Filter 是扩展 Dubbo 功能的首选方案 ,并且 Dubbo 自身也提供了非常多的 Filter 实现来扩展自身功能。 Filter 链的组装逻辑设计得非常灵活,其中可以通过-配置手动剔除 Dubbo 原生提供的、默认加载的 Filter,通过default来代替 Dubbo 原生提供的 Filter,这样就可以很好地控制哪些 Filter 要加载,以及 Filter 的真正执行顺序。
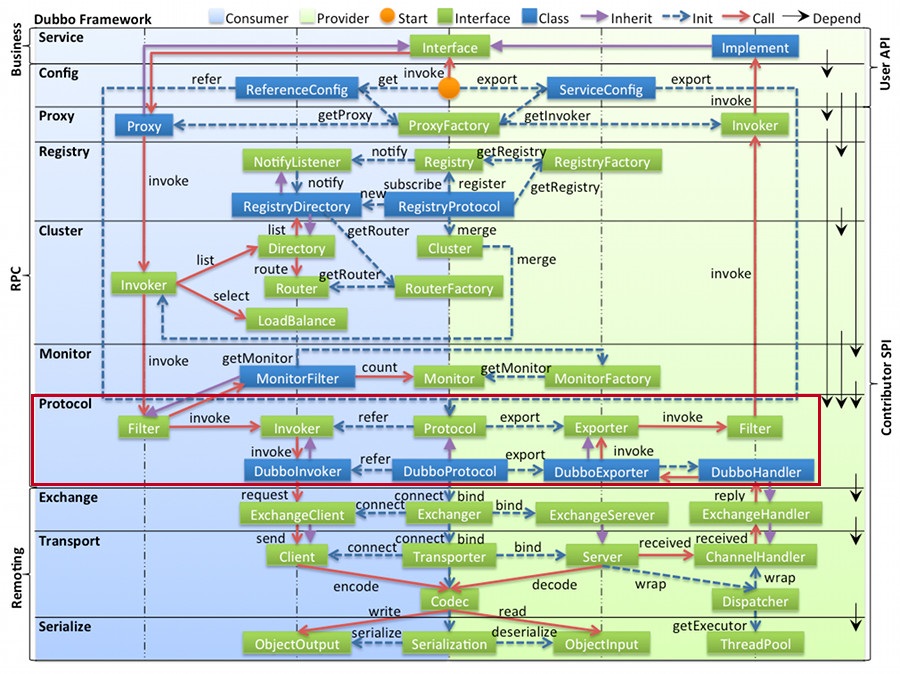
Filter 在 Dubbo 架构中的位置如下图所示:
本章,我就对Dubbo内置的各种Filter的功能和源码实现进行分析,同时讲解自定义扩展Filter的方法。
一、内置Filter
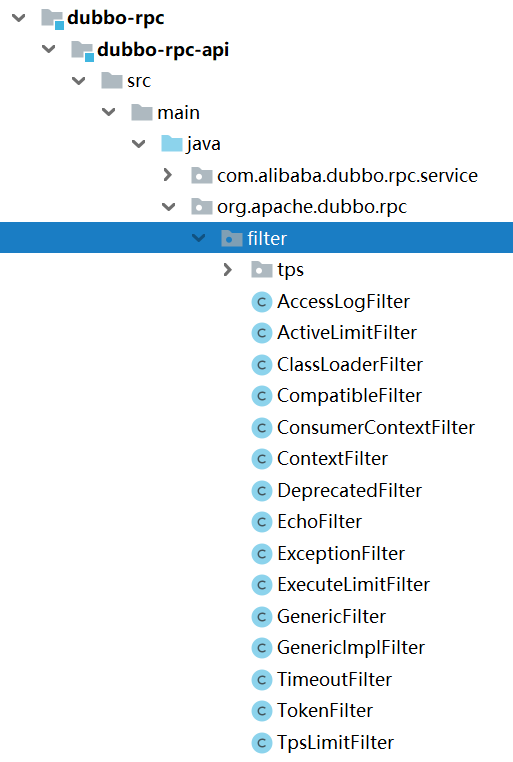
Dubbo PRC 层提供的各种内置Filter均位于 dubbo-rpc-api 模块的 org.apache.dubbo.rpc.filter包中:
1.1 ConsumerContextFilter
ConsumerContextFilter 是一个非常简单的 Consumer 端 的 Filter 实现,它会在当前的 RpcContext 中记录本地调用的一些状态信息(记录到 LOCAL 对应的 RpcContext 中):包含调用相关的 Invoker、Invocation 以及调用的本地地址、远端地址信息等等。
// ConsumerContextFilter.java
@Activate(group = CONSUMER, order = -10000)
public class ConsumerContextFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
RpcContext context = RpcContext.getContext();
context.setInvoker(invoker) // 记录Invoker
.setInvocation(invocation) // 记录Invocation
.setLocalAddress(NetUtils.getLocalHost(), 0) // 记录本地地址
.setRemoteAddress(invoker.getUrl().getHost(), invoker.getUrl().getPort()) // 记录远端地址
.setRemoteApplicationName(invoker.getUrl().getParameter(REMOTE_APPLICATION_KEY))
.setAttachment(REMOTE_APPLICATION_KEY, invoker.getUrl().getParameter(APPLICATION_KEY));
if (invocation instanceof RpcInvocation) {
((RpcInvocation) invocation).setInvoker(invoker);
}
// 检测是否超时
Object countDown = context.get(TIME_COUNTDOWN_KEY);
if (countDown != null) {
TimeoutCountDown timeoutCountDown = (TimeoutCountDown) countDown;
// 请求超时
if (timeoutCountDown.isExpired()) {
return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(new RpcException(RpcException.TIMEOUT_TERMINATE,
"No time left for making the following call: " + invocation.getServiceName() + "."
+ invocation.getMethodName() + ", terminate directly."), invocation);
}
}
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
}
这里使用的 TimeoutCountDown 对象用于检测当前调用是否超时,其中有三个字段:
- timeoutInMillis(long 类型):超时时间,单位为毫秒;
- deadlineInNanos(long 类型):超时的时间戳,单位为纳秒;
- expired(boolean 类型):标识当前 TimeoutCountDown 关联的调用是否已超时。
在 TimeoutCountDown.isExpire() 方法中,会比较当前时间与 deadlineInNanos 字段记录的超时时间戳。正如上面看到的逻辑,如果请求超时,则不再发起远程调用,直接让 AsyncRpcResult 异常结束。
1.2 ActiveLimitFilter
ActiveLimitFilter 是一个用于控制 Consumer 并发调用量的Filter,也可以称为“客户端限流”。下面我们就来看下 ActiveLimitFilter 的具体实现:
