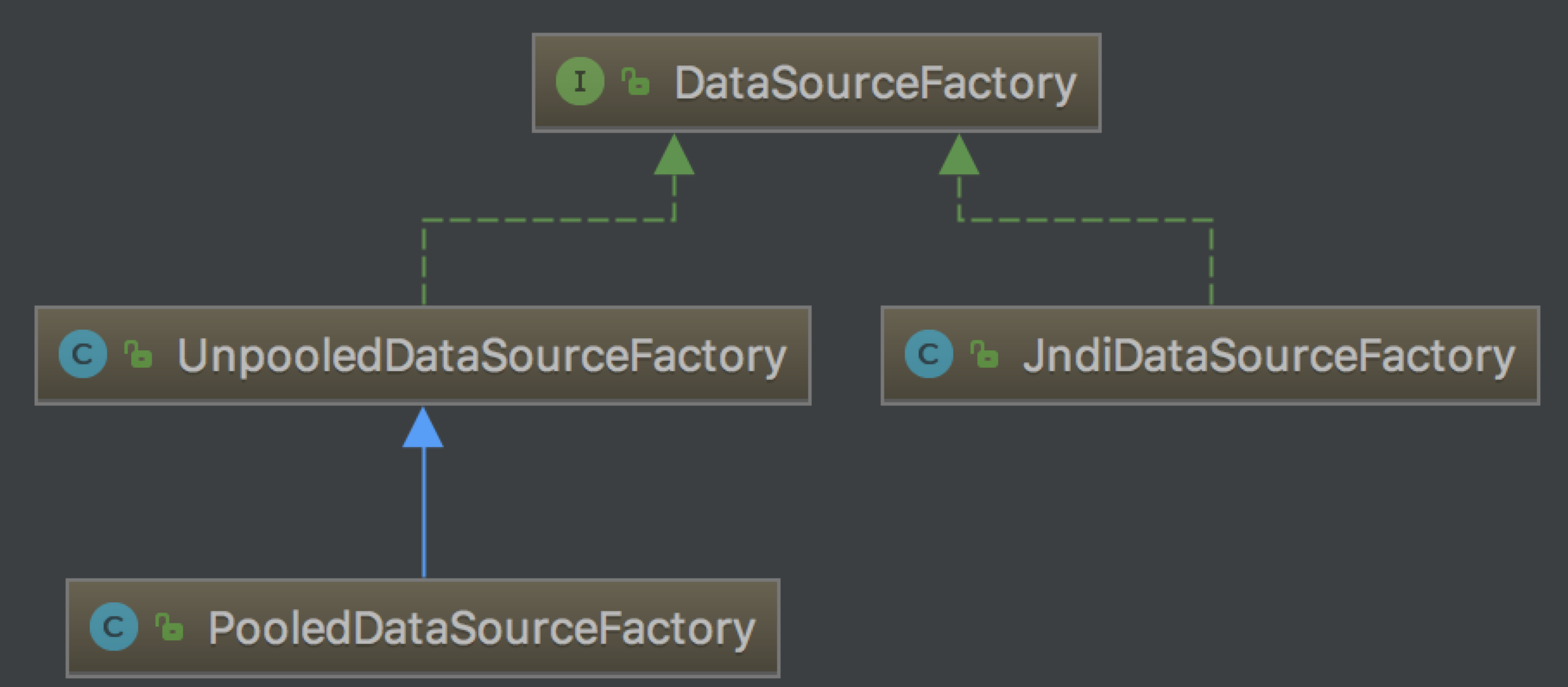
Mybatis中DataSourceFactory是负责创建DataSource对象的,Mybatis一共为我们提供了3种DataSourceFactory的实现,不同的DataSourceFactory创建不同的DataSource,分别为UnpooledDataSourceFactory,PooledDataSourceFactory和JndiDataSourceFactory。具体使用哪种DataSourceFactory我们在《SqlSessionFactory的创建过程》中分析过了,下面详细说一下PooledDataSourceFactory和UnpooledDataSourceFactory。PooledDataSourceFactory继承了UnpooledDataSourceFactory,除了构造函数中创建的DataSource不同其余完全相同。
public class PooledDataSourceFactory extends UnpooledDataSourceFactory {
public PooledDataSourceFactory() {
this.dataSource = new PooledDataSource();
}
}
public UnpooledDataSourceFactory() {
this.dataSource = new UnpooledDataSource();
}
UnpooledDataSourceFactory比较简单除了getDataSource方法以外还有另一个public的方法setProperties。
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
Properties driverProperties = new Properties();
MetaObject metaDataSource = SystemMetaObject.forObject(dataSource);
for (Object key : properties.keySet()) {
String propertyName = (String) key;
if (propertyName.startsWith(DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX)) {
String value = properties.getProperty(propertyName);
driverProperties.setProperty(propertyName.substring(DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX_LENGTH), value);
} else if (metaDataSource.hasSetter(propertyName)) {
String value = (String) properties.get(propertyName);
Object convertedValue = convertValue(metaDataSource, propertyName, value);
metaDataSource.setValue(propertyName, convertedValue);
} else {
throw new DataSourceException("Unknown DataSource property: " + propertyName);
}
}
if (driverProperties.size() > 0) {
metaDataSource.setValue("driverProperties", driverProperties);
}
}
这个方法就将datasource标签的子元素设置到构造方法创建的DataSource对象中去,其中包括url,username,password等必要的属性,如果属性中存在DataSource中没有与之对应的Getter方法则抛异常。简单配置如下:
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
而getDataSource方法则是原封不动的放回DataSource对象。
public DataSource getDataSource() {
return dataSource;
}
下面分别看看这两种DataSource,UnpooledDataSource和PooledDataSource。
- UnpooledDataSource 中getConnection方法直接调用了doGetConnection方法,方法中可以看到每次获取Connection对象都是通过DriverManager的getConnection方法创建一个新的Connection对象,所以说UnpooledDataSource就像它的名字一样非池化的数据源不会缓存创建的数据库连接,所以对于频繁操作数据库的应用来说不建议使用这种DataSource。
private Connection doGetConnection(Properties properties) throws SQLException {
initializeDriver();
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties);
configureConnection(connection);
return connection;
}
