随着 Spring Boot 和 Spring Cloud 在许多中大型企业中被普及,可能你已经忘记当年经典的 Servlet + Spring MVC 的组合,是否还记得那个 web.xml 配置文件。在开始本文之前,请先抛开 Spring Boot 到一旁,回到从前,一起来看看 Servlet 是怎么和 Spring MVC 集成,怎么来初始化 Spring 容器的,在开始阅读本文之前,最好有一定的 Servlet 和 Spring IOC 容器方面的知识,比较容易理解
概述
在开始看具体的源码实现之前,我们先一起来看看现在“陌生”的 web.xml 文件,可以查看我的另一篇 MyBatis 使用手册 文档中 集成 Spring 小节涉及到的 web.xml 的文件,部分内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd"
version="3.0">
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<!-- 【1】 Spring 配置 -->
<!-- 在容器(Tomcat、Jetty)启动时会被 ContextLoaderListener 监听到,
从而调用其 contextInitialized() 方法,初始化 Root WebApplicationContext 容器 -->
<!-- 声明 Spring Web 容器监听器 -->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!-- Spring 和 MyBatis 的配置文件 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-mybatis.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!-- 【2】 Spring MVC 配置 -->
<!-- 1.SpringMVC 配置 前置控制器(SpringMVC 的入口)
DispatcherServlet 是一个 Servlet,所以可以配置多个 DispatcherServlet -->
<servlet>
<!-- 在 DispatcherServlet 的初始化过程中,框架会在 web 应用 的 WEB-INF 文件夹下,
寻找名为 [servlet-name]-servlet.xml 的配置文件,生成文件中定义的 Bean. -->
<servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!-- 配置需要加载的配置文件 -->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<!-- 程序运行时从 web.xml 开始,加载顺序为:context-param -> Listener -> Filter -> Structs -> Servlet
设置 web.xml 文件启动时加载的顺序(1 代表容器启动时首先初始化该 Servlet,让这个 Servlet 随 Servlet 容器一起启动)
load-on-startup 是指这个 Servlet 是在当前 web 应用被加载的时候就被创建,而不是第一次被请求的时候被创建 -->
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
<async-supported>true</async-supported>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<!-- 这个 Servlet 的名字是 SpringMVC,可以有多个 DispatcherServlet,是通过名字来区分的
每一个 DispatcherServlet 有自己的 WebApplicationContext 上下文对象,同时保存在 ServletContext 中和 Request 对象中
ApplicationContext(Spring 容器)是 Spring 的核心
Context 我们通常解释为上下文环境,Spring 把 Bean 放在这个容器中,在需要的时候,可以 getBean 方法取出-->
<servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name>
<!-- Servlet 拦截匹配规则,可选配置:*.do、*.action、*.html、/、/xxx/* ,不允许:/* -->
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
【1】 处,配置了 org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener 对象,它实现了 Servlet 的 javax.servlet.ServletContextListener 接口,能够监听 ServletContext 对象的生命周期,也就是监听 Web 应用的生命周期,当 Servlet 容器启动或者销毁时,会触发相应的 ServletContextEvent 事件,ContextLoaderListener 监听到启动事件,则会初始化一个 Root Spring WebApplicationContext 容器,监听到销毁事件,则会销毁该容器
【2】 处,配置了 org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet 对象,它继承了 javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet 抽象类,也就是一个 Servlet。Spring MVC 的核心类,处理请求,会初始化一个 属于它 的 Spring WebApplicationContext 容器,并且这个容器是以 【1】 处的 Root 容器作为父容器
- 为什么有了
【2】创建了容器,还需要【1】创建 Root 容器呢?因为可以配置多个【2】呀,当然,实际场景下,不太会配置多个【2】 - 再总结一次,
【1】和【2】分别会创建其对应的 Spring WebApplicationContext 容器,并且它们是父子容器的关系
Root WebApplicationContext 容器
在 概述 的 web.xml中,我们已经看到,Root WebApplicationContext 容器的初始化,通过 ContextLoaderListener 来实现。在 Servlet 容器启动时,例如 Tomcat、Jetty 启动后,则会被 ContextLoaderListener 监听到,从而调用 contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) 方法,初始化 Root WebApplicationContext 容器
而 ContextLoaderListener 的类图如下:
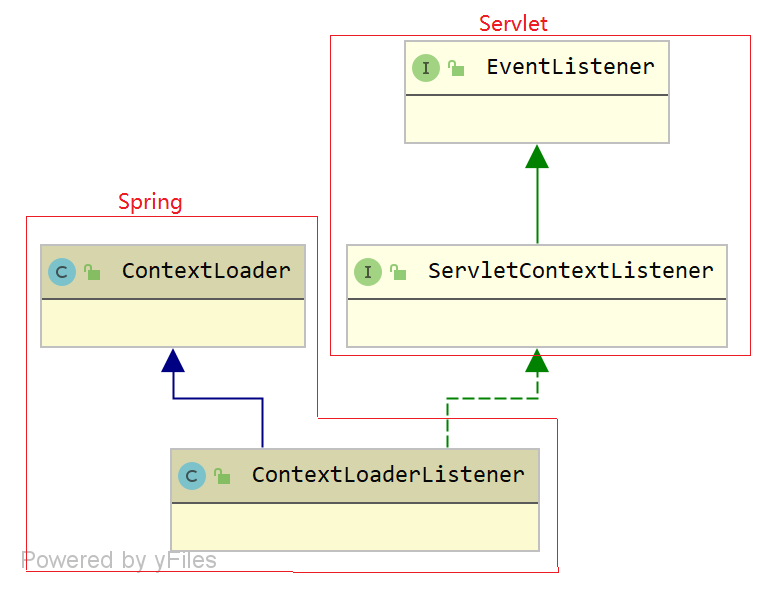
ContextLoaderListener
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener 类,实现 javax.servlet.ServletContextListener 接口,继承 ContextLoader 类,实现 Servlet 容器启动和关闭时,分别初始化和销毁 WebApplicationContext 容器,代码如下:
