配置MyCat
3. 配置conf/rule.xml
1.5GA版本中的规则配置比较笨,2.0中优化了一些,将tableRule标签和function标签合并了,并且支持Velocity模板语言,更加灵活。这里先介绍1.5GA的,2.0等以后稳定了,会推的:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mycat:rule SYSTEM "rule.dtd">
<mycat:rule xmlns:mycat="http://org.opencloudb/">
<tableRule name="mod-long">
<rule>
<columns>id</columns>
<algorithm>mod-long</algorithm>
</rule>
</tableRule>
<function name="mod-long" class="org.opencloudb.route.function.PartitionByMod">
<!-- how many data nodes -->
<property name="count">2</property>
</function>
</mycat:rule>
-
tableRule标签(多个表可以对应一个表规则)
- name 属性指定唯一的名字,用于标识不同的表规则。
内嵌的rule标签则指定对物理表中的哪一列进行拆分和使用什么路由算法。 - columns 内指定要拆分的列名字。
- algorithm 使用function标签中的name属性。连接表规则和具体路由算法。当然,多个表规则可以连接到同一个路由算法上。
- name 属性指定唯一的名字,用于标识不同的表规则。
-
function标签
- name 指定算法的名字。
- class 制定路由算法具体的类名字。
- property 为具体算法需要用到的一些属性。
上面的例子有一个表规则,对应一个算法,是MyCat1.5GA中内置的算法。我们也可以实现自己的算法。
这里配置文件实现的原理,其实就是反射,MyCat动态加载里面的规则,并动态设置class中的filed的值。
分片规则涉及到的类(算法实现类不完整)图:
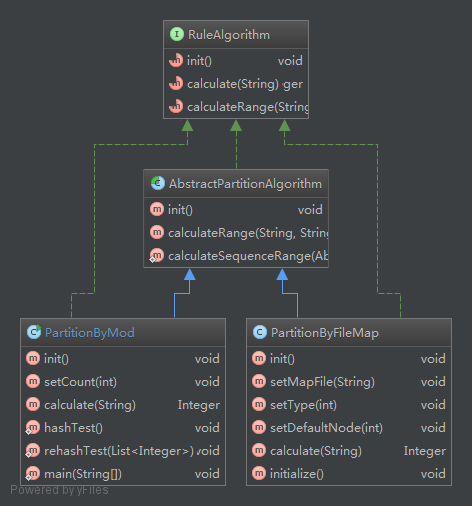
RuleAlgorithm :路由规则接口抽象,规定了分片规则的初始化(init),路由分片计算(calculate),及路由多值分片计算(calculateRange)。
分片规则中calculate方法是基本的分片路由计算方法,根据分片字段值,计算出分片。
分片规则中calculateRange方法是范围查询时分片计算,即如果查询类似:
select * from t_user t where t.id<100;
需要解析出指定范围的所有值对应分片。
自定义的分片规则只需要继承AbstractPartitionAlgorithm,按照自己的规则初始化配置文件(即正在介绍的rule.xml),并且实现calculate或者calculateRange方法即可。
AbstractPartitionAlgorithm是一个抽象类,只实现了多值路由计算。并且,根据下面的代码我们可以了解到路由算法必须继承AbstractPartitionAlgorithm
AbstractPartitionAlgorithm.java:
public abstract class AbstractPartitionAlgorithm implements RuleAlgorithm {
@Override
public void init() {
}
/**
* 返回所有被路由到的节点的编号
* 返回长度为0的数组表示所有节点都被路由(默认)
* 返回null表示没有节点被路由到
*/
@Override
public Integer[] calculateRange(String beginValue, String endValue) {
return new Integer[0];
}
/**
* 对于存储数据按顺序存放的字段做范围路由,可以使用这个函数
* @param algorithm
* @param beginValue
* @param endValue
* @return
*/
public static Integer[] calculateSequenceRange(AbstractPartitionAlgorithm algorithm, String beginValue, String endValue) {
Integer begin = 0, end = 0;
begin = algorithm.calculate(beginValue);
end = algorithm.calculate(endValue);
if(begin == null || end == null){
return new Integer[0];
}
if (end >= begin) {
int len = end-begin+1;
Integer [] re = new Integer[len];
for(int i =0;i<len;i++){
re[i]=begin+i;
}
return re;
}else{
return null;
}
}
}
下面看看PartitionByMod的源代码:
org.opencloudb.route.function.PartitionByMod:
private int count;
@Override
public void init() {
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
@Override
public Integer calculate(String columnValue) {
BigInteger bigNum = new BigInteger(columnValue).abs();
return (bigNum.mod(BigInteger.valueOf(count))).intValue();
}
这段代码很简单,就是将列的值传入后,对count取模,之后的值就是分片节点id。分片节点个数就是count。查看rule.xml里面的配置,我们在function标签传入了count值,并且在tableRule标签定义是哪一列作为分片字段。
可以优化下这段代码,根据习惯,我们一般取2的n次方作为分片个数(这样做有很多好处)。对2的n次方取模等于对2的n次方-1取与运算。代码如下:
private int count;
private boolean watch = false;
@Override
public void init() {
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
if ((count & (count - 1)) == 0) {
watch = true;
}
}
@Override
public Integer calculate(String columnValue) {
BigInteger bigNum = new BigInteger(columnValue).abs();
if (watch) {
System.out.println("sigoui");
return bigNum.intValue() & (count - 1);
}
return (bigNum.mod(BigInteger.valueOf(count))).intValue();
}
下面我们更深入些,实现使用篇(2)中的7.多重规则-可扩容哈希路由:是从分片字段中抽取一段做分片路由,再取另一段做自动哈希分片。同时再规定某个范围内是某个分片规则,另一范围是另一个分片规则。
通过读取外部规则配置文件scalable-route-hash.txt,来实现灵活的规则配置。增加规则时,修改scalable-route-hash.txt之后在9066端口的控制台动态加载即可(之后会介绍)。