// ActiveLimitFilter.java
@Activate(group = CONSUMER, value = ACTIVES_KEY)
public class ActiveLimitFilter implements Filter, Filter.Listener {
private static final String ACTIVELIMIT_FILTER_START_TIME = "activelimit_filter_start_time";
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
// 获得url对象
URL url = invoker.getUrl();
// 获得服务的方法名称
String methodName = invocation.getMethodName();
// 获取最大并发数
int max = invoker.getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, ACTIVES_KEY, 0);
// 获取该方法的状态信息
final RpcStatus rpcStatus = RpcStatus.getStatus(invoker.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName());
// 尝试并发数加1
if (!RpcStatus.beginCount(url, methodName, max)) {
long timeout = invoker.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), TIMEOUT_KEY, 0);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
long remain = timeout;
synchronized (rpcStatus) {
// 再次尝试并发数加1
while (!RpcStatus.beginCount(url, methodName, max)) {
try {
// 阻塞当前线程,等待并发数降低
rpcStatus.wait(remain);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
// 检测是否超时
long elapsed = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
remain = timeout - elapsed;
if (remain <= 0) {
throw new RpcException(RpcException.LIMIT_EXCEEDED_EXCEPTION,
"Waiting concurrent invoke timeout in client-side for service: " +
invoker.getInterface().getName() + ", method: " + invocation.getMethodName() +
", elapsed: " + elapsed + ", timeout: " + timeout + ". concurrent invokes: " +
rpcStatus.getActive() + ". max concurrent invoke limit: " + max);
}
}
}
}
// 添加一个attribute
invocation.put(ACTIVELIMIT_FILTER_START_TIME, System.currentTimeMillis());
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
}
从 ActiveLimitFilter.invoke() 方法的代码中可以看到,其核心实现与 RpcStatus 对象密切相关。RpcStatus 中维护了两个集合,分别是:
SERVICE_STATISTICS集合(ConcurrentMap<String, RpcStatus>类型),这个集合记录了当前 Consumer 调用每个服务的状态信息,其中 Key 是 URL,Value 是对应的 RpcStatus 对象;METHOD_STATISTICS集合(ConcurrentMap<String, ConcurrentMap<String, RpcStatus>>类型),这个集合记录了当前 Consumer 调用每个服务方法的状态信息,其中第一层 Key 是 URL ,第二层 Key 是方法名称,第三层是对应的 RpcStatus 对象。
RpcStatus 中统计了很多调用相关的信息,核心字段有如下几个:
- active(AtomicInteger 类型):当前并发数;
- total(AtomicLong 类型):调用的总数;
- failed(AtomicInteger 类型):失败的调用数;
