本文将介绍@RequestBody注解常见的一些用法和原理,这个注解日常用到的特别多。
1、预备知识
2、@RequestBody介绍
标注在接口的参数上,用来获取HTTP请求body中的值,下面通过案例列出常见的用法。
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RequestBody {
/**
* body是不是必须的,默认为true,若不传body,会有异常;若为false,这body可不传
*/
boolean required() default true;
}
推荐阅读: 尚硅谷 Java 学科全套教程(总 207.77GB)
3、案例1:使用字符串接收body中的数据
3.1、接口代码
注意方法的参数,使用@RequestBody标注,参数类型是String,表示以字符串的方式接收body的数据。
@RequestMapping("/requestbody/test1")
public String test1(@RequestBody String body) {
System.out.println("body:" + body);
return "ok";
}
下面来模拟发送5种格式的数据,然后看控制台的输出。
3.2、用例1:发送纯文本数据
Content-Type用来指定客户端发送的数据的类型。
### 发送纯文本
POST http://localhost:8080/chat18/requestbody/test1
Content-Type: text/plain
这里是body部分,欢迎访问我的博客:itsoku.com,上面有更多系列文章
运行,接口内部控制台输出
body:这里是body部分,欢迎访问我的博客:itsoku.com,上面有更多系列文章
3.3、用例2:发送表单数据,相当于提交表单
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded 相当于页面中提交表单,表单中的所有元素会以name=value&name=value的方式拼接起来,然后在进行urlencoded,之后丢在body中发送。
### 发送表单数据,相当于提交表单
POST http://localhost:8080/chat18/requestbody/test1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
name=路人&blogs=itsoku.com
运行输出如下,可以看出来是乱码的格式,是由于被中文被urlencoded编码了。
body:name=%E8%B7%AF%E4%BA%BA&blogs=itsoku.com
3.4、用例3:发送xml数据
### 发送xml数据
POST http://localhost:8080/chat18/requestbody/test1
Content-Type: text/xml
<CourseList>
<Course>Java高并发系列</Course>
<Course>MyBatis系列</Course>
<Course>MySQL系列</Course>
<Course>Spring高手系列</Course>
<Course>分布式事务高手系列</Course>
</CourseList>
运行,控制台输出
body:<CourseList>
<Course>Java高并发系列</Course>
<Course>MyBatis系列</Course>
<Course>MySQL系列</Course>
<Course>Spring高手系列</Course>
<Course>分布式事务高手系列</Course>
</CourseList>
3.5、用例4:发送json数据
### 发送json数据
POST http://localhost:8080/chat18/requestbody/test1
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"blog": "itsoku.com",
"course": [
"Spring高手系列",
"MySQL系列",
"高并发系列"
]
}
运行,控制台输出
body:{
"blog": "itsoku.com",
"course": [
"Spring高手系列",
"MySQL系列",
"高并发系列"
]
}
从上面可以看出,接口参数body的值为http请求body中的原始数据。
推荐阅读: 2021 最新版 Java 微服务学习线路图 + 视频
4、案例2:使用对象接收json格式的数据
4.1、用法
发送json格式的数据,这种用到的比较多,http请求发送这种数据,有3点要求:
- Content-Type的值需要为:application/json;charset=UTF-8,告诉服务器端客户端body中的数据是json格式 & UTF-8编码
- body中数据为json格式
- 接口端用对象接收,参数使用@RequestBody标注
4.2、接口代码
@RequestMapping("/requestbody/test2")
public String test2(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("user:" + user);
return "ok";
}
User类
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private List<String> skills;
//省略get、set
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", skills=" + skills +
'}';
}
}
4.3、调用接口
重点注意了,头中需要加上Content-Type: application/json
### 发送json数据,后端用对象接收
POST http://localhost:8080/chat18/requestbody/test2
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"name": "路人",
"age": 35,
"skills": [
"高并发",
"Spring",
"分布式事务",
"MQ",
"MySQL"
]
}
4.4、控制台输出
user:User{name='路人', age=35, skills=[高并发, Spring, 分布式事务, MQ, MySQL]}
推荐阅读: 阿里技术大佬整理的《Spring 学习笔记.pdf》
5、案例3:使用Resource资源对象接收
5.1、用法