- PooledDataSource 中有2个比较重要的成员变量,一个是state一个是dataSource。dataSource就是UnpooledDataSource,PooledDataSource产生的数据库连接就是通过dataSource产生的所以可以说PooledDataSource是一个静态代理。state是一个PoolState对象它代表了当前连接池的状态详情,之所以叫池化的数据源就是因为state有两个List,分别代表活跃的数据库连接和空闲的数据库连接。
public class PoolState {
protected PooledDataSource dataSource;
protected final List<PooledConnection> idleConnections = new ArrayList<PooledConnection>();
protected final List<PooledConnection> activeConnections = new ArrayList<PooledConnection>();
我们分析一下PooledDataSource的getConnection方法。
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return popConnection(dataSource.getUsername(), dataSource.getPassword()).getProxyConnection();
}
private PooledConnection popConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
boolean countedWait = false;
PooledConnection conn = null;
long t = System.currentTimeMillis();
int localBadConnectionCount = 0;
while (conn == null) {
synchronized (state) {
if (!state.idleConnections.isEmpty()) {
// Pool has available connection
conn = state.idleConnections.remove(0);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Checked out connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " from pool.");
}
} else {
// Pool does not have available connection
if (state.activeConnections.size() < poolMaximumActiveConnections) {
// Can create new connection
conn = new PooledConnection(dataSource.getConnection(), this);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Created connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
} else {
// Cannot create new connection
PooledConnection oldestActiveConnection = state.activeConnections.get(0);
long longestCheckoutTime = oldestActiveConnection.getCheckoutTime();
if (longestCheckoutTime > poolMaximumCheckoutTime) {
// Can claim overdue connection
state.claimedOverdueConnectionCount++;
state.accumulatedCheckoutTimeOfOverdueConnections += longestCheckoutTime;
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += longestCheckoutTime;
state.activeConnections.remove(oldestActiveConnection);
if (!oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
try {
oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().rollback();
} catch (SQLException e) {
/*
Just log a message for debug and continue to execute the following
statement like nothing happend.
Wrap the bad connection with a new PooledConnection, this will help
to not intterupt current executing thread and give current thread a
chance to join the next competion for another valid/good database
connection. At the end of this loop, bad {@link @conn} will be set as null.
