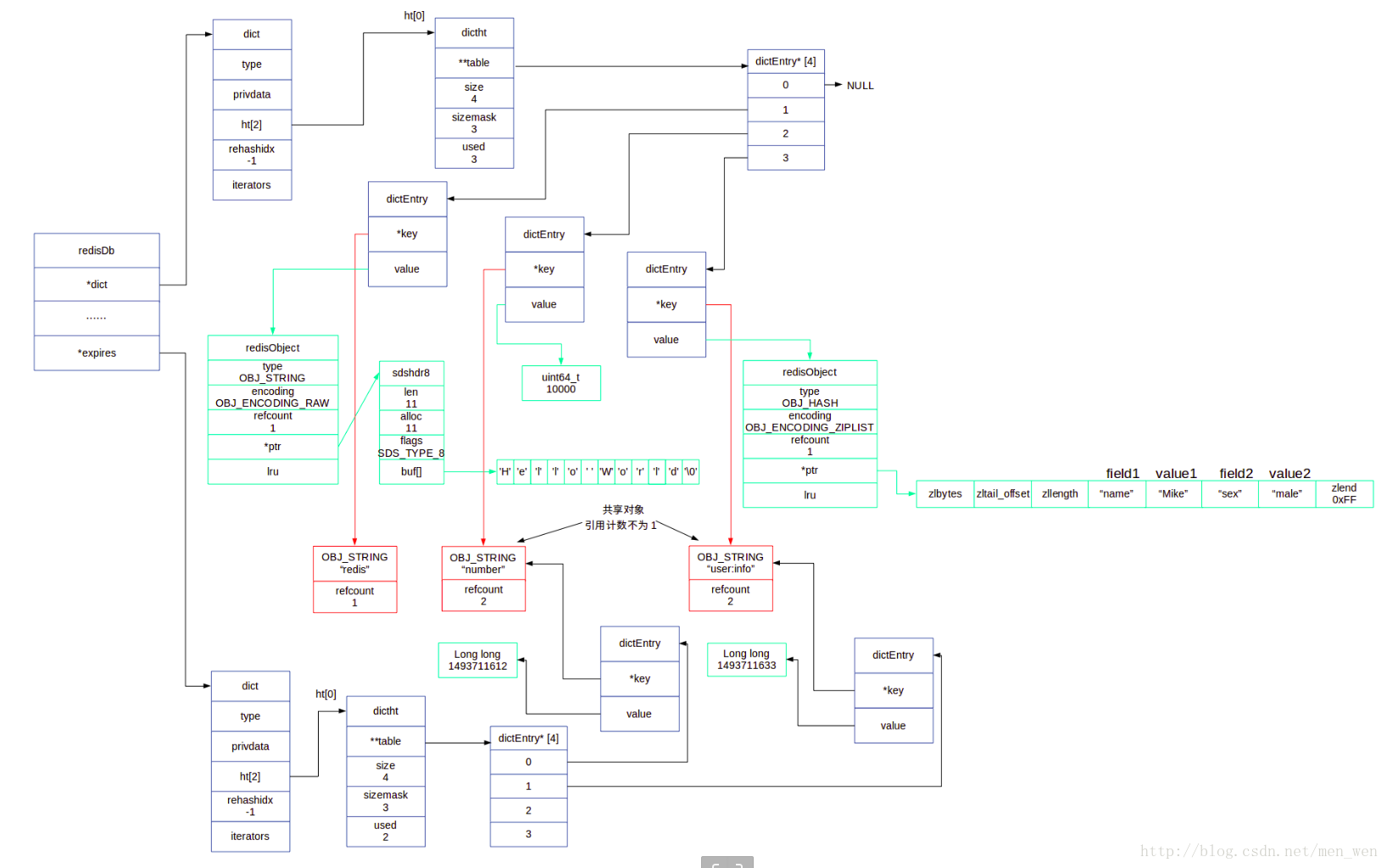
- 很明显,键值对字典和过期字典中的相同对象只占一份空间,只是增加 引用计数 。
我们重点讨论过期键的删除策略:
- 惰性删除 :当客户度读出带有超时属性的键时,如果已经超过键设置的过期时间,会执行删除并返回空。
- 定时删除 :Redis内部维护一个定时任务,默认每秒运行10次。
我们给出 惰性删除的代码 ,这个函数 expireIfNeeded(),所有读写数据库的Redis命令在执行前都会调用,删除过期键。
// 检查键是否过期,如果过期,从数据库中删除
// 返回0表示没有过期或没有过期时间,返回1 表示键被删除
int expireIfNeeded(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
//得到过期时间,单位毫秒
mstime_t when = getExpire(db,key);
mstime_t now;
// 没有过期时间,直接返回
if (when < 0) return 0; /* No expire for this key */
/* Don't expire anything while loading. It will be done later. */
// 服务器正在载入,那么不进行过期检查
if (server.loading) return 0;
/* If we are in the context of a Lua script, we claim that time is
* blocked to when the Lua script started. This way a key can expire
* only the first time it is accessed and not in the middle of the
* script execution, making propagation to slaves / AOF consistent.
