ResourceLoader 接口是用来加载 Resource 对象的,换句话说,就是当一个对象需要获取 Resource 实例时,可以选择实现 ResourceLoader 接口。
public interface ResourceLoader {
/** Pseudo URL prefix for loading from the class path: "classpath:" */
String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = ResourceUtils.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX;
Resource getResource(String location);
@Nullable
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}
当你在指定应用上下文调用 getResource() 方法时,而指定的位置路径又没有包含特定的前缀,spring 会根据当前应用上下文来决定返回哪一种类型 Resource。举个例子,假设下面的代码片段是通过 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 实例来调用的,
Resource template = ctx.getResource("some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt");"some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt");
那 spring 会返回一个 ClassPathResource 对象;类似的,如果是通过实例 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 实例调用的,返回的是一个 FileSystemResource 对象;如果是通过 WebApplicationContext 实例的,返回的是一个 ServletContextResource 对象…… 如上所说,你就可以在指定的应用上下中使用 Resource 实例来加载当前应用上下文的资源。
还有另外一种场景里,如在其他应用上下文里,你可能会强制需要获取一个 ClassPathResource 对象,这个时候,你可以通过加上指定的前缀来实现这一需求,如:
Resource template = ctx.getResource("classpath:some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt");"classpath:some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt");
类似的,你可以通过其他任意的 url 前缀来强制获取 UrlResource 对象:
Resource template = ctx.getResource("file:///some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt");"file:///some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt");
Resource template = ctx.getResource("http://myhost.com/resource/path/myTemplate.txt");"http://myhost.com/resource/path/myTemplate.txt");
下面,给出一个表格来总结一下 spring 根据各种位置路径加载资源的策略:
| Prefix | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| classpath: | classpath:com/myapp/config.xml | Loadedfromtheclasspath. |
| file: | file:///data/config.xml | Loadedasa URL,fromthefilesystem. [3] |
| http: | http://myserver/logo.png | Loadedasa URL. |
| (none) | /data/config.xml | Dependsontheunderlying ApplicationContext. |
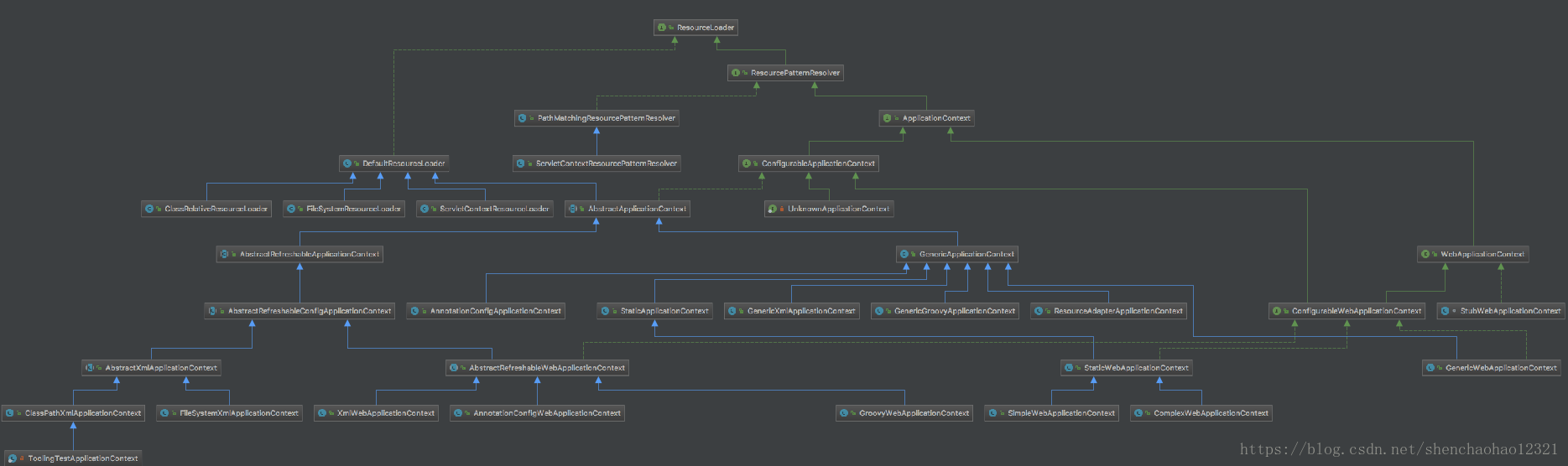
ResourcePatternResolver是ResourceLoader唯一的扩展接口,增加了一个方法通过一个path可以返回多个Resource:
public interface ResourcePatternResolver extends ResourceLoader {
String CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX = "classpath*:";
Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException;
}
- 以ResourceLoader结尾的类实现了ResourceLoader接口,Spring给出的默认实现是DefaultResourceLoader。
- 以ResourcePatternResolver结尾的类实现了ResourcePatternResolver接口,Spring给出了两个实现类PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver和ServletContextResourcePatternResolver。
- 以ApplicationContext结尾的类也实现了ResourcePatternResolver接口,最上层的实现类是AbstractApplicationContext,继承了DefaultResourceLoader并默认持有一个PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver的引用。
下面分析一下DefaultResourceLoader和PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver。
public class DefaultResourceLoader implements ResourceLoader {
@Nullable
private ClassLoader classLoader;
private final Set<ProtocolResolver> protocolResolvers = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
private final Map<Class<?>, Map<Resource, ?>> resourceCaches = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(4);
public DefaultResourceLoader() {
this.classLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}
public DefaultResourceLoader(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.classLoader = classLoader;
}
public void setClassLoader(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.classLoader = classLoader;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
return (this.classLoader != null ? this.classLoader : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
public void addProtocolResolver(ProtocolResolver resolver) {
Assert.notNull(resolver, "ProtocolResolver must not be null");
this.protocolResolvers.add(resolver);
}
public Collection<ProtocolResolver> getProtocolResolvers() {
return this.protocolResolvers;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> Map<Resource, T> getResourceCache(Class<T> valueType) {
return (Map<Resource, T>) this.resourceCaches.computeIfAbsent(valueType, key -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