scalable-route-hash.txt:
北京(A0000000~A9999999)=0,1,2,3,4
北京(B0000000)=5,6,7,8,9
上海(00000000~10000000)=10,11
上海=10,11,12,13,14,15
意思就是,开头为北京的范围在A0000000~A9999999的根据后面的哈希值对5取模平均分布在0,1,2,3,4分片节点上。开头为北京的范围在B0000000以上的根据后面的哈希值对5取模平均分布在5,6,7,8,9分片节点上。开头为上海的范围在00000000~10000000的根据后面的哈希值对2取模平均分布在10,11分片节点上,剩下的开头为上海的,对6取模平均分布在10,11,12,13,14,15上。
这样,在发现某个开头的分片不够用时,可以随时改变分片规则,只要不删除之前的分片规则,就不影响以前数据的访问。在完成数据迁移后,可以删除之前的规则。
实现方法就是采用hashmap存储这些对应关系:
/**
* 首先实现不带范围约定的复合规则,即配置文件中为:
* 北京=0,1,2,3,4
* 上海=10,11
*/
public class PartitionByRouteHash extends AbstractPartitionAlgorithm implements RuleAlgorithm {
protected String routeFile;
private Map<String, List<Integer>> routeNodeMap;
protected static final String DEFAULT_NODE = "DEFAULT_NODE";
protected int keyStartIndex;
protected int keyEndIndex;
protected int valueStartIndex;
protected int valueEndIndex;
public void setKeyStartIndex(int keyStartIndex) {
this.keyStartIndex = keyStartIndex;
}
public void setKeyEndIndex(int keyEndIndex) {
this.keyEndIndex = keyEndIndex;
}
public void setValueStartIndex(int valueStartIndex) {
this.valueStartIndex = valueStartIndex;
}
public void setValueEndIndex(int valueEndIndex) {
this.valueEndIndex = valueEndIndex;
}
public void setRouteFile(String routeFile) {
this.routeFile = routeFile;
}
@Override
public void init() {
initialize();
}
@Override
public Integer calculate(String columnValue) {
String key = columnValue.substring(keyStartIndex,keyEndIndex);
String value = columnValue.substring(valueStartIndex,valueEndIndex);
List<Integer> nodes = routeNodeMap.get(key);
if(nodes == null)
nodes = routeNodeMap.get(DEFAULT_NODE);
BigInteger bigNum = new BigInteger(""+value.hashCode());
return nodes.get((bigNum.mod(BigInteger.valueOf(nodes.size()))).intValue());
}
/**
* 读取文件,创建哈希表保存对应关系
*/
private void initialize() {
BufferedReader in = null;
try {
// FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream(new File(fileMapPath));
InputStream fin = this.getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream(routeFile);
if (fin == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("can't find class resource file "
+ routeFile);
}
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fin));
routeNodeMap = new HashMap<String, List<Integer>>();
for (String line = null; (line = in.readLine()) != null;) {
line = line.trim();
if (line.startsWith("#") || line.startsWith("//"))
continue;
int ind = line.indexOf('=');
if (ind < 0)
continue;
try {
String key = line.substring(0, ind).trim();
String value = line.substring(ind+1).trim();
String []nodes = value.split(",");
List<Integer> values = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i = 0 ; i< nodes.length ; i++){
values.add(Integer.parseInt(nodes[i].trim()));
}
routeNodeMap.put(key,values);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("something wrong in the route hash configuration!");
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (e instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) e;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} finally {
try {
in.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
}
}
}
}
/**
* 实现范围约定的复合规则
*/
public class PartitionByScalableRouteHash extends PartitionByRouteHash {
private Map<String,Map<String[],List<Integer>>> routeNodeMap;
@Override
public void init() {
initialize();
}
@Override
public Integer calculate(String columnValue) {
String key = columnValue.substring(keyStartIndex,keyEndIndex);