* See issue #1525 on Github for more information. */
// 返回一个Unix时间,单位毫秒
now = server.lua_caller ? server.lua_time_start : mstime();
/* If we are running in the context of a slave, return ASAP:
* the slave key expiration is controlled by the master that will
* send us synthesized DEL operations for expired keys.
*
* Still we try to return the right information to the caller,
* that is, 0 if we think the key should be still valid, 1 if
* we think the key is expired at this time. */
// 如果服务器正在进行主从节点的复制,从节点的过期键应该被 主节点发送同步删除的操作 删除,而自己不主动删除
// 从节点只返回正确的逻辑信息,0表示key仍然没有过期,1表示key过期。
if (server.masterhost != NULL) return now > when;
/* Return when this key has not expired */
// 当键还没有过期时,直接返回0
if (now <= when) return 0;
/* Delete the key */
// 键已经过期,删除键
server.stat_expiredkeys++; //过期键的数量加1
propagateExpire(db,key); //将过期键key传播给AOF文件和从节点
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_EXPIRED, //发送"expired"事件通知
"expired",key,db->id);
return dbDelete(db,key); //从数据库中删除key
}
3. 数据库相关命令实现
我们只列举部分命令实现,所有代码注释可以上github查看:Redis 数据库实现(db.c)
3.1 键空间命令
- SCAN 一类命令的底层实现
// SCAN cursor [MATCH pattern] [COUNT count]
// SCAN、HSCAN、SSCAN、ZSCAN一类命令底层实现
// o对象必须是哈希对象或集合对象,否则命令将操作当前数据库
// 如果o不是NULL,那么说明他是一个哈希或集合对象,函数将跳过这些键对象,对参数进行分析
// 如果是哈希对象,返回返回的是键值对
void scanGenericCommand(client *c, robj *o, unsigned long cursor) {
int i, j;
list *keys = listCreate(); //创建一个列表
listNode *node, *nextnode;
long count = 10;
sds pat = NULL;
int patlen = 0, use_pattern = 0;
dict *ht;
/* Object must be NULL (to iterate keys names), or the type of the object
* must be Set, Sorted Set, or Hash. */
// 输入类型的检查,要么迭代键名,要么当前集合对象,要么迭代哈希对象,要么迭代有序集合对象
serverAssert(o == NULL || o->type == OBJ_SET || o->type == OBJ_HASH ||
o->type == OBJ_ZSET);
/* Set i to the first option argument. The previous one is the cursor. */
// 计算第一个参数的下标,如果是键名,要条跳过该键
i = (o == NULL) ? 2 : 3; /* Skip the key argument if needed. */
/* Step 1: Parse options. */
// 1. 解析选项
while (i < c->argc) {
j = c->argc - i;
// 设定COUNT参数,COUNT 选项的作用就是让用户告知迭代命令, 在每次迭代中应该返回多少元素。
if (!strcasecmp(c->argv[i]->ptr, "count") && j >= 2) {
//保存个数到count
if (getLongFromObjectOrReply(c, c->argv[i+1], &count, NULL)
!= C_OK)
{
goto cleanup;
}
// 如果个数小于1,语法错误
if (count < 1) {
addReply(c,shared.syntaxerr);
goto cleanup;
}
i += 2; //参数跳过两个已经解析过的
// 设定MATCH参数,让命令只返回和给定模式相匹配的元素。
} else if (!strcasecmp(c->argv[i]->ptr, "match") && j >= 2) {
pat = c->argv[i+1]->ptr; //pattern字符串
patlen = sdslen(pat); //pattern字符串长度
/* The pattern always matches if it is exactly "*", so it is
* equivalent to disabling it. */
// 如果pattern是"*",就不用匹配,全部返回,设置为0
use_pattern = !(pat[0] == '*' && patlen == 1);
i += 2;
} else {
addReply(c,shared.syntaxerr);
goto cleanup;
}
}
/* Step 2: Iterate the collection.