}
public void clearResourceCaches() {
this.resourceCaches.clear();
}
@Override
public Resource getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");
for (ProtocolResolver protocolResolver : this.protocolResolvers) {
Resource resource = protocolResolver.resolve(location, this);
if (resource != null) {
return resource;
}
}
if (location.startsWith("/")) {
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
else if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader());
}
else {
try {
// Try to parse the location as a URL...
URL url = new URL(location);
return (ResourceUtils.isFileURL(url) ? new FileUrlResource(url) : new UrlResource(url));
}
catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
// No URL -> resolve as resource path.
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
}
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
return new ClassPathContextResource(path, getClassLoader());
}
protected static class ClassPathContextResource extends ClassPathResource implements ContextResource {
public ClassPathContextResource(String path, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
super(path, classLoader);
}
@Override
public String getPathWithinContext() {
return getPath();
}
@Override
public Resource createRelative(String relativePath) {
String pathToUse = StringUtils.applyRelativePath(getPath(), relativePath);
return new ClassPathContextResource(pathToUse, getClassLoader());
}
}
}
DefaultResourceLoader的getResource()方法中,首先会循环protocolResolvers,直到碰到一个能处理此location的ProtocolResolver,返回其非null的经过resolver处理返回的Resource对象。Spring Framework4.3提供了一个协议扩展机制方法:
addProtocolResolver()来加入我们自定义的ProtocolResolver来改变DefaultResourceLoader默认的行为。
其默认根据location的格式来返回不同的Resource实例。
- 以/开头返回一个ClassPathContextResource对象,继承于ClassPathResource,增加了一个方法getPathWithinContext()。
- 以classpath:开头的返回new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader())。
- 否则尝试以location构造URL对象,如果是file|vfsfile|vfs开头的返回FileUrlResource否则返回UrlResource
- 构造URL失败,还是以ClassPathContextResource返回。
其中UrlResource利用Java API URL获取资源内容,通常资源连接由URL.openConnection()方法桥接获取,具体原理参考《Java URL协议实现扩展原理》。
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 是ResourcePatternResolver仅有的实现类需要关联零到一个ResourceLoader实例,同时它又被AbstractApplicationContext关联,作为AbstractApplicationContext.getResources()方法的底层实现:
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext {
public AbstractApplicationContext() {
this.resourcePatternResolver = getResourcePatternResolver();
}
protected ResourcePatternResolver getResourcePatternResolver() {
return new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(this);
}
@Override
public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
return this.resourcePatternResolver.getResources(locationPattern);
}
}
resourcePatternResolver所关联的ResourceLoader又是AbstractApplicationContext 对象本身。值得注意的是AbstractApplicationContext扩展了ResourceLoader接口实现类DefaultResourceLoader,也就是说AbstractApplicationContext对象也是ResourceLoader对象。同时AbstractApplicationContext实现ConfigurableApplicationContext接口,而该接口又扩展了ResourcePatternResolver,故AbstractApplicationContext实例也是ResourcePatternResolver对象,并且AbstractApplicationContext没有覆盖父类DefaultResourceLoader.getResource()方法。综上所述DefaultResourceLoader实际上是Spring Framework中唯一的ResourceLoader实现。
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 内还有一个很重要的成员变量pathMatcher,是一个AntPathMatcher实例,对参数的解析主要用到它,先看看它的简单介绍:
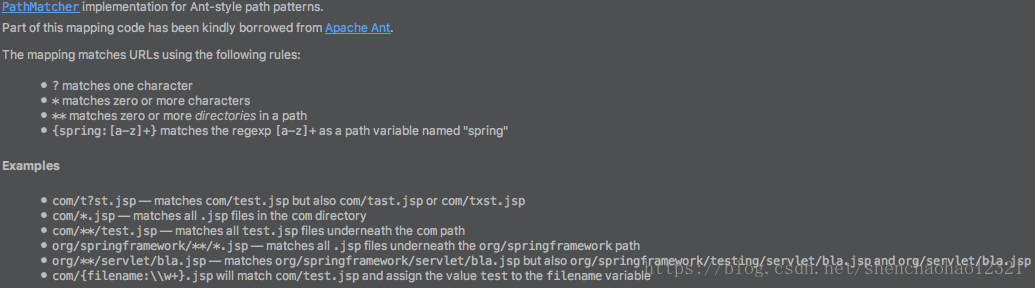
下面主要看一下PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver的getResources()方法。
public class PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver implements ResourcePatternResolver {
private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
private PathMatcher pathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver() {
this.resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader();
}
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
Assert.notNull(resourceLoader, "ResourceLoader must not be null");
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader(classLoader);
}
@Override
public Resource getResource(String location) {
return getResourceLoader().getResource(location);
}
