invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors调用处理器方法
继续我们前面的讲,后置处理器创建出来了,然后要进行处理了,遍历所有的进行处理。
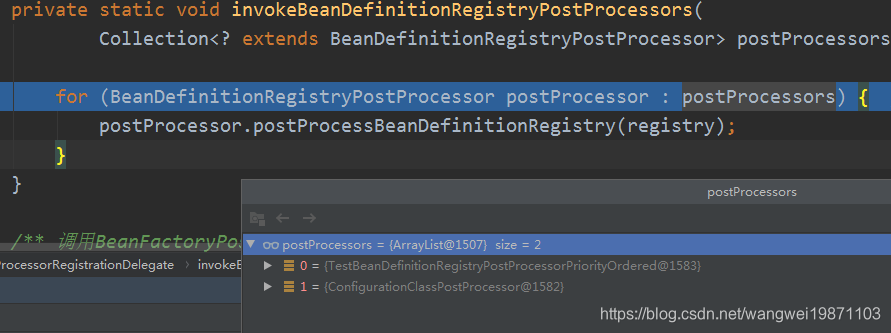
private static void invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(
Collection<? extends BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> postProcessors, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
for (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
}
}
当然也包括我们刚才的扩展的,而且我们扩展的优先级最高,已经被排到前面了:
调用了处理方法,只是打个信息。
大致处理流程
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的处理
这里才是重要的,看看这个处理器怎么来解析配置类。
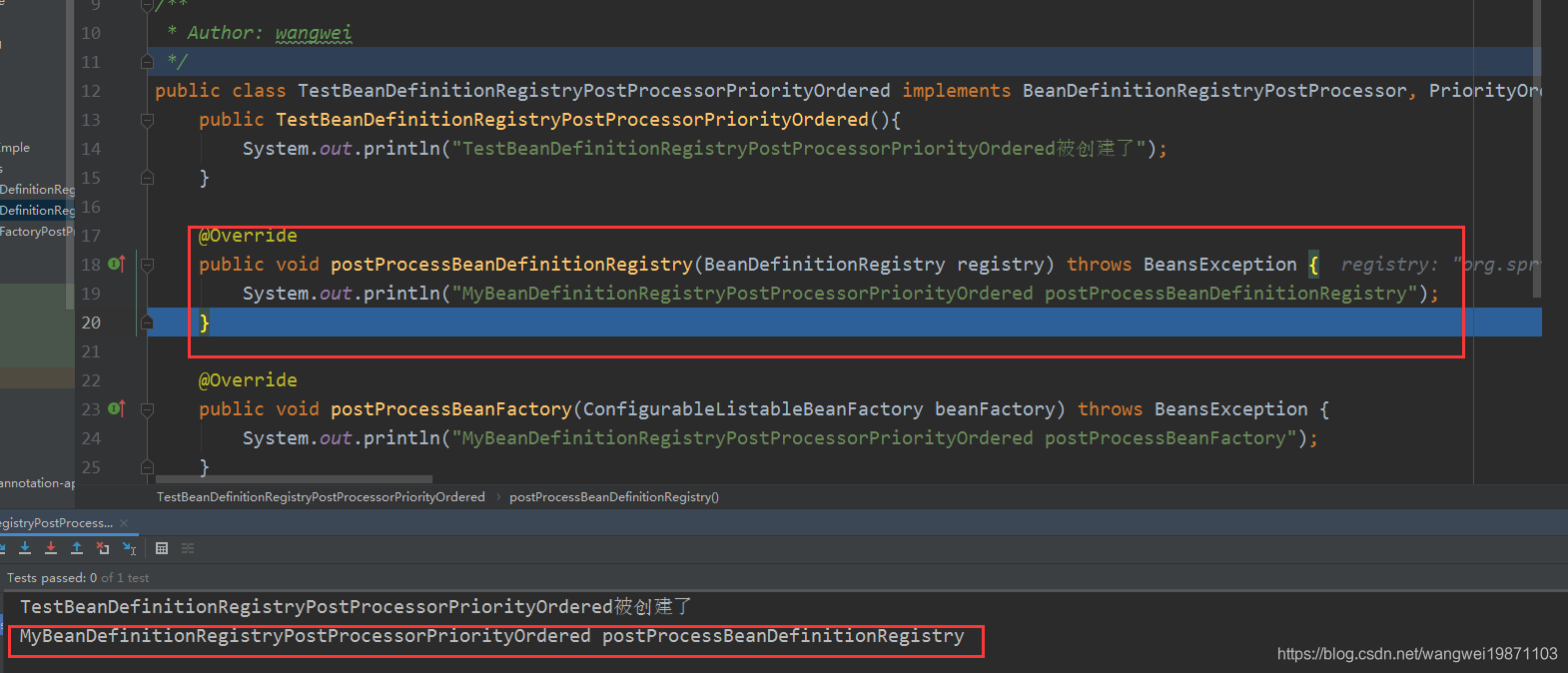
先检测是否已经处理过,再调用processConfigBeanDefinitions处理。
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
int registryId = System.identityHashCode(registry);
if (this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
}
if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
}
this.registriesPostProcessed.add(registryId);//先添加表示处理了
processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry);
}
processConfigBeanDefinitions
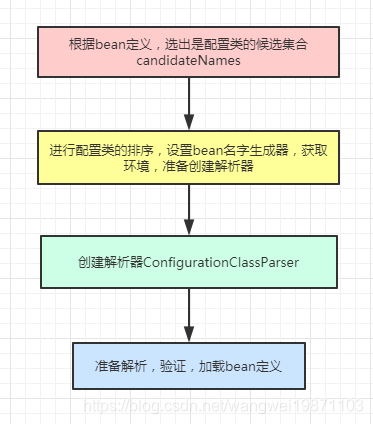
首先选出配置类的bean定义
取出所有的bean定义名字,遍历获取bean定义,然后判断是否有配置属性CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE,没有的话就检查是否是配置类,是就话就封装成BeanDefinitionHolder添加到configCandidates中。
List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();//获取所有bean定义名字
for (String beanName : candidateNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (beanDef.getAttribute(ConfigurationClassUtils.CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {//如果有这个属性表示处理过了
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef);
}
}
else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName));//把Configuration注解的bean定义到configCandidates
}
}
// Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were found
if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) {//没有配置候选就返回
return;
}
ConfigurationClassUtils的checkConfigurationClassCandidate
别看代码很长,其实就是先获取bean的全限定名,然后判断是否是注解类型,是的话就取出注解元数据,否则就判断是否存在BeanClass,有的话就取他的元数据,否则就用URL去加载类名对应的类,取出元数据。然后获取元数据上的Configuration注解的属性,默认proxyBeanMethods=true,后面会使用CGLIB动态代理增强,所以要设置一个full的属性,否则就设置lite属性。最后如果设置了Order注解,就设置序号属性。
public static boolean checkConfigurationClassCandidate(
BeanDefinition beanDef, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) {