*
* Note that if the object is encoded with a ziplist, intset, or any other
* representation that is not a hash table, we are sure that it is also
* composed of a small number of elements. So to avoid taking state we
* just return everything inside the object in a single call, setting the
* cursor to zero to signal the end of the iteration. */
/* Handle the case of a hash table. */
// 2.如果对象是ziplist、intset或其他而不是哈希表,那么这些类型只是包含少量的元素
// 我们一次将其所有的元素全部返回给调用者,并设置游标cursor为0,标示迭代完成
ht = NULL;
// 迭代目标是数据库
if (o == NULL) {
ht = c->db->dict;
// 迭代目标是HT编码的集合对象
} else if (o->type == OBJ_SET && o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {
ht = o->ptr;
// 迭代目标是HT编码的哈希对象
} else if (o->type == OBJ_HASH && o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {
ht = o->ptr;
count *= 2; /* We return key / value for this type. */
// 迭代目标是skiplist编码的有序集合对象
} else if (o->type == OBJ_ZSET && o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST) {
zset *zs = o->ptr;
ht = zs->dict;
count *= 2; /* We return key / value for this type. */
}
if (ht) {
void *privdata[2];
/* We set the max number of iterations to ten times the specified
* COUNT, so if the hash table is in a pathological state (very
* sparsely populated) we avoid to block too much time at the cost
* of returning no or very few elements. */
// 设置最大的迭代长度为10*count次
long maxiterations = count*10;
/* We pass two pointers to the callback: the list to which it will
* add new elements, and the object containing the dictionary so that
* it is possible to fetch more data in a type-dependent way. */
// 回调函数scanCallback的参数privdata是一个数组,保存的是被迭代对象的键和值
// 回调函数scanCallback的另一个参数,是一个字典对象
// 回调函数scanCallback的作用,从字典对象中将键值对提取出来,不用管字典对象是什么数据类型
privdata[0] = keys;
privdata[1] = o;
// 循环扫描ht,从游标cursor开始,调用指定的scanCallback函数,提出ht中的数据到刚开始创建的列表keys中
do {
cursor = dictScan(ht, cursor, scanCallback, privdata);
} while (cursor &&
maxiterations-- &&
listLength(keys) < (unsigned long)count);//没迭代完,或没迭代够count,就继续循环
// 如果是集合对象但编码不是HT是整数集合
} else if (o->type == OBJ_SET) {
int pos = 0;
int64_t ll;
// 将整数值取出来,构建成字符串对象加入到keys列表中,游标设置为0,表示迭代完成
while(intsetGet(o->ptr,pos++,&ll))
listAddNodeTail(keys,createStringObjectFromLongLong(ll));
cursor = 0;
// 如果是哈希对象,或有序集合对象,但是编码都不是HT,是ziplist
} else if (o->type == OBJ_HASH || o->type == OBJ_ZSET) {
unsigned char *p = ziplistIndex(o->ptr,0);
unsigned char *vstr;
unsigned int vlen;
long long vll;
while(p) {
// 将值取出来,根据不同类型的值,构建成相同的字符串对象,加入到keys列表中
ziplistGet(p,&vstr,&vlen,&vll);
listAddNodeTail(keys,
(vstr != NULL) ? createStringObject((char*)vstr,vlen) :
createStringObjectFromLongLong(vll));
p = ziplistNext(o->ptr,p);
}
cursor = 0;
} else {
serverPanic("Not handled encoding in SCAN.");
}
/* Step 3: Filter elements. */