- totalElapsed(AtomicLong 类型):所有调用的总耗时;
- failedElapsed(AtomicLong 类型):所有失败调用的总耗时;
- maxElapsed(AtomicLong 类型):所有调用中最长的耗时;
- failedMaxElapsed(AtomicLong 类型):所有失败调用中最长的耗时;
- succeededMaxElapsed(AtomicLong 类型):所有成功调用中最长的耗时。
RpcStatus 中的 beginCount() 方法会在远程调用开始之前执行,其中会从 SERVICE_STATISTICS 集合和 METHOD_STATISTICS 集合中获取服务和服务方法对应的 RpcStatus 对象,然后分别将它们的 active 字段加1,相关实现如下:
// RpcStatus.java
public static boolean beginCount(URL url, String methodName, int max) {
max = (max <= 0) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : max;
// 获取服务对应的RpcStatus对象
RpcStatus appStatus = getStatus(url);
// 获取服务方法对应的RpcStatus对象
RpcStatus methodStatus = getStatus(url, methodName);
if (methodStatus.active.get() == Integer.MAX_VALUE) { // 并发数溢出
return false;
}
for (int i; ; ) {
i = methodStatus.active.get();
if (i + 1 > max) { // 并发数超过max上限,直接返回false
return false;
}
if (methodStatus.active.compareAndSet(i, i + 1)) { // CAS操作
break; // 更新成功后退出当前循环
}
}
appStatus.active.incrementAndGet(); // 单个服务的并发数加1
return true;
}
ActiveLimitFilter 在继承 Filter 接口的同时,还继承了 Filter.Listener 这个内部接口,在其 onResponse() 方法的实现中,不仅会调用 RpcStatus.endCount() 方法完成调用监控的统计,还会调用 notifyFinish() 方法唤醒阻塞在对应 RpcStatus 对象上的线程,具体实现如下:
// ActiveLimitFilter.java
public void onResponse(Result appResponse, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
// 获取调用的方法名称
String methodName = invocation.getMethodName();
URL url = invoker.getUrl();
int max = invoker.getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, ACTIVES_KEY, 0);
// 调用 RpcStatus.endCount() 方法完成调用监控的统计
RpcStatus.endCount(url, methodName, getElapsed(invocation), true);
// 调用 notifyFinish() 方法唤醒阻塞在对应 RpcStatus 对象上的线程
notifyFinish(RpcStatus.getStatus(url, methodName), max);
}
1.3 ContextFilter
ContextFilter 是 Provider 端的一个 Filter 实现,它主要用来初始化 Provider 端的 RpcContext:
- ContextFilter 首先会从 Invocation 中获取 Attachments 集合,并对该集合中的 Key 进行过滤,将
UNLOADING_KEYS集合中的全部 Key 过滤掉; - 之后,会初始化 RpcContext 以及 Invocation 的各项信息,例如,Invocation、Attachments、localAddress、remoteApplication、超时时间等;
- 最后,调用 Invoker.invoke() 方法执行 Provider 的业务逻辑。ContextFilter.Invoke() 方法的具体逻辑如下所示:
// ContextFilter.java
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
Map<String, Object> attachments = invocation.getObjectAttachments();
//...