@Override
public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
Assert.notNull(locationPattern, "Location pattern must not be null");
if (locationPattern.startsWith(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX)) {
// a class path resource (multiple resources for same name possible)
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()))) {
// a class path resource pattern
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
// all class path resources with the given name
return findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()));
}
}
else {
// Generally only look for a pattern after a prefix here,
// and on Tomcat only after the "*/" separator for its "war:" protocol.
int prefixEnd = (locationPattern.startsWith("war:") ? locationPattern.indexOf("*/") + 1 :
locationPattern.indexOf(":") + 1);
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd))) {
// a file pattern
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
// a single resource with the given name
return new Resource[] {getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
}
}
}
}
以classpath*:开头并且路径其余部分还包含*或?则调用findPathMatchingResources()方法,找出所有classpath下可以匹配locationPattern的Resource。
protected Resource[] findPathMatchingResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
String rootDirPath = determineRootDir(locationPattern);
String subPattern = locationPattern.substring(rootDirPath.length());
Resource[] rootDirResources = getResources(rootDirPath);
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<>(16);
for (Resource rootDirResource : rootDirResources) {
rootDirResource = resolveRootDirResource(rootDirResource);
URL rootDirUrl = rootDirResource.getURL();
if (equinoxResolveMethod != null) {
if (rootDirUrl.getProtocol().startsWith("bundle")) {
URL resolvedUrl = (URL) ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(equinoxResolveMethod, null, rootDirUrl);
if (resolvedUrl != null) {
rootDirUrl = resolvedUrl;
}
rootDirResource = new UrlResource(rootDirUrl);
}
}
if (rootDirUrl.getProtocol().startsWith(ResourceUtils.URL_PROTOCOL_VFS)) {
result.addAll(VfsResourceMatchingDelegate.findMatchingResources(rootDirUrl, subPattern, getPathMatcher()));
}
else if (ResourceUtils.isJarURL(rootDirUrl) || isJarResource(rootDirResource)) {
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingJarResources(rootDirResource, rootDirUrl, subPattern));
}
else {
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingFileResources(rootDirResource, subPattern));
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Resolved location pattern [" + locationPattern + "] to resources " + result);
}
return result.toArray(new Resource[result.size()]);
}
rootDirPath为包含*或?上一级目录,例如locationPattern="classpath*:org/springframework/core/io/sup*/*.class",则rootDirPath="classpath*:org/springframework/core/io/",subPattern="sup*/*.class",接下来调用getResources()方法,这次getResources的入参是不带非前缀通配符的了,所以会走findAllClassPathResources()方法。
protected Resource[] findAllClassPathResources(String location) throws IOException {
String path = location;
if (path.startsWith("/")) {
path = path.substring(1);
}
Set<Resource> result = doFindAllClassPathResources(path);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Resolved classpath location [" + location + "] to resources " + result);
}
return result.toArray(new Resource[result.size()]);
}
如果以“/”开头会去掉“/”,因为doFindAllClassPathResources()方法内是调用ClassLoader的getResources方法获取指定的URL,这里有必要提一句,ClassLoader的getResources()方法会返回所有classpath下的URL,就是如果有多个jar(也包含当前工程)包含有path指定的资源路径,都会找出来包装为URLResource返回。
protected Set<Resource> doFindAllClassPathResources(String path) throws IOException {
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<>(16);
ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader();
Enumeration<URL> resourceUrls = (cl != null ? cl.getResources(path) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(path));
while (resourceUrls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = resourceUrls.nextElement();
result.add(convertClassLoaderURL(url));
}
if ("".equals(path)) {
// The above result is likely to be incomplete, i.e. only containing file system references.