// 3. 如果设置MATCH参数,要进行过滤
node = listFirst(keys); //链表首节点地址
while (node) {
robj *kobj = listNodeValue(node); //key对象
nextnode = listNextNode(node); //下一个节点地址
int filter = 0; //默认为不过滤
/* Filter element if it does not match the pattern. */
//pattern不是"*"因此要过滤
if (!filter && use_pattern) {
// 如果kobj是字符串对象
if (sdsEncodedObject(kobj)) {
// kobj的值不匹配pattern,设置过滤标志
if (!stringmatchlen(pat, patlen, kobj->ptr, sdslen(kobj->ptr), 0))
filter = 1;
// 如果kobj是整数对象
} else {
char buf[LONG_STR_SIZE];
int len;
serverAssert(kobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INT);
// 将整数转换为字符串类型,保存到buf中
len = ll2string(buf,sizeof(buf),(long)kobj->ptr);
//buf的值不匹配pattern,设置过滤标志
if (!stringmatchlen(pat, patlen, buf, len, 0)) filter = 1;
}
}
/* Filter element if it is an expired key. */
// 迭代目标是数据库,如果kobj是过期键,则过滤
if (!filter && o == NULL && expireIfNeeded(c->db, kobj)) filter = 1;
/* Remove the element and its associted value if needed. */
// 如果该键满足了上述的过滤条件,那么将其从keys列表删除并释放
if (filter) {
decrRefCount(kobj);
listDelNode(keys, node);
}
/* If this is a hash or a sorted set, we have a flat list of
* key-value elements, so if this element was filtered, remove the
* value, or skip it if it was not filtered: we only match keys. */
// 如果当前迭代目标是有序集合或哈希对象,因此keys列表中保存的是键值对,如果key键对象被过滤,值对象也应当被过滤
if (o && (o->type == OBJ_ZSET || o->type == OBJ_HASH)) {
node = nextnode;
nextnode = listNextNode(node); //值对象的节点地址
// 如果该键满足了上述的过滤条件,那么将其从keys列表删除并释放
if (filter) {
kobj = listNodeValue(node); //取出值对象
decrRefCount(kobj);
listDelNode(keys, node); //删除
}
}
node = nextnode;
}
/* Step 4: Reply to the client. */
// 4. 回复信息给client
addReplyMultiBulkLen(c, 2); //2部分,一个是游标,一个是列表
addReplyBulkLongLong(c,cursor); //回复游标
addReplyMultiBulkLen(c, listLength(keys)); //回复列表长度
//循环回复列表中的元素,并释放
while ((node = listFirst(keys)) != NULL) {
robj *kobj = listNodeValue(node);
addReplyBulk(c, kobj);
decrRefCount(kobj);
listDelNode(keys, node);
}
// 清理代码
cleanup:
listSetFreeMethod(keys,decrRefCountVoid); //设置特定的释放列表的方式decrRefCountVoid
listRelease(keys); //释放
}
- RENAME、RENAMENX命令底层实现
// RENAME key newkey
// RENAMENX key newkey
// RENAME、RENAMENX命令底层实现
void renameGenericCommand(client *c, int nx) {
robj *o;
long long expire;
int samekey = 0;
/* When source and dest key is the same, no operation is performed,
* if the key exists, however we still return an error on unexisting key. */
// key和newkey相同的话,设置samekey标志
if (sdscmp(c->argv[1]->ptr,c->argv[2]->ptr) == 0) samekey = 1;
// 以写操作读取key的值对象
if ((o = lookupKeyWriteOrReply(c,c->argv[1],shared.nokeyerr)) == NULL)
return;
// 如果key和newkey相同,nx为1发送0,否则为ok
if (samekey) {
addReply(c,nx ? shared.czero : shared.ok);
return;
}
// 增加值对象的引用计数,保护起来,用于关联newkey,以防删除了key顺带将值对象也删除