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
public ContextLoaderListener() {
}
/**
* As of Spring 3.1, supports injecting the root web application context
*/
public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {
super(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
// <1> 初始化 Root WebApplicationContext
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
/**
* Close the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
// <2> 销毁 Root WebApplicationContext
closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
}
- 监听到 Servlet 容器启动事件,则调用父类 ContextLoader 的
initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext)方法,初始化 WebApplicationContext 容器 - 监听到 Servlet 销毁启动事件,则调用父类 ContextLoader 的
closeWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext)方法,销毁 WebApplicationContext 容器
ContextLoader
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader 类,真正实现初始化和销毁 WebApplicationContext 容器的逻辑的类
静态代码块
public class ContextLoader {
/**
* Name of the class path resource (relative to the ContextLoader class)
* that defines ContextLoader's default strategy names.
*/
private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "ContextLoader.properties";
/**
* 默认的配置 Properties 对象
*/
private static final Properties defaultStrategies;
static {
// Load default strategy implementations from properties file.
// This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized by application developers.
try {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
从 ContextLoader.properties 中,读取默认的配置 Properties 对象。实际上,正如 Load default strategy implementations from properties file. This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized by application developers. 所注释,这是一个应用开发者无需关心的配置,而是 Spring 框架自身所定义的
打开来该文件瞅瞅,代码如下:
# Default WebApplicationContext implementation class for ContextLoader.
# Used as fallback when no explicit context implementation has been specified as context-param.
# Not meant to be customized by application developers.
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
这意味着什么呢?如果我们没有在 <context-param /> 标签中指定 WebApplicationContext,则默认使用 XmlWebApplicationContext 类,我们在使用 Spring 的过程中一般情况下不会主动指定
构造方法
public class ContextLoader {
/**
* Name of servlet context parameter (i.e., {@value}) that can specify the
* config location for the root context, falling back to the implementation's default otherwise.
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext#DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION
*/
public static final String CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM = "contextConfigLocation";
/** Map from (thread context) ClassLoader to corresponding 'current' WebApplicationContext. */
private static final Map<ClassLoader, WebApplicationContext> currentContextPerThread = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(1);
/** The 'current' WebApplicationContext, if the ContextLoader class is deployed in the web app ClassLoader itself. */
@Nullable
private static volatile WebApplicationContext currentContext;
/** The root WebApplicationContext instance that this loader manages. */
@Nullable
private WebApplicationContext context;
/**
* Create a new {@code ContextLoader} that will create a web application context
* based on the "contextClass" and "contextConfigLocation" servlet context-params.