// 获取RpcContext
RpcContext context = RpcContext.getContext();
// 设置RpcContext中的信息
context.setInvoker(invoker)
.setInvocation(invocation)
.setLocalAddress(invoker.getUrl().getHost(), invoker.getUrl().getPort());
String remoteApplication = (String) invocation.getAttachment(REMOTE_APPLICATION_KEY);
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(remoteApplication)) {
context.setRemoteApplicationName(remoteApplication);
} else {
context.setRemoteApplicationName((String) context.getAttachment(REMOTE_APPLICATION_KEY));
}
// 设置超时时间
long timeout = RpcUtils.getTimeout(invocation, -1);
if (timeout != -1) {
context.set(TIME_COUNTDOWN_KEY, TimeoutCountDown.newCountDown(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
// 向RpcContext中设置Attachments
if (attachments != null) {
if (context.getObjectAttachments() != null) {
context.getObjectAttachments().putAll(attachments);
} else {
context.setObjectAttachments(attachments);
}
}
// 向Invocation设置Invoker
if (invocation instanceof RpcInvocation) {
((RpcInvocation) invocation).setInvoker(invoker);
}
try {
// 在整个调用过程中,需要保持当前RpcContext不被删除,这里会将remove开关关掉,这样,removeContext()方法不会删除LOCAL RpcContext了
context.clearAfterEachInvoke(false);
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
} finally {
// 重置remove开关
context.clearAfterEachInvoke(true);
// 清理RpcContext,当前线程处理下一个调用的时候,会创建新的RpcContext
RpcContext.removeContext(true);
RpcContext.removeServerContext();
}
}
ContextFilter 继承 Filter 接口的同时,还继承了 Filter.Listener 这个内部接口。在 ContextFilter.onResponse() 方法中,会将 SERVER_LOCAL 这个 RpcContext 中的附加信息添加到 AppResponse 的 attachments 字段中,返回给 Consumer。
// ContextFilter.java
public void onResponse(Result appResponse, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
appResponse.addObjectAttachments(RpcContext.getServerContext().getObjectAttachments());
}
1.4 AccessLogFilter
AccessLogFilter 主要用于记录日志,它的主要功能是将 Provider 或者 Consumer 的日志信息写入文件中。AccessLogFilter 会先将日志消息放入内存日志集合中缓存,当缓存大小超过一定阈值之后,会触发日志的写入。若长时间未触发日志文件写入,则由定时任务定时写入。
AccessLogFilter.invoke() 方法的核心实现如下:
// AccessLogFilter.java
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation inv) throws RpcException {
// 获取ACCESS_LOG_KEY
String accessLogKey = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(ACCESS_LOG_KEY);
if (ConfigUtils.isNotEmpty(accessLogKey)) {
// 构造AccessLogData对象,其中记录了日志信息,例如,调用的服务名称、方法名称、version等
AccessLogData logData = buildAccessLogData(invoker, inv);
// 写日志
log(accessLogKey, logData);
}
// 调用下一个Invoker
return invoker.invoke(inv);
}
在 AccessLogFilter.log() 方法中,会按照 ACCESS_LOG_KEY 的值,找到对应的 AccessLogData 集合,然后完成缓存写入;如果缓存大小超过阈值,则触发文件写入,具体实现如下:
// AccessLogFilter.java
private void log(String accessLog, AccessLogData accessLogData) {
// 根据ACCESS_LOG_KEY获取对应的缓存集合
Set<AccessLogData> logSet = LOG_ENTRIES.computeIfAbsent(accessLog, k -> new ConcurrentHashSet<>());
// 缓存大小未超过阈值
if (logSet.size() < LOG_MAX_BUFFER) {
logSet.add(accessLogData);
}
// 缓存大小超过阈值,触发缓存数据写入文件
else {
writeLogSetToFile(accessLog, logSet);
// 完成文件写入之后,再次写入缓存
logSet.add(accessLogData);
}
}
在 writeLogSetToFile() 方法中,会按照 ACCESS_LOG_KEY 的值将日志信息写入不同的日志文件中:
- 如果
ACCESS_LOG_KEY配置的值为 true 或 default,会使用 Dubbo 默认提供的统一日志框架,输出到日志文件中; - 如果
ACCESS_LOG_KEY配置的值不为 true 或 default,则ACCESS_LOG_KEY配置值会被当作 access log 文件的名称,AccessLogFilter 会创建相应的目录和文件,并完成日志的输出。
// AccessLogFilter.java
