FastThreadLocal
先说下这个,简单说就是你可以理解为跟线程相关的数据,每个线程都可以有相同key的不同数据。比如netty想让每个线程对应有自己的内存arena,当然也可以让他们共有一块大内存,但是这样会导致很多多线程竞争的问题,所以能不能设计成让每个线程独有自己的内存,尽量跟别的线程少竞争,提高效率,所以可以用ThreadLocal,但是netty嫌效率不够,因此开发了FastThreadLocal,用空间换时间,提高效率。
怎么提高效率
要搞清楚怎么就能提高效率,怎么个用空间换时间,就得先搞清楚ThreadLocal是怎么来处理的。
ThreadLocal的处理方式
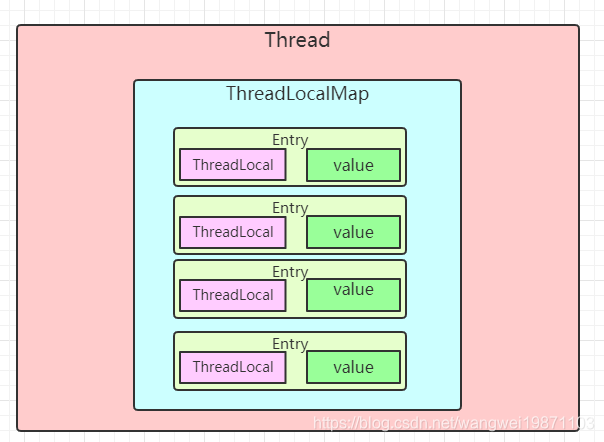
这个介绍网上文章太多了,我就简单的说,Thread内部都有一个ThreadLocalMap属性,内部是一个Entry数组,Entry里面保存着ThreadLocal和对应的值,而且是个弱引用,引用对象就是ThreadLocal,这个可以在gc的时候回收ThreadLocal,然后调用相应的方法再对值和Entry进行回收:
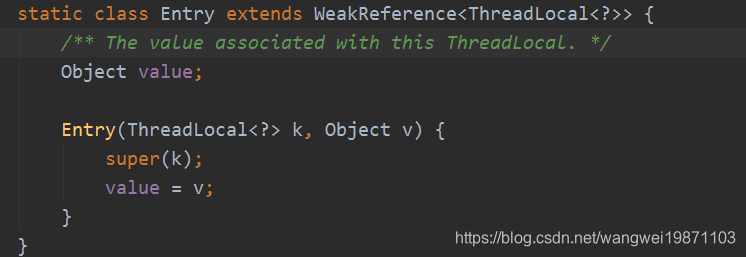
这里比较耗时的地方就是,在放入ThreadLocalMap的时候,用的是hash算法,然后对数组取模算出索引,但是这样可能会冲突,解决冲突的方式叫线性探测法,就是看冲突索引的下一个能不能放,不能就继续往后找,不够就扩容,直到能放下为止。所以一次放的操作就可能消耗很大了。
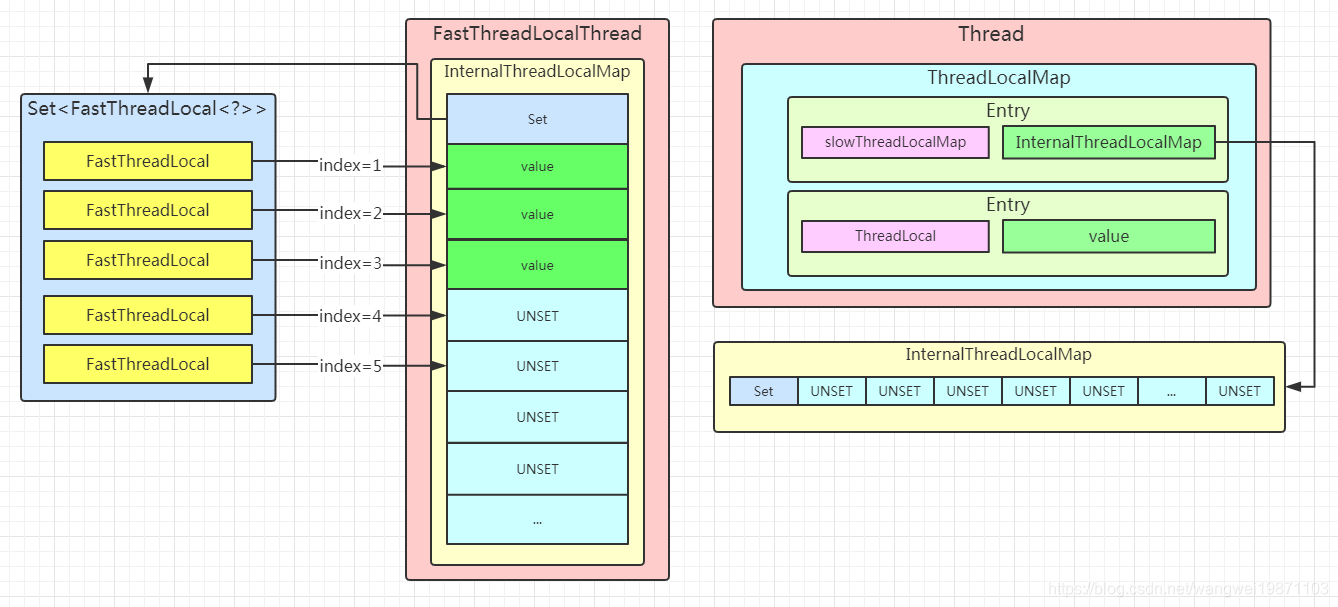
FastThreadLocal的处理方式
这个就不一样,他直接就给每个线程设置一个InternalThreadLocalMap,不管是FastThreadLocalThread直接设置,还是JDK的普通线程Thread,设置进ThreadLocalMap间接设置。InternalThreadLocalMap内部维护着一个对象数组和索引,要放进去直接将值放进对象数组,返回一个索引,记录在FastThreadLocal中,取的时候直接拿这个索引去对象数组里取,非常方便。但是这样的一个缺点就是内存消耗比较大,因为只会扩容,而且索引只会递增,这样数组就会越来越大。所以就是空间换时间了。
UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap
这个定义了一些跟线程独有的属性,slowThreadLocalMap 其实就是用了原始的ThreadLocal,但是存的是InternalThreadLocalMap,就是普通线程用FastThreadLocal的时候先创建一个InternalThreadLocalMap放入,然后后面就可以取来用了,这个过程当然比FastThreadLocalThread直接获取InternalThreadLocalMap慢啦。
class UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap {
//从ThreadLocal中获取InternalThreadLocalMap
static final ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap> slowThreadLocalMap = new ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap>();
static final AtomicInteger nextIndex = new AtomicInteger();//索引
/** Used by {@link FastThreadLocal} */
Object[] indexedVariables;//放对象的数组
// Core thread-locals
int futureListenerStackDepth;//未来监听器栈的深度
int localChannelReaderStackDepth;//本地通道读的栈深度
Map<Class<?>, Boolean> handlerSharableCache;//处理器共享缓存
IntegerHolder counterHashCode;
ThreadLocalRandom random;//
Map<Class<?>, TypeParameterMatcher> typeParameterMatcherGetCache;//参数类型匹配缓存
Map<Class<?>, Map<String, TypeParameterMatcher>> typeParameterMatcherFindCache;//参数类型匹配寻找缓存
// String-related thread-locals
StringBuilder stringBuilder;
Map<Charset, CharsetEncoder> charsetEncoderCache;//编码器缓存
Map<Charset, CharsetDecoder> charsetDecoderCache;//解码器缓存
// ArrayList-related thread-locals
ArrayList<Object> arrayList;
UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap(Object[] indexedVariables) {
this.indexedVariables = indexedVariables;
}
}
InternalThreadLocalMap
继承了上面那个,但是提供了一系列的操作。功能类似于普通线程的ThreadLocalMap,效率高。
主要方法
InternalThreadLocalMap
直接创建32个空对象的数组。
private InternalThreadLocalMap() {