// We need to have pointers to each of the jar files on the classpath as well...
addAllClassLoaderJarRoots(cl, result);
}
return result;
}
然后做三个判断,对不同协议的rootDirUrl分别调用不同的方法来找到匹配的资源。
if (rootDirUrl.getProtocol().startsWith(ResourceUtils.URL_PROTOCOL_VFS)) {
result.addAll(VfsResourceMatchingDelegate.findMatchingResources(rootDirUrl, subPattern, getPathMatcher()));
}
else if (ResourceUtils.isJarURL(rootDirUrl) || isJarResource(rootDirResource)) {
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingJarResources(rootDirResource, rootDirUrl, subPattern));
}
else {
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingFileResources(rootDirResource, subPattern));
}
我们看一下非vfs协议和非jar中的路径情况是如何匹配到subPattern的资源的。
protected Set<Resource> doFindPathMatchingFileResources(Resource rootDirResource, String subPattern)
throws IOException {
File rootDir;
try {
rootDir = rootDirResource.getFile().getAbsoluteFile();
}
catch (IOException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Cannot search for matching files underneath " + rootDirResource +
" because it does not correspond to a directory in the file system", ex);
}
return Collections.emptySet();
}
return doFindMatchingFileSystemResources(rootDir, subPattern);
}
首先获取到rootDirResource的绝对路径为了可以使用File定位到具体文件,调用doFindMatchingFileSystemResources()方法
protected Set<Resource> doFindMatchingFileSystemResources(File rootDir, String subPattern) throws IOException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking for matching resources in directory tree [" + rootDir.getPath() + "]");
}
Set<File> matchingFiles = retrieveMatchingFiles(rootDir, subPattern);
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<>(matchingFiles.size());
for (File file : matchingFiles) {
result.add(new FileSystemResource(file));
}
return result;
}
retrieveMatchingFiles方法找出rootDir下能与subPattern匹配的文件,将File包装成FileSystemResource类型返回。看一下具体找文件的过程:
protected Set<File> retrieveMatchingFiles(File rootDir, String pattern) throws IOException {
if (!rootDir.exists()) {
// Silently skip non-existing directories.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping [" + rootDir.getAbsolutePath() + "] because it does not exist");
}
return Collections.emptySet();
}
if (!rootDir.isDirectory()) {
// Complain louder if it exists but is no directory.
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Skipping [" + rootDir.getAbsolutePath() + "] because it does not denote a directory");
}
return Collections.emptySet();
}
if (!rootDir.canRead()) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Cannot search for matching files underneath directory [" + rootDir.getAbsolutePath() +
"] because the application is not allowed to read the directory");
}
return Collections.emptySet();
}
String fullPattern = StringUtils.replace(rootDir.getAbsolutePath(), File.separator, "/");
if (!pattern.startsWith("/")) {
fullPattern += "/";
}
fullPattern = fullPattern + StringUtils.replace(pattern, File.separator, "/");
Set<File> result = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);
doRetrieveMatchingFiles(fullPattern, rootDir, result);
return result;
}
其中将路径分隔符统一为“/”,避免windows系统下路径为\\导致AntPathMatcher不能处理,然后调用doRetrieveMatchingFiles()方法,
protected void doRetrieveMatchingFiles(String fullPattern, File dir, Set<File> result) throws IOException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Searching directory [" + dir.getAbsolutePath() +
"] for files matching pattern [" + fullPattern + "]");
}
File[] dirContents = dir.listFiles();
if (dirContents == null) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Could not retrieve contents of directory [" + dir.getAbsolutePath() + "]");
}
return;
}
Arrays.sort(dirContents);
for (File content : dirContents) {
String currPath = StringUtils.replace(content.getAbsolutePath(), File.separator, "/");
if (content.isDirectory() && getPathMatcher().matchStart(fullPattern, currPath + "/")) {
if (!content.canRead()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping subdirectory [" + dir.getAbsolutePath() +
"] because the application is not allowed to read the directory");
}
}
else {
doRetrieveMatchingFiles(fullPattern, content, result);
}
}
if (getPathMatcher().match(fullPattern, currPath)) {
result.add(content);
}
}
}
遍历dir下所有的文件或文件夹,如果是文件则调用AntPathMatcher的match()方法判断当前文件的绝对路径是否满足fullPattern的匹配规则,满足则加入result里保存下来。如果是文件夹,则递归调用doRetrieveMatchingFiles()方法,超出此文件夹下满足上述条件的文件。
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