incrRefCount(o);
// 备份key的过期时间,将来作为newkey的过期时间
expire = getExpire(c->db,c->argv[1]);
// 判断newkey的值对象是否存在
if (lookupKeyWrite(c->db,c->argv[2]) != NULL) {
// 设置nx标志,则不符合已存在的条件,发送0
if (nx) {
decrRefCount(o);
addReply(c,shared.czero);
return;
}
/* Overwrite: delete the old key before creating the new one
* with the same name. */
dbDelete(c->db,c->argv[2]); //将旧的newkey对象删除
}
// 将newkey和key的值对象关联
dbAdd(c->db,c->argv[2],o);
// 如果newkey设置过过期时间,则为newkey设置过期时间
if (expire != -1) setExpire(c->db,c->argv[2],expire);
// 删除key
dbDelete(c->db,c->argv[1]);
// 发送这两个键被修改的信号
signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[1]);
signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[2]);
// 发送不同命令的事件通知
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_GENERIC,"rename_from",
c->argv[1],c->db->id);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_GENERIC,"rename_to",
c->argv[2],c->db->id);
server.dirty++; //更新脏键
addReply(c,nx ? shared.cone : shared.ok);
}
- MOVE 命令
// MOVE key db 将当前数据库的 key 移动到给定的数据库 db 当中。
// MOVE 命令实现
void moveCommand(client *c) {
robj *o;
redisDb *src, *dst;
int srcid;
long long dbid, expire;
// 服务器处于集群模式,不支持多数据库
if (server.cluster_enabled) {
addReplyError(c,"MOVE is not allowed in cluster mode");
return;
}
/* Obtain source and target DB pointers */
// 获得源数据库和源数据库的id
src = c->db;
srcid = c->db->id;
// 将参数db的值保存到dbid,并且切换到该数据库中
if (getLongLongFromObject(c->argv[2],&dbid) == C_ERR ||
dbid < INT_MIN || dbid > INT_MAX ||
selectDb(c,dbid) == C_ERR)
{
addReply(c,shared.outofrangeerr);
return;
}
// 目标数据库
dst = c->db;
// 切换回源数据库
selectDb(c,srcid); /* Back to the source DB */
/* If the user is moving using as target the same
* DB as the source DB it is probably an error. */
// 如果前后切换的数据库相同,则返回有关错误
if (src == dst) {
addReply(c,shared.sameobjecterr);
return;
}
/* Check if the element exists and get a reference */
// 以写操作取出源数据库的对象
o = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,c->argv[1]);
if (!o) {
addReply(c,shared.czero); //不存在发送0
return;
}
// 备份key的过期时间
expire = getExpire(c->db,c->argv[1]);
/* Return zero if the key already exists in the target DB */
// 判断当前key是否存在于目标数据库,存在直接返回,发送0
if (lookupKeyWrite(dst,c->argv[1]) != NULL) {
addReply(c,shared.czero);
return;
}
// 将key-value对象添加到目标数据库中
dbAdd(dst,c->argv[1],o);
// 设置移动后key的过期时间
if (expire != -1) setExpire(dst,c->argv[1],expire);
incrRefCount(o); //增加引用计数
/* OK! key moved, free the entry in the source DB */
// 从源数据库中将key和关联的值对象删除
dbDelete(src,c->argv[1]);
server.dirty++; //更新脏键
addReply(c,shared.cone); //回复1
}
3.2 过期命令
- EXPIRE, PEXPIRE, EXPIREAT,PEXPIREAT命令的底层实现
// EXPIRE key seconds
// EXPIREAT key timestamp
// PEXPIRE key milliseconds
// PEXPIREAT key milliseconds-timestamp