super(newIndexedVariableTable());
}
private static Object[] newIndexedVariableTable() {
Object[] array = new Object[32];
Arrays.fill(array, UNSET);
return array;
}
UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap(Object[] indexedVariables) {
this.indexedVariables = indexedVariables;
}
getIfSet
获取当前线程,如果是FastThreadLocalThread就直接获取InternalThreadLocalMap,如果不是就用ThreadLocal获取,获取不到就返回null。
public static InternalThreadLocalMap getIfSet() {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {
return ((FastThreadLocalThread) thread).threadLocalMap();//快速获取
}
return slowThreadLocalMap.get();//常规获取
}
get
获取InternalThreadLocalMap ,如果获取不到就创建一个,如果是FastThreadLocalThread就用快速的方法,否则就慢的方法。
public static InternalThreadLocalMap get() {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {
return fastGet((FastThreadLocalThread) thread);
} else {
return slowGet();
}
}
fastGet
快方法就是直接获取,获取不到就创建一个设置进去,返回。
private static InternalThreadLocalMap fastGet(FastThreadLocalThread thread) {
InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = thread.threadLocalMap();
if (threadLocalMap == null) {
thread.setThreadLocalMap(threadLocalMap = new InternalThreadLocalMap());
}
return threadLocalMap;
}
slowGet
从ThreadLocal中获取,不存在就创建一个,再设置进去,里面可能涉及一堆hash算法,冲突解决,扩容,所以相对就慢啦。
private static InternalThreadLocalMap slowGet() {
ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap> slowThreadLocalMap = UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap.slowThreadLocalMap;
InternalThreadLocalMap ret = slowThreadLocalMap.get();
if (ret == null) {
ret = new InternalThreadLocalMap();
slowThreadLocalMap.set(ret);
}
return ret;
}
nextVariableIndex
获取索引值,FastThreadLocal构造的时候需要,因为有索引值才可以从数组中获取值啊。
public static int nextVariableIndex() {
int index = nextIndex.getAndIncrement();//获取后自增
if (index < 0) {//溢出就抛异常了,那也太多了
nextIndex.decrementAndGet();
throw new IllegalStateException("too many thread-local indexed variables");
}
return index;
}
indexedVariable
获取索引对应的值,如果超边界就返回UNSET,表示没设置过值。
public Object indexedVariable(int index) {
Object[] lookup = indexedVariables;
return index < lookup.length? lookup[index] : UNSET;
}
setIndexedVariable
设置索引和对应的值,如果在范围内,就替换旧值,返回旧值是否是UNSET,是就表示第一次设置,返回true,不是就表示更新,返回false。超出范围就扩容。
public boolean setIndexedVariable(int index, Object value) {
Object[] lookup = indexedVariables;
if (index < lookup.length) {
Object oldValue = lookup[index];
lookup[index] = value;
return oldValue == UNSET;
} else {
expandIndexedVariableTableAndSet(index, value);
return true;
}
}
expandIndexedVariableTableAndSet
这段代码在内存分配里的规范容量操作遇到过,扩容到大于index的最小的2的幂次,比如index=32,扩容到64,然后把老的数组拷贝到新的数组里去,不满的地方用UNSET填满。