String value = columnValue.substring(valueStartIndex,valueEndIndex);
Map<String[],List<Integer>> scaleMap = routeNodeMap.get(key);
if(scaleMap==null){
scaleMap = routeNodeMap.get(this.DEFAULT_NODE);
}
String []ranges = new String[1];
for(String []range:scaleMap.keySet()){
if(range[0].equals(this.DEFAULT_NODE))
continue;
if(range[0].compareTo(value)<0&&range[1].compareTo(value)>0)
ranges = range;
}
if(ranges.length==1) {
for(String []range:scaleMap.keySet()){
if(range[0].equals(this.DEFAULT_NODE)){
ranges = range;
break;
}
}
}
List<Integer> nodes = scaleMap.get(ranges);
BigInteger bigNum = new BigInteger(""+value.hashCode());
return nodes.get((bigNum.mod(BigInteger.valueOf(nodes.size()))).intValue());
}
private void initialize(){
BufferedReader in = null;
try {
// FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream(new File(fileMapPath));
InputStream fin = this.getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream(routeFile);
if (fin == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("can't find class resource file "
+ routeFile);
}
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fin));
routeNodeMap = new HashMap<String, Map<String[], List<Integer>>>();
for (String line = null; (line = in.readLine()) != null;) {
line = line.trim();
if (line.startsWith("#") || line.startsWith("//"))
continue;
int lb = line.indexOf('('),rb = line.indexOf(')'),mb = line.indexOf(':');
int ind = line.indexOf('=');
if((lb!=-1&&rb!=-1&&mb!=-1)&&(mb<lb||mb>rb||lb>rb||rb>ind)){
throw new RuntimeException("Wrong format! Error use of (),:,=!");
}
if (ind < 0)
continue;
try {
String key = line.substring(0, lb<0?ind:lb).trim();
Map<String[],List<Integer>> scaleMap = routeNodeMap.get(key);
if(scaleMap == null){
scaleMap = new HashMap<String[],List<Integer>>();
routeNodeMap.put(key,scaleMap);
}
String[] valueRange = new String[2];
if(lb!=-1&&rb!=-1&&mb!=-1) {
String minValue = line.substring(lb + 1, mb).trim();
String maxValue = line.substring(mb + 1, rb).trim();
if (minValue.length() != maxValue.length() || minValue.compareTo(maxValue) >= 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("Wrong value range! ");
}
valueRange[0] = minValue;
valueRange[1] = maxValue;
}
else {
valueRange[0] = this.DEFAULT_NODE;
}
String value = line.substring(ind+1).trim();
String []nodes = value.split(",");
List<Integer> node = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i = 0 ; i< nodes.length ; i++){
node.add(Integer.parseInt(nodes[i].trim()));
}
scaleMap.put(valueRange,node);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("something wrong in the route hash configuration!");
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (e instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) e;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} finally {
try {
in.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
}
}
}
}
之后如果想用这个规则,在rule.xml中添加如下配置即可:
<tableRule name="scalable-route-hash">
<rule>
<columns>order_id</columns>
<algorithm>scalable-route-hash</algorithm>
</rule>
</tableRule>
<function name="scalable-route-hash" class="org.opencloudb.route.function.PartitionByRouteHash">
<property name="routeFile">scalable-route-hash.txt</property>
<property name="keyStartIndex">0</property>
<property name="keyEndIndex">5</property>
<property name="valueStartIndex">5</property>
<property name="valueEndIndex">11</property>
</function>
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