* See class-level documentation for details on default values for each.
*/
public ContextLoader() {
}
/**
* Create a new {@code ContextLoader} with the given application context.
* This constructor is useful in Servlet 3.0+ environments where instance-based
* registration of listeners is possible through the {@link ServletContext#addListener} API.
*/
public ContextLoader(WebApplicationContext context) {
this.context = context;
}
// ... 省略其他相关配置属性
}
- 在 概述 的
web.xml文件中可以看到定义的contextConfigLocation参数为 spring-mybatis.xml 配置文件路径 currentContextPerThread:用于保存当前 ClassLoader 类加载器与 WebApplicationContext 对象的映射关系currentContext:如果当前线程的类加载器就是 ContextLoader 类所在的类加载器,则该属性用于保存 WebApplicationContext 对象context:WebApplicationContext 实例对象
关于类加载器涉及到 JVM 的“双亲委派机制”,在《精尽MyBatis源码分析 - 基础支持层》 有简单的讲述到,可以参考一下
initWebApplicationContext
initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) 方法,初始化 WebApplicationContext 对象,代码如下:
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
// <1> 若已经存在 ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE 对应的 WebApplicationContext 对象,则抛出 IllegalStateException 异常。
// 例如,在 web.xml 中存在多个 ContextLoader
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
// <2> 打印日志
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
// 记录开始时间
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
// <3> 初始化 context ,即创建 context 对象
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
// <4> 如果是 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 的子类,如果未刷新,则进行配置和刷新
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) { // <4.1> 未刷新( 激活 )
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) { // <4.2> 无父容器,则进行加载和设置。
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
// <4.3> 配置 context 对象,并进行刷新
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
// <5> 记录在 servletContext 中
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
// <6> 记录到 currentContext 或 currentContextPerThread 中
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext initialized in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
// <7> 返回 context
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
}
- 若 ServletContext(Servlet 的上下文)已存在 Root WebApplicationContext 对象,则抛出异常,因为不能再初始化该对象
- 打印日志,在启动 SSM 项目的时候,是不是都会看到这个日志“Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext”
- 如果
context为空,则调用createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc)方法,初始化一个 Root WebApplicationContext 对象,方法如下:
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
// <1> 获得 context 的类(默认情况是从 ContextLoader.properties 配置文件读取的,为 XmlWebApplicationContext)
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
// <2> 判断 context 的类,是否符合 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 的类型
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
// <3> 创建 context 的类的对象
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
-
如果是 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 的子类,并且未刷新,则进行配置和刷新