//获取Bean全限定名
String className = beanDef.getBeanClassName();
if (className == null || beanDef.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return false;
}
AnnotationMetadata metadata;
//是注解类型,元数据类名跟bean类名一样
if (beanDef instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition &&
className.equals(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanDef).getMetadata().getClassName())) {
// Can reuse the pre-parsed metadata from the given BeanDefinition...
metadata = ((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanDef).getMetadata();//获得注解的元数据
}
else if (beanDef instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef).hasBeanClass()) {
// Check already loaded Class if present...存在BeanClass就取出来
// since we possibly can't even load the class file for this Class.
Class<?> beanClass = ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef).getBeanClass();
if (BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) ||
BeanPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) ||
AopInfrastructureBean.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) ||
EventListenerFactory.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass)) {
return false;
}
metadata = AnnotationMetadata.introspect(beanClass);//取出元数据
}
else {
try {
MetadataReader metadataReader = metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(className);
metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
}
catch (IOException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not find class file for introspecting configuration annotations: " +
className, ex);
}
return false;
}
}
//获取Configuration注解的属性
Map<String, Object> config = metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(Configuration.class.getName());
if (config != null && !Boolean.FALSE.equals(config.get("proxyBeanMethods"))) {//如果proxyBeanMethods=true,可能会用动态代理
beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_FULL);//设置属性为full
}
else if (config != null || isConfigurationCandidate(metadata)) {//设置属性为lite
beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_LITE);
}
else {
return false;
}
// It's a full or lite configuration candidate... Let's determine the order value, if any.