有时候,我们想以流的方式接收body中的数据,那么可以参考下面的写法,参数类型为[ByteArrayResource,InputStreamResource]这2种类型即可,第一种类型获取的是一个字节数组,第二个是一个InputStream输入流。
比如我们需要快速上传文件到阿里云,那么接口接收到客户端的流之后,直接将流转发到oss,效率更高。
/**
* 参数为如果为 org.springframework.core.io.Resource 类型,
* 则只能为Resource的[ByteArrayResource,InputStreamResource]这2种子类型:
*
* @param body
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
@RequestMapping("/requestbody/test3")
public String test3(@RequestBody InputStreamResource body) throws IOException {
String content = IOUtils.toString(body.getInputStream(), "UTF-8");
System.out.println("content:" + content);
return "ok";
}
5.2、调用接口
### 后端使用Resource接收数据
POST http://localhost:8080/chat18/requestbody/test3
Content-Type: text/plain;charset=UTF-8
后端使用Resource接收数据
5.3、控制台输出
content:后端使用Resource接收数据
推荐阅读: 阿里大佬的《MySQL 学习笔记高清.pdf》
6、案例4:以字节数组接受数据
6.1、代码
/**
* 使用字节数组接收
*
* @param bodyBytes
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/requestbody/test4")
public String test4(@RequestBody byte[] bodyBytes) {
System.out.println("body长度(bytes):" + bodyBytes.length);
System.out.println("body内容:" + new String(bodyBytes));
return "ok";
}
6.2、调用接口
### 后端使用字节数组接收数据
POST http://localhost:8080/chat18/requestbody/test4
Content-Type: text/plain;charset=UTF-8
itsoku.com
6.3、控制台输出
body长度(bytes):10
body内容:itsoku.com
推荐阅读: 2021 版 java 高并发常见面试题汇总.pdf
7、案例5:使用HttpEntity接收数据
7.1、HttpEntity:含有头和body信息
如果想同时拿到头和body的数据,可以使用,org.springframework.http.HttpEntity来接收数据,这个类中包含了头和body的信息,body是一个泛型,http请求的数据会被转换为body对应的T类型。
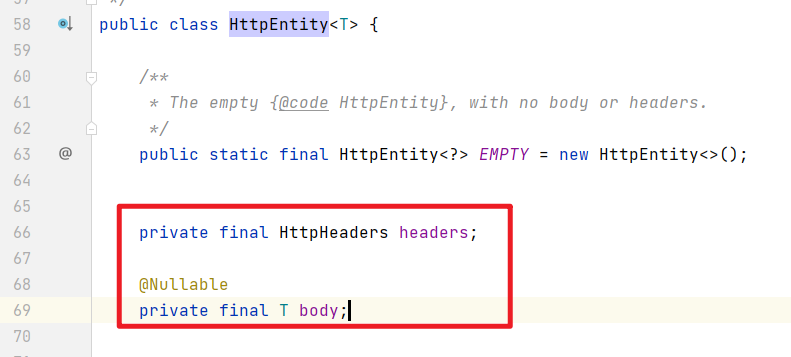
7.2、案例代码
注意:HttpEntity类型的参数不要用@RequestBody标注。
@RequestMapping("/requestbody/test5")
public String test5(HttpEntity<User> httpEntity) {
//header信息
HttpHeaders headers = httpEntity.getHeaders();
System.out.println("headers:" + headers);
//body中的内容会自动转换为HttpEntity中泛型指定的类型
User user = httpEntity.getBody();
System.out.println("body:" + user);
return "ok";
}
7.3、调用案例接口
### 发送json数据,后端用HttpEntity<User>接收
POST http://localhost:8080/chat18/requestbody/test5
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"name": "路人",
"age": 35,
"skills": [
"高并发",
"Spring",
"分布式事务",
"MQ",
"MySQL"
]
}
7.4、控制台输出
headers:[content-type:"application/json;charset=UTF-8", content-length:"130", host:"localhost:8080", connection:"Keep-Alive", user-agent:"Apache-HttpClient/4.5.12 (Java/11.0.10)", accept-encoding:"gzip,deflate"]
body:User{name='路人', age=35, skills=[高并发, Spring, 分布式事务, MQ, MySQL]}
推荐阅读: Idea 快捷键大全.pdf
8、案例6:使用RequestEntity接受数据
8.1、RequestEntity:包含更多请求信息(头、method、url,body)
RequestEntity的用法和案例5中的HttpEntity用法类似,RequestEntity继承了HttpEntity,包含了更多的信息,比RequestEntity多了2个http请求信息(method和url)
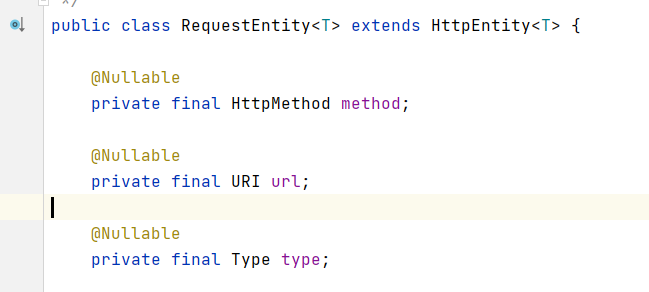
8.2、案例代码
@RequestMapping("/requestbody/test6")
public String test6(RequestEntity<User> requestEntity) {
//请求方式
HttpMethod method = requestEntity.getMethod();
System.out.println("method:" + method);
//请求地址
URI url = requestEntity.getUrl();
System.out.println("url:" + url);
//body的类型,即RequestEntity后面尖括号中的类型