// EXPIRE, PEXPIRE, EXPIREAT,PEXPIREAT命令的底层实现
// basetime参数可能是绝对值,可能是相对值。执行AT命令时basetime为0,否则保存的是当前的绝对时间
// unit 是UNIT_SECONDS 或者 UNIT_MILLISECONDS,但是basetime总是以毫秒为单位的。
void expireGenericCommand(client *c, long long basetime, int unit) {
robj *key = c->argv[1], *param = c->argv[2];
long long when; /* unix time in milliseconds when the key will expire. */
// 取出时间参数保存到when中
if (getLongLongFromObjectOrReply(c, param, &when, NULL) != C_OK)
return;
// 如果过期时间是以秒为单位,则转换为毫秒值
if (unit == UNIT_SECONDS) when *= 1000;
// 绝对时间
when += basetime;
/* No key, return zero. */
// 判断key是否在数据库中,不在返回0
if (lookupKeyWrite(c->db,key) == NULL) {
addReply(c,shared.czero);
return;
}
/* EXPIRE with negative TTL, or EXPIREAT with a timestamp into the past
* should never be executed as a DEL when load the AOF or in the context
* of a slave instance.
*
* Instead we take the other branch of the IF statement setting an expire
* (possibly in the past) and wait for an explicit DEL from the master. */
// 如果当前正在载入AOF数据或者在从节点环境中,即使EXPIRE的TTL为负数,或者EXPIREAT的时间戳已经过期
// 服务器都不会执行DEL命令,且将过期TTL设置为键的过期时间,等待主节点发来的DEL命令
// 如果when已经过时,服务器为主节点且没有载入AOF数据
if (when <= mstime() && !server.loading && !server.masterhost) {
robj *aux;
// 将key从数据库中删除
serverAssertWithInfo(c,key,dbDelete(c->db,key));
server.dirty++; //更新脏键
/* Replicate/AOF this as an explicit DEL. */
// 创建一个"DEL"命令
aux = createStringObject("DEL",3);
rewriteClientCommandVector(c,2,aux,key); //修改客户端的参数列表为DEL命令
decrRefCount(aux);
// 发送键被修改的信号
signalModifiedKey(c->db,key);
// 发送"del"的事件通知
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_GENERIC,"del",key,c->db->id);
addReply(c, shared.cone);
return;
// 如果当前服务器是从节点,或者服务器正在载入AOF数据
// 不管when有没有过时,都设置为过期时间
} else {
// 设置过期时间
setExpire(c->db,key,when);
addReply(c,shared.cone);
signalModifiedKey(c->db,key); //发送键被修改的信号
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_GENERIC,"expire",key,c->db->id); //发送"expire"的事件通知
server.dirty++; //更新脏键
return;
}
}
- TTL、PTTL 命令底层实现
// TTL key
// PTTL key
// TTL、PTTL命令底层实现,output_ms为1,返回毫秒,为0返回秒
void ttlGenericCommand(client *c, int output_ms) {
long long expire, ttl = -1;
/* If the key does not exist at all, return -2 */
// 判断key是否存在于数据库,并且不修改键的使用时间
if (lookupKeyReadWithFlags(c->db,c->argv[1],LOOKUP_NOTOUCH) == NULL) {
addReplyLongLong(c,-2);
return;
}
/* The key exists. Return -1 if it has no expire, or the actual
* TTL value otherwise. */
// 如果key存在,则备份当前key的过期时间
expire = getExpire(c->db,c->argv[1]);
// 如果设置了过期时间
if (expire != -1) {
ttl = expire-mstime(); //计算生存时间
if (ttl < 0) ttl = 0;
}
// 如果键是永久的
if (ttl == -1) {
addReplyLongLong(c,-1); //发送-1
} else {
addReplyLongLong(c,output_ms ? ttl : ((ttl+500)/1000)); //发送生存时间
}
}
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