- 如果未刷新(激活),默认情况下,是符合这个条件的,所以会往下执行
- 如果无父容器,则进行加载和设置。默认情况下,
loadParentContext(ServletContext servletContext)方法返回一个空对象,也就是没有父容器了 - 调用
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc)方法,配置context对象,并进行刷新
-
将
context对象保存在 ServletContext 中 -
将
context对象设置到currentContext或者currentContextPerThread对象中,差异就是类加载器是否相同,具体用途目前不清楚 -
返回已经初始化的
context对象
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) 方法,配置 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 对象,并进行刷新,方法如下:
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
// <1> 如果 wac 使用了默认编号,则重新设置 id 属性
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
// 情况一,使用 contextId 属性
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);
if (idParam != null) {
wac.setId(idParam);
}
else { // 情况二,自动生成
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
// <2>设置 context 的 ServletContext 属性
wac.setServletContext(sc);
// <3> 设置 context 的配置文件地址
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);
}
// <4> 对 context 进行定制化处理
customizeContext(sc, wac);
// <5> 刷新 context ,执行初始化
wac.refresh();
}
- 如果
wac使用了默认编号,则重新设置id属性。默认情况下,我们不会对wac设置编号,所以会执行进去。而实际上,id的生成规则,也分成使用contextId在<context-param />标签中由用户配置,和自动生成两种情况。 默认情况下,会走第二种情况 - 设置
wac的 ServletContext 属性 - 【关键】 设置
context的配置文件地址。例如我们在 概述 中的web.xml中所看到的
<!-- Spring 和 MyBatis 的配置文件 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-mybatis.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
- 对
wac进行定制化处理,暂时忽略 - 【关键】 触发
wac的刷新事件,执行初始化。此处,就会进行一些的 Spring 容器的初始化工作,涉及到 Spring IOC 相关内容
closeWebApplicationContext
closeWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) 方法,关闭 WebApplicationContext 容器对象,方法如下:
public void closeWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
servletContext.log("Closing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
try {
// 关闭 context
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
((ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context).close();
}
}
finally {
// 移除 currentContext 或 currentContextPerThread
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = null;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.remove(ccl);
}
// 从 ServletContext 中移除
servletContext.removeAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
}
在 Servlet 容器销毁时被调用,用于关闭 WebApplicationContext 对象,以及清理相关资源对象
Servlet WebApplicationContext 容器
在 概述 的 web.xml中,我们已经看到,除了会初始化一个 Root WebApplicationContext 容器外,还会往 Servlet 容器的 ServletContext 上下文中注入一个 DispatcherServlet 对象,初始化该对象的过程也会初始化一个 Servlet WebApplicationContext 容器
DispatcherServlet 的类图如下:
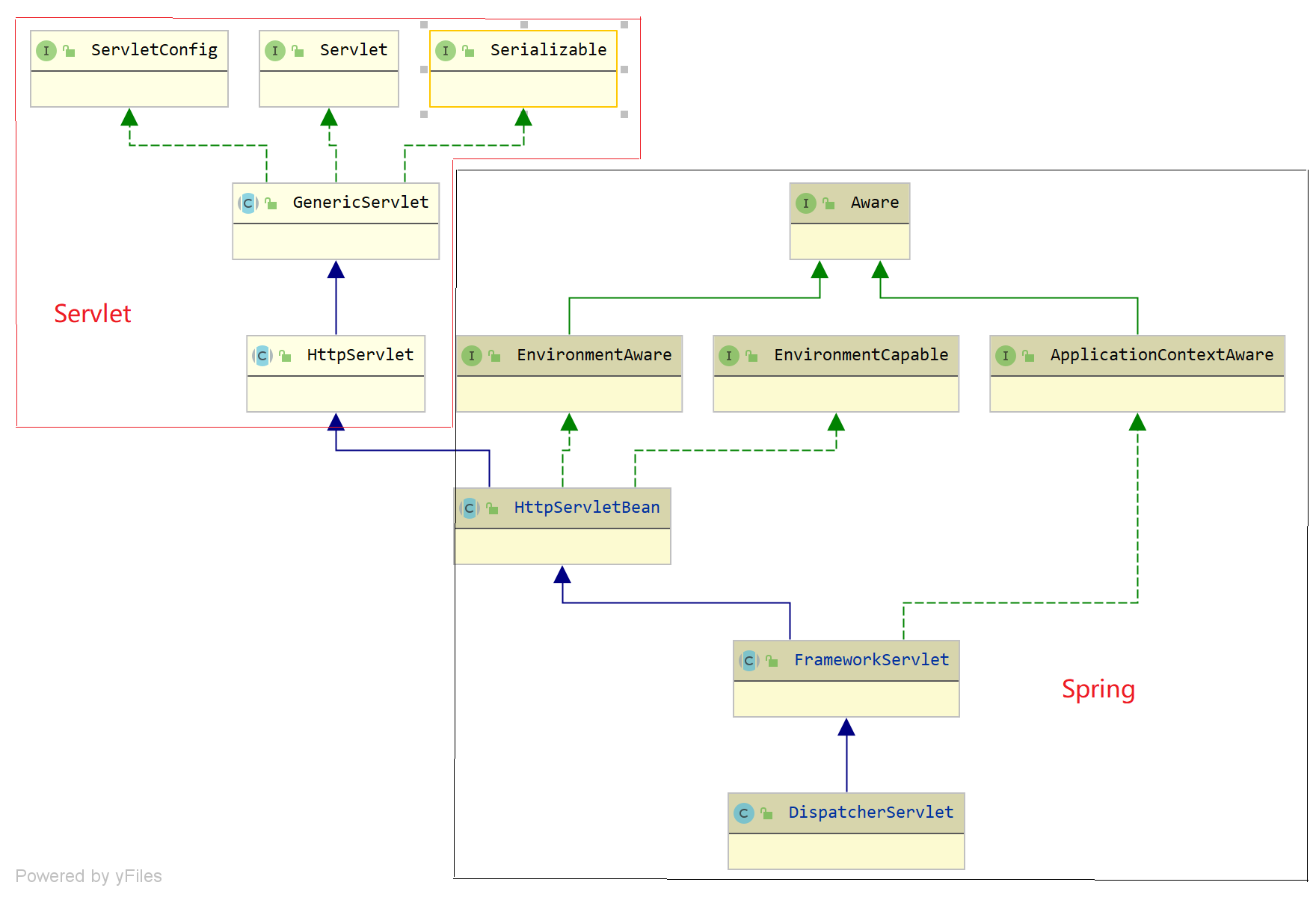
可以看到 DispatcherServlet 是一个 Servlet 对象,在注入至 Servlet 容器会调用其 init 方法,完成一些初始化工作
- HttpServletBean ,负责将 ServletConfig 设置到当前 Servlet 对象中,它的 Java doc:
/**
* Simple extension of {@link javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet} which treats
* its config parameters ({@code init-param} entries within the
* {@code servlet} tag in {@code web.xml}) as bean properties.