private void writeLogSetToFile(String accessLog, Set<AccessLogData> logSet) {
try {
// ACCESS_LOG_KEY配置值为true或是default
if (ConfigUtils.isDefault(accessLog)) {
processWithServiceLogger(logSet);
}
// ACCESS_LOG_KEY配置既不是true也不是default
else {
File file = new File(accessLog);
// 创建目录
createIfLogDirAbsent(file);
// 创建日志文件,这里会以日期为后缀,滚动创建
renameFile(file);
// 遍历logSet集合,将日志逐条写入文件
processWithAccessKeyLogger(logSet, file);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
private void processWithAccessKeyLogger(Set<AccessLogData> logSet, File file) throws IOException {
// 创建FileWriter,写入指定的日志文件
try (FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(file, true)) {
for (Iterator<AccessLogData> iterator = logSet.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();
iterator.remove()) {
writer.write(iterator.next().getLogMessage());
writer.write(System.getProperty("line.separator"));
}
writer.flush();
}
}
在 AccessLogFilter 的构造方法中,会启动一个定时任务,定时调用上面介绍的 writeLogSetToFile() 方法,定时写入日志,具体实现如下:
// AccessLogFilter.java
// 启动一个线程池
private static final ScheduledExecutorService LOG_SCHEDULED =
Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(new NamedThreadFactory("Dubbo-Access-Log", true));
// 启动一个定时任务,定期执行writeLogSetToFile()方法,完成日志写入
public AccessLogFilter() {
LOG_SCHEDULED.scheduleWithFixedDelay(
this::writeLogToFile, LOG_OUTPUT_INTERVAL,
LOG_OUTPUT_INTERVAL, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
1.5 ClassLoaderFilter
ClassLoaderFilter 是 Provider 端的一个 Filter 实现,主要功能是切换类加载器。
在 ClassLoaderFilter.invoke() 方法中,首先获取当前线程关联的 contextClassLoader,然后将其 ContextClassLoader 设置为 invoker.getInterface().getClassLoader(),也就是加载服务接口类的类加载器;之后执行 invoker.invoke() 方法,执行后续的 Filter 逻辑以及业务逻辑;最后,将当前线程关联的 contextClassLoader 重置为原来的 contextClassLoader。ClassLoaderFilter 的核心逻辑如下:
// ClassLoaderFilter.java
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
ClassLoader ocl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// 更新当前线程绑定的ClassLoader
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(invoker.getInterface().getClassLoader());
try {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
} finally {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(ocl);
}
}
1.6 ExecuteLimitFilter
ExecuteLimitFilter 是 Dubbo 在 Provider 端的限流实现 ,与 Consumer 端的限流实现 ActiveLimitFilter 相对应。ExecuteLimitFilter 的核心实现与 ActiveLimitFilter类似,也是依赖 RpcStatus 的 beginCount() 方法和 endCount() 方法来实现 RpcStatus.active 字段的增减,具体实现如下:
// ExecuteLimitFilter.java
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
URL url = invoker.getUrl();
String methodName = invocation.getMethodName();
int max = url.getMethodParameter(methodName, EXECUTES_KEY, 0);
// 尝试增加active的值,当并发度达到executes配置指定的阈值,则直接抛出异常
if (!RpcStatus.beginCount(url, methodName, max)) {
throw new RpcException("...");
}
invocation.put(EXECUTE_LIMIT_FILTER_START_TIME, System.currentTimeMillis());
// 执行后续Filter以及业务逻辑
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
ExecuteLimitFilter 同时还实现了 Filter 内部的 Listener 接口,在 onResponse() 方法和 onError() 方法中会调用 RpcStatus.endCount() 方法,减小 active 的值,同时完成对一次调用的统计,具体实现比较简单,这里就不再赘述。
1.7 TimeoutFilter
TimeoutFilter 是 Provider 端另一个涉及超时时间的 Filter 实现,其 invoke() 方法实现比较简单,直接将请求转发给后续 Filter 处理。在 TimeoutFilter 对 onResponse() 方法的实现中,会从 RpcContext 中读取上述 TimeoutCountDown 对象,并检查此次请求是否超时。如果请求已经超时,则会将 AppResponse 中的结果清空,同时打印一条警告日志,具体实现如下:
// TimeoutFilter.java
public void onResponse(Result appResponse, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
Object obj = RpcContext.getContext().get(TIME_COUNTDOWN_KEY);
if (obj != null) {
TimeoutCountDown countDown = (TimeoutCountDown) obj;
// 检查结果是否超时
if (countDown.isExpired()) {
// 清理结果信息
((AppResponse) appResponse).clear();
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("...");
}
}
}
}
1.8 TpsLimitFilter
TpsLimitFilter 是 Provider 端对 TPS 限流的实现 。TpsLimitFilter 中维护了一个 TPSLimiter 接口类型的对象,其默认实现是 DefaultTPSLimiter,由它来控制 Provider 端的 TPS 上限值为多少。TpsLimitFilter.invoke() 方法的具体实现如下:
// TpsLimitFilter.java
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
// 超过限流之后,直接抛出异常
if (!tpsLimiter.isAllowable(invoker.getUrl(), invocation)) {
throw new RpcException("... ");
}
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
TPSLimiter 接口中的核心是 isAllowable() 方法。在 DefaultTPSLimiter 实现中,使用ConcurrentHashMap(stats 字段)为每个 ServiceKey 维护了一个相应的 StatItem 对象;在 isAllowable() 方法实现中,会从 URL 中读取 tps 参数值(默认为 -1,即没有限流),对于需要限流的请求,会从 stats 集合中获取(或创建)相应 StatItem 对象,然后调用 StatItem 对象的isAllowable() 方法判断是否被限流,具体实现如下:
// TpsLimitFilter.java
public boolean isAllowable(URL url, Invocation invocation) {
int rate = url.getParameter(TPS_LIMIT_RATE_KEY, -1);
long interval = url.getParameter(TPS_LIMIT_INTERVAL_KEY, DEFAULT_TPS_LIMIT_INTERVAL);
String serviceKey = url.getServiceKey();
// 需要限流,尝试从stats集合中获取相应的StatItem对象
if (rate > 0) {
StatItem statItem = stats.get(serviceKey);
// 查询stats集合失败,则创建新的StatItem对象
if (statItem == null) {
stats.putIfAbsent(serviceKey, new StatItem(serviceKey, rate, interval));
statItem = stats.get(serviceKey);
}
// URL中参数发生变化时,会重建对应的StatItem
else {
if (statItem.getRate() != rate || statItem.getInterval() != interval) {
stats.put(serviceKey, new StatItem(serviceKey, rate, interval));
statItem = stats.get(serviceKey);
}
}
return statItem.isAllowable();
}
// 不需要限流,则从stats集合中清除相应的StatItem对象
else {
StatItem statItem = stats.get(serviceKey);
if (statItem != null) {
stats.remove(serviceKey);
}
}
return true;
}
在 StatItem 中会记录如下一些关键信息:
- name(String 类型):对应的 ServiceKey;
- rate(int 类型):一段时间内能通过的 TPS 上限;
- token(LongAdder 类型):初始值为 rate 值,每通过一个请求 token 递减一,当减为 0 时,不再通过任何请求,实现限流的作用;
- interval(long 类型):重置 token 值的时间周期,这样就实现了在 interval 时间段内能够通过 rate 个请求的效果。
下面我们来看 StatItem 中 isAllowable() 方法的实现:
// StatItem.java
public boolean isAllowable() {
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 周期性重置token
if (now > lastResetTime + interval) {
token = buildLongAdder(rate);
// 记录最近一次重置token的时间戳
lastResetTime = now;
}
// 请求限流
if (token.sum() < 0) {
return false;
}
// 请求正常通过
token.decrement();
return true;
}
二、自定义Filter
了解完 Dubbo 提供的多种 Filter 实现之后,下面我实现一个自定义的 Filter,来进一步扩展 Dubbo 的功能。这里我编写两个自定义的 Filter 实现类—— JarVersionConsumerFilter 和 JarVersionProviderFilter。
- JarVersionConsumerFilter: 作用于Consumer端,获取服务接口所在 jar 包的版本,并作为 attachment 随请求发送到 Provider 端;
- JarVersionProviderFilter: 作用于Provider端,统计请求中携带的 jar 包版本,并周期性打印。
2.1 JarVersionConsumerFilter
首先,我们来看 JarVersionConsumerFilter 实现中的几个关键点:
- JarVersionConsumerFilter 被
@Activate注解修饰,其中的group字段值为 CommonConstants.CONSUMER,会在 Consumer 端自动激活,order 字段值为 -1 ,是最后执行的 Filter; - JarVersionConsumerFilter 中维护了一个
LoadingCache用于缓存各个业务接口与对应 jar 包版本号之间的映射关系; - 在 invoke() 方法的实现中,会通过