private void expandIndexedVariableTableAndSet(int index, Object value) {
Object[] oldArray = indexedVariables;
final int oldCapacity = oldArray.length;
int newCapacity = index;
newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 1;
newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 2;
newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 4;
newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 8;
newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 16;
newCapacity ++;
Object[] newArray = Arrays.copyOf(oldArray, newCapacity);
Arrays.fill(newArray, oldCapacity, newArray.length, UNSET);
newArray[index] = value;
indexedVariables = newArray;
}
removeIndexedVariable
删除数组中的值并返回,其实就是用UNSET替换了。溢出就返回UNSET。
public Object removeIndexedVariable(int index) {
Object[] lookup = indexedVariables;
if (index < lookup.length) {
Object v = lookup[index];
lookup[index] = UNSET;
return v;
} else {
return UNSET;
}
}
isIndexedVariableSet
该数组在索引是否有设置了值。
public boolean isIndexedVariableSet(int index) {
Object[] lookup = indexedVariables;
return index < lookup.length && lookup[index] != UNSET;
}
remove
把线程本地变量的删除,避免内存泄露。
public static void remove() {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {
((FastThreadLocalThread) thread).setThreadLocalMap(null);
} else {
slowThreadLocalMap.remove();
}
}
destroy
ThreadLocal的删除,避免内存泄露。
public static void destroy() {
slowThreadLocalMap.remove();
}
size
获取InternalThreadLocalMap已经设置了多少有用对象,不包括UNSET,还数组中的第0个元素set集合,除了对象数组indexedVariables外,还可能会有其他的属性。
public int size() {
int count = 0;
if (futureListenerStackDepth != 0) {
count ++;
}
if (localChannelReaderStackDepth != 0) {
count ++;
}
if (handlerSharableCache != null) {
count ++;
}
if (counterHashCode != null) {
count ++;
}
if (random != null) {
count ++;
}
if (typeParameterMatcherGetCache != null) {
count ++;
}
if (typeParameterMatcherFindCache != null) {
count ++;
}
if (stringBuilder != null) {
count ++;
}
if (charsetEncoderCache != null) {
count ++;
}
if (charsetDecoderCache != null) {
count ++;
}
if (arrayList != null) {
count ++;
}
for (Object o: indexedVariables) {
if (o != UNSET) {
count ++;
}
}
// We should subtract 1 from the count because the first element in 'indexedVariables' is reserved
// by 'FastThreadLocal' to keep the list of 'FastThreadLocal's to remove on 'FastThreadLocal.removeAll()'. set集合为了保证FastThreadLocal能调用removeAll删除所有的removeAll
return count - 1;//第一个是set集合,不算
}
本篇主要介绍一下基本的操作和概念,具体还需要自己去调试看下方法怎么怎么执行的,加深理解,光看是没用的。
好了,今天就到这里了,希望对学习理解有帮助,大神看见勿喷,仅为自己的学习理解,能力有限,请多包涵。
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