*/
- FrameworkServlet ,负责初始化 Spring Servlet WebApplicationContext 容器,同时该类覆写了 doGet、doPost 等方法,并将所有类型的请求委托给 doService 方法去处理,doService 是一个抽象方法,需要子类实现,它的 Java doc:
/**
* Base servlet for Spring's web framework. Provides integration with
* a Spring application context, in a JavaBean-based overall solution.
*/
- DispatcherServlet ,负责初始化 Spring MVC 的各个组件,以及处理客户端的请求,协调各个组件工作,它的 Java doc:
/**
* Central dispatcher for HTTP request handlers/controllers, e.g. for web UI controllers
* or HTTP-based remote service exporters. Dispatches to registered handlers for processing
* a web request, providing convenient mapping and exception handling facilities.
*/
每一层的 Servlet 实现类,负责执行相应的逻辑,条理清晰,我们逐个来看
HttpServletBean
org.springframework.web.servlet.HttpServletBean 抽象类,实现 EnvironmentCapable、EnvironmentAware 接口,继承 HttpServlet 抽象类,负责将 ServletConfig 集成到 Spring 中
构造方法
public abstract class HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet implements EnvironmentCapable, EnvironmentAware {
@Nullable
private ConfigurableEnvironment environment;
/**
* 必须配置的属性的集合,在 {@link ServletConfigPropertyValues} 中,会校验是否有对应的属性
* 默认为空
*/
private final Set<String> requiredProperties = new HashSet<>(4);
protected final void addRequiredProperty(String property) {
this.requiredProperties.add(property);
}
/**
* 实现了 EnvironmentAware 接口,自动注入 Environment 对象
*/
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(ConfigurableEnvironment.class, environment, "ConfigurableEnvironment required");
this.environment = (ConfigurableEnvironment) environment;
}
/**
* 实现了 EnvironmentAware 接口,返回 Environment 对象
*/
@Override
public ConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment() {
if (this.environment == null) {
// 如果 Environment 为空,则创建 StandardServletEnvironment 对象
this.environment = createEnvironment();
}
return this.environment;
}
/**
* Create and return a new {@link StandardServletEnvironment}.
*/
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() {
return new StandardServletEnvironment();
}
}
关于 xxxAware 接口,在 Spring 初始化该 Bean 的时候会调用其 setXxx 方法来注入一个对象,本文暂不分析
init方法
init()方法,重写 GenericServlet 中的方法,负责将 ServletConfig 设置到当前 Servlet 对象中,方法如下:
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
// <1> 解析 <init-param /> 标签,封装到 PropertyValues pvs 中
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
// <2.1> 将当前的这个 Servlet 对象,转化成一个 BeanWrapper 对象。从而能够以 Spring 的方式来将 pvs 注入到该 BeanWrapper 对象中
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
// <2.2> 注册自定义属性编辑器,一旦碰到 Resource 类型的属性,将会使用 ResourceEditor 进行解析
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
// <2.3> 空实现,留给子类覆盖,目前没有子类实现
initBeanWrapper(bw);
// <2.4> 以 Spring 的方式来将 pvs 注入到该 BeanWrapper 对象中
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
// 交由子类去实现,查看 FrameworkServlet#initServletBean() 方法
initServletBean();
}
- 解析 Servlet 配置的
<init-param />标签,封装成 PropertyValuespvs对象。其中,ServletConfigPropertyValues 是 HttpServletBean 的私有静态类,继承 MutablePropertyValues 类, ServletConfig 的 封装实现类 ,该类的代码如下:
private static class ServletConfigPropertyValues extends MutablePropertyValues {
public ServletConfigPropertyValues(ServletConfig config, Set<String> requiredProperties) throws ServletException {
// 获得缺失的属性的集合
Set<String> missingProps = (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(requiredProperties) ? new HashSet<>(requiredProperties) : null);
// <1> 遍历 ServletConfig 的初始化参数集合,添加到 ServletConfigPropertyValues 中,并从 missingProps 移除
Enumeration<String> paramNames = config.getInitParameterNames();
while (paramNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String property = paramNames.nextElement();
Object value = config.getInitParameter(property);
// 添加到 ServletConfigPropertyValues 中
addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue(property, value));
// 从 missingProps 中移除
if (missingProps != null) {
missingProps.remove(property);
}
}
// Fail if we are still missing properties.