LoadingCache查询接口所在 jar 包的版本号,然后记录到 Invocation 的attachment之中,发送到 Provider 端。
下面是 JarVersionConsumerFilter 的具体实现:
// JarVersionConsumerFilter.java
@Activate(group = {CommonConstants.CONSUMER}, order = -1)
public class JarVersionConsumerFilter implements Filter {
private static final String JAR_VERSION_NAME_KEY = "dubbo.jar.version";
// 通过一个LoadingCache缓存各个Class所在的jar包版本
private LoadingCache<Class<?>, String> versionCache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(1024).build(new CacheLoader<Class<?>, String>() {
@Override
public String load(Class<?> key) throws Exception {
return getJarVersion(key);
}
});
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
Map<String, String> attachments = invocation.getAttachments();
String version = versionCache.getUnchecked(invoker.getInterface());
// 添加版本号
if (!StringUtils.isBlank(version)) {
attachments.put(JAR_VERSION_NAME_KEY, version);
}
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
// 读取Classpath下的"/META-INF/MANIFEST.MF"文件,获取jar包版本
private String getJarVersion(Class clazz) {
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(clazz.getResourceAsStream("/META-INF/MANIFEST.MF")))) {
String s = null;
while ((s = reader.readLine()) != null) {
int i = s.indexOf("Implementation-Version:");
if (i > 0) {
return s.substring(i);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// 省略异常处理逻辑
}
return "";
}
}
2.2 JarVersionProviderFilter
JarVersionProviderFilter 的实现非常简单,它会读取请求中的版本信息,并将关联的计数器加1。另外,JarVersionProviderFilter 的构造方法中会启动一个定时任务,每隔一分钟执行一次,将统计结果打印到日志。
JarVersionProviderFilter 既然要运行在 Provider 端,那就需要将其 @Activate 注解的 group 字段设置为 CommonConstants.PROVIDER 常量。
// JarVersionProviderFilter.java
@Activate(group = {CommonConstants.PROVIDER}, order = -1)
public class JarVersionProviderFilter implements Filter {
private static final String JAR_VERSION_NAME_KEY = "dubbo.jar.version";
private static final Map<String, AtomicLong> versionState = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static final ScheduledExecutorService SCHEDULED_EXECUTOR_SERVICE = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
public JarVersionProviderFilter() { // 启动定时任务
SCHEDULED_EXECUTOR_SERVICE.schedule(() -> {
for (Map.Entry<String, AtomicLong> entry : versionState.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue().getAndSet(0)); // 打印日志并将统计数据重置
}
}, 1, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
}
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
String versionAttachment = invocation.getAttachment(JAR_VERSION_NAME_KEY);
if (!StringUtils.isBlank(versionAttachment)) {
AtomicLong count = versionState.computeIfAbsent(versionAttachment, v -> new AtomicLong(0L));
count.getAndIncrement(); // 递增该版本的统计值
}
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
}
最后,我们需要在 Provider 项目的 /resources/META-INF/dubbo 目录下添加一个 SPI 配置文件,文件名为 org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Filter,内容如下:
version-provider = org.apache.dubbo.demo.provider.JarVersionProviderFilter
同样,也需要在 Consumer 项目相同位置添加相同的 SPI 配置文件(文件名称也相同),具体内容如下:
version-consumer=org.apache.dubbo.demo.consumer.JarVersionConsumerFilter
三、总结
本章,我对 Dubbo 中 Filter 接口的相关实现进行了讲解,重点分析了 Dubbo 中多个内置的 Filter 实现,这些内置 Filter 对于实现 Dubbo 核心功能是不可或缺的。最后,我还讲解了自定义 Filter 扩展 Dubbo 功能的流程,并通过一个统计 jar 包版本的示例进行说明。
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