Integer order = getOrder(metadata);
if (order != null) {//如果有排序,设置序号属性
beanDef.setAttribute(ORDER_ATTRIBUTE, order);
}
return true;
}
最后执行完就只有一个配置类:
isConfigurationCandidate是否是配置候选类(重点)
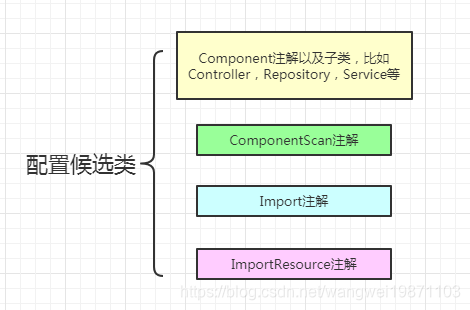
我们知道加了Configuration注解肯定是配置类,但是不加其实也可以是配置类,只要不是接口类型,有Component ComponentScan Import ImportResource任意一个注解,或者有bean注解的方法。只是加了Configuration注解后,里面有个默认proxyBeanMethods=true的属性,可以使用动态代理做增强的,具体用法后面会总结。我们看这个是否是配置候选类的方法:
//是配置候选类型的集合
private static final Set<String> candidateIndicators = new HashSet<>(8);
static {//添加配置类型的集合Component ComponentScan Import ImportResource
candidateIndicators.add(Component.class.getName());
candidateIndicators.add(ComponentScan.class.getName());
candidateIndicators.add(Import.class.getName());
candidateIndicators.add(ImportResource.class.getName());
}
public static boolean isConfigurationCandidate(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
// Do not consider an interface or an annotation...
if (metadata.isInterface()) {//非接口
return false;
}
// Any of the typical annotations found?存在 Component ComponentScan Import ImportResource任意一个注解
for (String indicator : candidateIndicators) {
if (metadata.isAnnotated(indicator)) {
return true;
}
}
// Finally, let's look for @Bean methods...
try {//或者bean方法注解
return metadata.hasAnnotatedMethods(Bean.class.getName());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Failed to introspect @Bean methods on class [" + metadata.getClassName() + "]: " + ex);
}
return false;
}
}
排序,设置bean名字生成器,获取环境
这里就是把上面的configCandidates进行排序,然后设置bean名字生成器,一般就是默认的,然后获取环境
configCandidates.sort((bd1, bd2) -> {
int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition());
int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition());
return Integer.compare(i1, i2);
});
//检测是否有自定义的bean name生成器
// Detect any custom bean name generation strategy supplied through the enclosing application context
SingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null;
if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) {
sbr = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry;
if (!this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet) {
BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(
AnnotationConfigUtils.CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR);
if (generator != null) {//如果有自定义的beanname生成器,就是何止进去
this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator;
this.importBeanNameGenerator = generator;
}
}
}
if (this.environment == null) {
this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();
}
创建配置类解析器,开始解析
创建解析器,将配置类集合转成LinkedHashSet,并创建一个已经解析成ConfigurationClass类型的HashSet表示已经解析好的配置类。然后开始解析,解析完后会进行验证,因为里面可能会进行CGLIB的动态代理,具体后面会讲,然后将解析好的ConfigurationClass集合返回,删除上一次已经解析过的,留下的就是新解析出来的,然后对解析出来的ConfigurationClass集合进行bean定义的加载,因为前面解析的时候可能会有@import,@bean等属性,会有新的bean定义。处理完就放入已解析过的集合alreadyParsed 中,然后清空,判断加载后的bean定义的数量是否有增加,有的话说明就有新的bean定义了,又要重新去判断是否是配置类,是的话就放到candidates中,然后继续解析,一直循环知道没有配置类为止。
// Parse each @Configuration class 创建配置解析器
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
//转成LinkedHashSet
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates);
Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size());//已经解析过的
do {//开始解析configCandidates元素
parser.parse(candidates);//解析配置类集合
parser.validate();//验证如果要CGLIB代理的话,条件是否满足,比如类不能final,bean注解方法要可覆盖
//获得解析好的ConfigurationClass
Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());
configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed);//删除已经解析的
// Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content
if (this.reader == null) {//创建配置类bean定义读取器
this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader(
registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment,
this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);//加载bean定义
alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);//添加到已处理的集合
candidates.clear();//处理完一次就清空
if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) {//如果有加载到新的bean定义,再继续加载
String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();//总的名字
Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames));//处理过的名字
Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>();
for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) {
alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
}
for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) {
if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) {//处理新的
BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) &&
!alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) {//符合配置类要求就添加到candidates
candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName));
}
}
}
candidateNames = newCandidateNames;//更新候选名字
}
}
while (!candidates.isEmpty());
其实就是一个解析配置类的过程,然后解析之后会发现可能配置类里面还会带有其他配置类的定义,然后就得循环去解析新的配置类,直到最后没有新的配置类的bean定义。
其中有几个核心的方法后面会介绍,里面涉及到如何解析配置类的注解,CGLIB的动态代理等等。
好了,今天就到这里了,希望对学习理解有帮助,大神看见勿喷,仅为自己的学习理解,能力有限,请多包涵。
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