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(missingProps)) {
throw new ServletException("...");
}
}
}
在它的构造方法中可以看到,将`<init-param />`标签定义的一些配置项解析成 PropertyValue 对象,例如在前面 **概述** 的`web.xml`中的配置,如下:
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
-
如果存在
<init-param />初始化参数- 将当前的这个 Servlet 对象,转化成一个 BeanWrapper 对象。从而能够以 Spring 的方式来将
pvs注入到该 BeanWrapper 对象中。简单来说,BeanWrapper 是 Spring 提供的一个用来操作 Java Bean 属性的工具, 使用它可以直接修改一个对象的属性 - 注册自定义属性编辑器,一旦碰到 Resource 类型的属性,将会使用 ResourceEditor 进行解析
- 调用
initBeanWrapper(BeanWrapper bw)方法,可初始化当前这个 Servlet 对象,空实现,留给子类覆盖,目前好像还没有子类实现 - 遍历
pvs中的属性值,注入到该 BeanWrapper 对象中,也就是设置到当前 Servlet 对象中,例如 FrameworkServlet 中的contextConfigLocation属性则会设置为上面的classpath:spring-mvc.xml值了
- 将当前的这个 Servlet 对象,转化成一个 BeanWrapper 对象。从而能够以 Spring 的方式来将
-
【关键】 调用
initServletBean()方法,空实现,交由子类去实现,完成自定义初始化逻辑,查看FrameworkServlet#initServletBean()方法
FrameworkServlet
org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet 抽象类,实现 ApplicationContextAware 接口,继承 HttpServletBean 抽象类,负责初始化 Spring Servlet WebApplicationContext 容器
构造方法
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
// ... 省略部分属性
/** Default context class for FrameworkServlet. */
public static final Class<?> DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS = XmlWebApplicationContext.class;
/** WebApplicationContext implementation class to create. */
private Class<?> contextClass = DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS;
/** Explicit context config location. 配置文件的地址 */
@Nullable
private String contextConfigLocation;
/** Should we publish the context as a ServletContext attribute?. */
private boolean publishContext = true;
/** Should we publish a ServletRequestHandledEvent at the end of each request?. */
private boolean publishEvents = true;
/** WebApplicationContext for this servlet. */
@Nullable
private WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext;
/** 标记是否是通过 {@link #setApplicationContext} 注入的 WebApplicationContext */
private boolean webApplicationContextInjected = false;
/** 标记已经是否接收到 ContextRefreshedEvent 事件,即 {@link #onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent)} */
private volatile boolean refreshEventReceived = false;
/** Monitor for synchronized onRefresh execution. */
private final Object onRefreshMonitor = new Object();
public FrameworkServlet() {
}
public FrameworkServlet(WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext) {
this.webApplicationContext = webApplicationContext;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
if (this.webApplicationContext == null && applicationContext instanceof WebApplicationContext) {
this.webApplicationContext = (WebApplicationContext) applicationContext;
this.webApplicationContextInjected = true;
}
}
}
-
contextClass属性:创建的 WebApplicationContext 类型,默认为 XmlWebApplicationContext.class ,在 Root WebApplicationContext 容器的创建过程中也是它 -
contextConfigLocation属性:配置文件的地址,例如:classpath:spring-mvc.xml -
webApplicationContext属性:WebApplicationContext 对象,即本文的关键, Servlet WebApplicationContext 容器 ,有四种创建方式- 通过上面的构造方法
- 实现了 ApplicationContextAware 接口,通过 Spring 注入,也就是
setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext)方法 - 通过
findWebApplicationContext()方法,下文见 - 通过
createWebApplicationContext(WebApplicationContext parent)方法,下文见
initServletBean
initServletBean() 方法,重写父类的方法,在 HttpServletBean 的 init() 方法的最后一步会调用,进一步初始化当前 Servlet 对象,当前主要是初始化 Servlet WebApplicationContext 容器 ,代码如下:
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// <1> 初始化 WebApplicationContext 对象
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
// <2> 空实现,留给子类覆盖,目前没有子类实现
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ?
"shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" :
"masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data";
logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails +
"': request parameters and headers will be " + value);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}
- 调用
initWebApplicationContext()方法,初始化 Servlet WebApplicationContext 对象 - 调用
initFrameworkServlet()方法,可对当前 Servlet 对象进行自定义操作,空实现,留给子类覆盖,目前好像还没有子类实现
initWebApplicationContext
initWebApplicationContext() 方法 【核心】 ,初始化 Servlet WebApplicationContext 对象,方法如下:
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
// <1> 获得根 WebApplicationContext 对象
WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
// <2> 获得 WebApplicationContext wac 对象
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
// 第一种情况,如果构造方法已经传入 webApplicationContext 属性,则直接使用
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
// 如果是 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 类型,并且未激活,则进行初始化
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) { // 未激活
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
// 配置和初始化 wac
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
// 第二种情况,从 ServletContext 获取对应的 WebApplicationContext 对象
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
// 第三种,创建一个 WebApplicationContext 对象
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
// <3> 如果未触发刷新事件,则主动触发刷新事件
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
// <4> 将 context 设置到 ServletContext 中
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
-
调用
WebApplicationContextUtils#getWebApplicationContext((ServletContext sc)方法,从 ServletContext 中获得 Root WebApplicationContext 对象,可以回到 ContextLoader#initWebApplicationContext 方法中的第5步,你会觉得很熟悉 -
获得 WebApplicationContext
wac对象,有三种情况-
如果构造方法已经传入 webApplicationContext 属性,则直接引用给
wac,也就是上面 构造方法 中提到的第 1、2 种创建方式如果
wac是 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 类型,并且未刷新(未激活),则调用configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac)方法,进行配置和刷新,下文见如果父容器为空,则设置为上面第
1步获取到的 Root WebApplicationContext 对象 -
调用
findWebApplicationContext()方法,从 ServletContext 获取对应的 WebApplicationContext 对象,也就是上面 构造方法 中提到的第 3 种创建方式
-
@Nullable
protected WebApplicationContext findWebApplicationContext() {
String attrName = getContextAttribute();
// 需要配置了 contextAttribute 属性下,才会去查找,一般我们不会去配置
if (attrName == null) {
return null;
}
// 从 ServletContext 中,获得属性名对应的 WebApplicationContext 对象
WebApplicationContext wac = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext(), attrName);
// 如果不存在,则抛出 IllegalStateException 异常
if (wac == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No WebApplicationContext found: initializer not registered?");
}
return wac;
}
一般不会这样做
3. 调用`createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable WebApplicationContext parent)`方法,创建一个 WebApplicationContext 对象
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
// <a> 获得 context 的类,XmlWebApplicationContext.class
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
// 如果非 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 类型,抛出 ApplicationContextException 异常
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
// <b> 创建 context 类的对象
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
// <c> 设置 environment、parent、configLocation 属性
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
wac.setParent(parent);
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
// <d> 配置和初始化 wac
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
`<a>` 获得 `context` 的 Class 对象,默认为 XmlWebApplicationContext.class,如果非 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 类型,则抛出异常
`<b>` 创建 `context` 的实例对象
`<c>` 设置 `environment`、`parent`、`configLocation` 属性。其中,`configLocation` 是个 **重要** 属性
`<d>` 调用 `configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac)` 方法,进行配置和刷新,下文见
- 如果未触发刷新事件,则调用
onRefresh(ApplicationContext context)方法,主动触发刷新事件,该方法为空实现,交由子类 DispatcherServlet 去实现 - 将
context设置到 ServletContext 中