*/
log.debug("Bad connection. Could not roll back");
}
}
conn = new PooledConnection(oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection(), this);
conn.setCreatedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getCreatedTimestamp());
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getLastUsedTimestamp());
oldestActiveConnection.invalidate();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Claimed overdue connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
} else {
// Must wait
try {
if (!countedWait) {
state.hadToWaitCount++;
countedWait = true;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Waiting as long as " + poolTimeToWait + " milliseconds for connection.");
}
long wt = System.currentTimeMillis();
state.wait(poolTimeToWait);
state.accumulatedWaitTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - wt;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
}
}
}
}
if (conn != null) {
// ping to server and check the connection is valid or not
if (conn.isValid()) {
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
conn.setConnectionTypeCode(assembleConnectionTypeCode(dataSource.getUrl(), username, password));
conn.setCheckoutTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
state.activeConnections.add(conn);
state.requestCount++;
state.accumulatedRequestTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - t;
} else {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") was returned from the pool, getting another connection.");
}
state.badConnectionCount++;
localBadConnectionCount++;
conn = null;
if (localBadConnectionCount > (poolMaximumIdleConnections + poolMaximumLocalBadConnectionTolerance)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
}
}
}
}
if (conn == null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection.");
}
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection.");
}
return conn;
}
代码有点长还是很好理解的。如果空闲列表中有空闲的连接,取出列表中第一个连接。否则:
1.当前活跃连接数小于我们设置的最大活跃连接数poolMaximumActiveConnections(默认10),new一个PooledConnection,其中包含一个从dataSource中获取的Connection和当前连接池对象并且实现了InvocationHandler接口,所以PooledConnection是Connection的动态代理,我们稍后先纤细分析这个代理版的Connection。
2.当前活跃连接数大于等于poolMaximumActiveConnections时又分为两种情况:
2.1 活跃列表中第一个连接(也就是时间最长的)在列表中时长超过poolMaximumCheckoutTime(默认20秒),则将其从列表中移除,取出真正的Connection对象放在一个新的PooledConnection中,将旧的PooledConnection设置为无效,这样一来当调用PooledConnection的非close方法(当然也除了从Object继承的方法)回去检测当前PooledConnection是否无效,如果无效则抛出异常。
2.2活跃列表中第一个连接在列表中时长小于poolMaximumCheckoutTime,则会等待poolTimeToWait(默认20秒),直到超时或者有连接被释放,重新竞争新一轮连接。
PooledConnection是如何做到连接重新利用的?
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
if (CLOSE.hashCode() == methodName.hashCode() && CLOSE.equals(methodName)) {
dataSource.pushConnection(this);
return null;
} else {
try {
if (!Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// issue #579 toString() should never fail
// throw an SQLException instead of a Runtime
checkConnection();
}
return method.invoke(realConnection, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
}
先说一下else的情况,当调用Connection的非close方法会检测一下当前代理连接是否无效(上面分析过超过poolMaximumCheckoutTime时就是设置为无效),如果无效则抛出异常。
到这我有个疑问,如果线程一顺利执行完checkConnection方法,线程二在从连接池获取连接的时候碰到了没有空闲连接并且活跃列表中第一个连接超过了poolMaximumCheckoutTime而执行了
oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().rollback();
然后线程一执行了目标对象的commit方法,岂不是造成了逻辑错乱,不知道这是不是Mybatis的一个Bug。
然后说一下释放连接的过程,当调用close方法的时候会调用连接池的pushConnection方法。
protected void pushConnection(PooledConnection conn) throws SQLException {
synchronized (state) {
state.activeConnections.remove(conn);
if (conn.isValid()) {
if (state.idleConnections.size() < poolMaximumIdleConnections && conn.getConnectionTypeCode() == expectedConnectionTypeCode) {
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime();
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
PooledConnection newConn = new PooledConnection(conn.getRealConnection(), this);
state.idleConnections.add(newConn);
newConn.setCreatedTimestamp(conn.getCreatedTimestamp());
newConn.setLastUsedTimestamp(conn.getLastUsedTimestamp());
conn.invalidate();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Returned connection " + newConn.getRealHashCode() + " to pool.");
}
state.notifyAll();
} else {
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime();
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
conn.getRealConnection().close();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Closed connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
conn.invalidate();
}
} else {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") attempted to return to the pool, discarding connection.");
}
state.badConnectionCount++;
}
}
}
大致逻辑就是首先将代理连接从活跃列表中移除
当前空闲连接小于最大空闲连接,则复用真实连接重新包装一个代理连接放入空闲列表中。
否则就调用真实连接的close方法,以保证不能超过最大空闲连接数。
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