Type type = requestEntity.getType();
System.out.println("body的类型,即RequestEntity后面尖括号中的类型:" + type);
//header信息
HttpHeaders headers = requestEntity.getHeaders();
System.out.println("headers:" + headers);
//body中的内容会自动转换为HttpEntity中泛型指定的类型
User user = requestEntity.getBody();
System.out.println("body:" + user);
return "ok";
}
8.3、调用案例接口
### 发送json数据,后端用对象接收
POST http://localhost:8080/chat18/requestbody/test6
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"name": "路人",
"age": 35,
"skills": [
"高并发",
"Spring",
"分布式事务",
"MQ",
"MySQL"
]
}
8.4、控制台输出
method:POST
url:http://localhost:8080/chat18/requestbody/test6
body的类型,即RequestEntity后面尖括号中的类型:class com.javacode2018.springmvc.chat18.controller.RequestBodyController$User
headers:[content-type:"application/json;charset=UTF-8", content-length:"130", host:"localhost:8080", connection:"Keep-Alive", user-agent:"Apache-HttpClient/4.5.12 (Java/11.0.10)", accept-encoding:"gzip,deflate"]
body:User{name='路人', age=35, skills=[高并发, Spring, 分布式事务, MQ, MySQL]}
9、@RequestBody还可以如何使用呢?
这里留给大家去研究,大家在运行一下案例1中的用例1
### 发送纯文本
POST http://localhost:8080/chat18/requestbody/test1
Content-Type: text/plain
这里是body部分,欢迎访问我的博客:itsoku.com,上面有更多系列文章
控制台有更详细的输出如下,注意里面的RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor,这个就是@ReqeustBody类型的参数处理器,@ReqeustBody标注的参数的值都是有这个类来解析请求得到的,大家可以去看看这个类的代码,debug一番,就知道@ReqeustBody还有那些更炫的用法了。
23:17:05.595 [http-nio-8080-exec-9] DEBUG org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet - POST "/chat18/requestbody/test1", parameters={}
23:17:05.595 [http-nio-8080-exec-9] DEBUG org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping - Mapped to com.javacode2018.springmvc.chat18.controller.RequestBodyController#test1(String)
23:17:05.596 [http-nio-8080-exec-9] DEBUG org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor - Read "text/plain;charset=UTF-8" to ["这里是body部分,欢迎访问我的博客:itsoku.com,上面有更多系列文章"]
body:这里是body部分,欢迎访问我的博客:itsoku.com,上面有更多系列文章
23:17:05.597 [http-nio-8080-exec-9] DEBUG org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor - Using 'text/plain', given [*/*] and supported [text/plain, */*, application/json, application/*+json]
23:17:05.597 [http-nio-8080-exec-9] DEBUG org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor - Writing ["ok"]
23:17:05.598 [http-nio-8080-exec-9] DEBUG org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet - Completed 200 OK
主要有5行日志,每行日志这里做一下解释
第1行:接收到了请求,请求的信息(url,参数)
第2行:找到了能够处理请求的方法,即RequestBodyController#test1(String)方法可以处理当前请求
第3行:参数解析器,@RequestBody对应的是RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor
第4行:接口中System.out.println输出的内容
第5行:返回值处理器,这个以后会有专题讲解
10、@RequestBody原理
@RequestBody标注的参数取值是由RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor#resolveArgument方法处理的,可以去看源码。
11、代码位置及说明
11.1、git地址
https://gitee.com/javacode2018/springmvc-series
11.2、本文案例代码结构说明
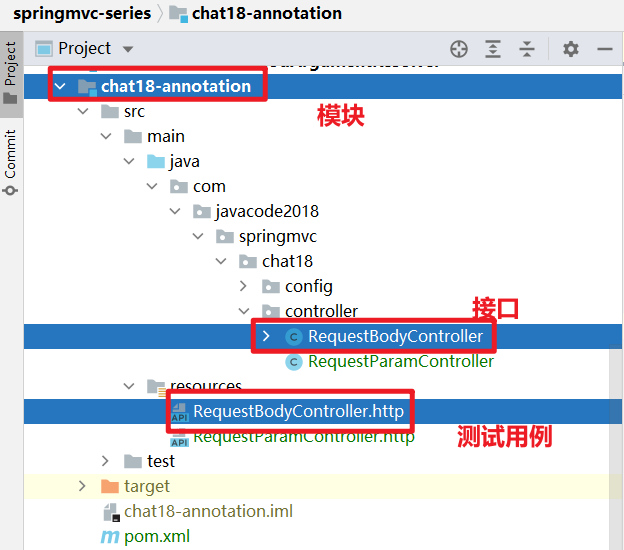
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