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) 方法,配置和初始化 wac 对象,方法如下:
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
// <1> 如果 wac 使用了默认编号,则重新设置 id 属性
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
// 情况一,使用 contextId 属性
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
// 情况二,自动生成
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());
}
}
// <2> 设置 wac 的 servletContext、servletConfig、namespace 属性
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
// <3> 添加监听器 SourceFilteringListener 到 wac 中
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
// <4>
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
// <5> 执行处理完 WebApplicationContext 后的逻辑。目前是个空方法,暂无任何实现
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
// <6> 执行自定义初始化 context
applyInitializers(wac);
// <7> 刷新 wac ,从而初始化 wac
wac.refresh();
}
实际上,处理逻辑和ContextLoader#configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext方法差不多
- 如果
wac使用了默认编号,则重新设置id属性 - 设置
wac的 servletContext、servletConfig、namespace 属性 - 添加监听器 SourceFilteringListener 到
wac中 - 配置 Environment 对象,暂时忽略
- 执行处理完 WebApplicationContext 后的逻辑,空方法,暂无任何实现
- 对
wac进行定制化处理,暂时忽略 - 【关键】 触发
wac的刷新事件,执行初始化。此处,就会进行一些的 Spring 容器的初始化工作,涉及到 Spring IOC 相关内容
onRefresh
onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) 方法,当 Servlet WebApplicationContext 刷新完成后,触发 Spring MVC 组件的初始化,方法如下:
/**
* Template method which can be overridden to add servlet-specific refresh work.
* Called after successful context refresh.
* <p>This implementation is empty.
* @param context the current WebApplicationContext
* @see #refresh()
*/
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
// For subclasses: do nothing by default.
}
这是一个空方法,具体的实现,在子类 DispatcherServlet 中,代码如下:
// DispatcherServlet.java
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses.
* <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
// 初始化 MultipartResolver
initMultipartResolver(context);
// 初始化 LocaleResolver
initLocaleResolver(context);
// 初始化 ThemeResolver
initThemeResolver(context);
// 初始化 HandlerMappings
initHandlerMappings(context);
// 初始化 HandlerAdapters
initHandlerAdapters(context);
// 初始化 HandlerExceptionResolvers
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
// 初始化 RequestToViewNameTranslator
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
// 初始化 ViewResolvers
initViewResolvers(context);
// 初始化 FlashMapManager
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
初始化九个组件,这里只是先提一下,在后续的文档中会进行分析
onRefresh方法的触发有两种方式:
- 方式一:如果
refreshEventReceived为false,也就是未接收到刷新事件(防止重复初始化相关组件),则在initWebApplicationContext方法中直接调用 - 方式二:通过在
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext方法中,触发wac的刷新事件
为什么上面的 方式二 可以触发这个方法的调用呢?
先看到 configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext 方法的第 3 步,添加了一个 SourceFilteringListener 监听器,如下:
// <3> 添加监听器 SourceFilteringListener 到 wac 中
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
监听到相关事件后,会委派给 ContextRefreshListener 进行处理,它是 FrameworkServlet 的私有内部类,来看看它又是怎么处理的,代码如下:
private class ContextRefreshListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
FrameworkServlet.this.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
}
直接将该事件委派给了 FrameworkServlet 的 onApplicationEvent 方法,如下:
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
// 标记 refreshEventReceived 为 true
this.refreshEventReceived = true;
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
// 处理事件中的 ApplicationContext 对象,空实现,子类 DispatcherServlet 会实现
onRefresh(event.getApplicationContext());
}
}
先设置 refreshEventReceived 为 true,表示已接收到刷新时间,然后再调用 onRefresh 方法,回到上面的 方式一 和 方式二 ,是不是连通起来了,所以说该方法是一定会被触发的
总结
本分对 Spring MVC 两种容器的创建过程进行分析,分别为 Root WebApplicationContext 和 Servlet WebApplicationContext 容器,它们是父子关系,创建过程并不是很复杂。前置是在 Tomcat 或者 Jetty 等 Servlet 容器启动后,由 ContextLoaderListener 监听到相应事件而创建的,后者是在 DispatcherServlet 初始化的过程中创建的,因为它是一个 HttpServlet 对象,会调用其 init 方法,完成初始化相关工作
DispatcherServlet 是 Spring MVC 的 核心类 ,相当于一个调度者,请求的处理过程都是通过它调度 各个组件 来完成的,在后续的文章中进行分析
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

