Bean定义
后面我们频繁的会跟bean定义打交道,所以我们先要知道什么是bean定义,定义了什么呢,如果不了解这个,后面看下去一头雾水,很多东西怎么得来的不清楚,所以还是要先有个了解,我把相关的一些借口和类先介绍下。
BeanMetadataElement元数据接口
首先我们要能获得源数据,也就是这个bean是来自哪个对象的,我们就可以获得一些相关的信息。
public interface BeanMetadataElement {
@Nullable
default Object getSource() {
return null;
}
}
BeanMetadataAttribute元数据属性
实现了元数据接口,增加了属性的名字和值。
public class BeanMetadataAttribute implements BeanMetadataElement {
//属性名字
private final String name;
//属性值
@Nullable
private final Object value;
//bean的来源
@Nullable
private Object source;
//将名字和值封装起来
public BeanMetadataAttribute(String name, @Nullable Object value) {
Assert.notNull(name, "Name must not be null");
this.name = name;
this.value = value;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
@Nullable
public Object getValue() {
return this.value;
}
public void setSource(@Nullable Object source) {
this.source = source;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object getSource() {
return this.source;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(@Nullable Object other) {
if (this == other) {
return true;
}
if (!(other instanceof BeanMetadataAttribute)) {
return false;
}
BeanMetadataAttribute otherMa = (BeanMetadataAttribute) other;
return (this.name.equals(otherMa.name) &&
ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.value, otherMa.value) &&
ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.source, otherMa.source));
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return this.name.hashCode() * 29 + ObjectUtils.nullSafeHashCode(this.value);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "metadata attribute '" + this.name + "'";
}
}
AttributeAccessor属性访问器
这个就是定义了属性的操作接口,增删改查,获取所有的。
public interface AttributeAccessor {
void setAttribute(String name, @Nullable Object value);
@Nullable
Object getAttribute(String name);
@Nullable
Object removeAttribute(String name);
boolean hasAttribute(String name);
String[] attributeNames();
}
AttributeAccessorSupport属性访问抽象实现类
这个是对AttributeAccessor接口的抽象实现,定义了一个map来存放名字和属性的映射关系。
public abstract class AttributeAccessorSupport implements AttributeAccessor, Serializable {
//名字和属性的对应
private final Map<String, Object> attributes = new LinkedHashMap<>();
//设置null就会删除
@Override
public void setAttribute(String name, @Nullable Object value) {
Assert.notNull(name, "Name must not be null");
if (value != null) {
this.attributes.put(name, value);
}
else {
removeAttribute(name);
}
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object getAttribute(String name) {
Assert.notNull(name, "Name must not be null");
return this.attributes.get(name);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object removeAttribute(String name) {
Assert.notNull(name, "Name must not be null");
return this.attributes.remove(name);
}
@Override
public boolean hasAttribute(String name) {
Assert.notNull(name, "Name must not be null");
return this.attributes.containsKey(name);
}
@Override
public String[] attributeNames() {
return StringUtils.toStringArray(this.attributes.keySet());
}
//属性的复制
protected void copyAttributesFrom(AttributeAccessor source) {
Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null");
String[] attributeNames = source.attributeNames();
for (String attributeName : attributeNames) {
setAttribute(attributeName, source.getAttribute(attributeName));
}
}
//得同一个属性对象,或者每一个属性都相同
@Override
public boolean equals(@Nullable Object other) {
return (this == other || (other instanceof AttributeAccessorSupport &&
this.attributes.equals(((AttributeAccessorSupport) other).attributes)));
}
//map的hashCode
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return this.attributes.hashCode();
}
}
BeanMetadataAttributeAccessor元数据属性访问器
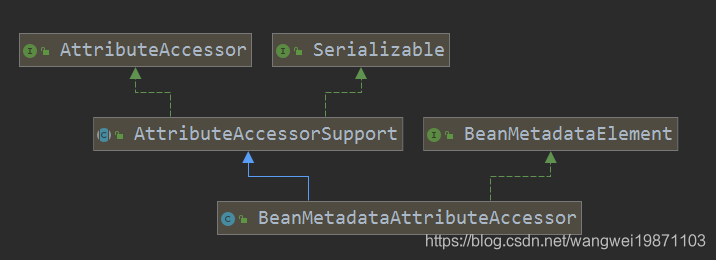
既能获取源数据,也能提供属性访问:
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class BeanMetadataAttributeAccessor extends AttributeAccessorSupport implements BeanMetadataElement {
//bean的源数据对象
@Nullable
private Object source;
public void setSource(@Nullable Object source) {
this.source = source;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object getSource() {
return this.source;
}
//添加进来的就是BeanMetadataAttribute
public void addMetadataAttribute(BeanMetadataAttribute attribute) {
super.setAttribute(attribute.getName(), attribute);
}
//获得之后都会转成BeanMetadataAttribute
@Nullable
public BeanMetadataAttribute getMetadataAttribute(String name) {
return (BeanMetadataAttribute) super.getAttribute(name);
}
//封装成BeanMetadataAttribute
@Override
public void setAttribute(String name, @Nullable Object value) {
super.setAttribute(name, new BeanMetadataAttribute(name, value));
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object getAttribute(String name) {
BeanMetadataAttribute attribute = (BeanMetadataAttribute) super.getAttribute(name);
return (attribute != null ? attribute.getValue() : null);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object removeAttribute(String name) {
BeanMetadataAttribute attribute = (BeanMetadataAttribute) super.removeAttribute(name);
return (attribute != null ? attribute.getValue() : null);
}
}
BeanDefinition
我们的bean定义接口就是继承他们的,也就是说,我们的bean定义得有来源BeanMetadataElement,得可以操作AttributeAccessor。比如我给你一个类,你要将他转换成bean,你到知道他的一些信息吧,不然等于什么都没有,别说获取注解什么的了,当然同时可能这些信息不够,所以要扩展,可以设置任务属性,只要是我需要的。我想spring的bean定义的意图也差不多吧。
主要方法
代码就不贴了,说一些熟悉方法,其他还有很多,要看的时候可以切过去看:
//单例字符串singleton
String SCOPE_SINGLETON = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON;
//原型字符串prototype
String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE;
//设置bean类名字,这个可能会在后置处理器中修改,比如用了GCLIB代理配置类的时候就会改
void setBeanClassName(@Nullable String beanClassName);
//设置范围,是单例,还是原型
void setScope(@Nullable String scope);
//设置是否是懒加载
void setLazyInit(boolean lazyInit);
//设置需要先加载的依赖的类名字数组
void setDependsOn(@Nullable String... dependsOn);
//设置是否适合给其他类做自动装配
void setAutowireCandidate(boolean autowireCandidate);
//设置是否优先自动装配
void setPrimary(boolean primary);
//设置FactoryBean的名字
void setFactoryBeanName(@Nullable String factoryBeanName);
//获取构造函数的参数
ConstructorArgumentValues getConstructorArgumentValues();
//设置初始化方法 对应@PostConstruct
void setInitMethodName(@Nullable String initMethodName);
//设置销毁时候的方法 对应@PreDestroy
void setDestroyMethodName(@Nullable String destroyMethodName);
可以看到,我们的bean定义是一步步来的,首先是定义这个bean的来源,然后是一些属性操作,然后是将两部分合起来作为bean定义的父接口,在这个基础上,再定义其他的一些操作。这样数据和操作接口分离,做到了很好的解耦和扩展。
好了,今天就到这里了,希望对学习理解有帮助,大神看见勿喷,仅为自己的学习理解,能力有限,请多包涵。
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

