Spring提供了一个Converter接口用于做类型装换,但我们需要将对象从一种类型转换为另一种类型只需要调用具体实现类的convert()方法。Spring也默认为我们提供了很多常用的实现类。
public interface Converter<S, T> {
T convert(S source);
}
上述接口有一个麻烦的地方是,如果我们需要将String转换到相应的枚举类,就不得不提供多个Converter的实现。ConverterFactory就是解决这个问题的,因为T extends R,表名可以为一类对象提供类型转换。针对上述问题Spring提供了一个StringToEnumConverterFactory
public interface ConverterFactory<S, R> {
<T extends R> Converter<S, T> getConverter(Class<T> targetType);
}
final class StringToEnumConverterFactory implements ConverterFactory<String, Enum> {
@Override
public <T extends Enum> Converter<String, T> getConverter(Class<T> targetType) {
return new StringToEnum(ConversionUtils.getEnumType(targetType));
}
private class StringToEnum<T extends Enum> implements Converter<String, T> {
private final Class<T> enumType;
public StringToEnum(Class<T> enumType) {
this.enumType = enumType;
}
@Override
public T convert(String source) {
if (source.isEmpty()) {
// It's an empty enum identifier: reset the enum value to null.
return null;
}
return (T) Enum.valueOf(this.enumType, source.trim());
}
}
}
Converter 接口只支持从一个原类型转换为一个目标类型; ConverterFactory 接口只支持从一个原类型转换为一个目标类型对应的子类型;而 GenericConverter 接口支持在多个不同的原类型和目标类型之间进行转换。
public interface GenericConverter {
@Nullable
Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes();
@Nullable
Object convert(@Nullable Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);
final class ConvertiblePair {
private final Class<?> sourceType;
private final Class<?> targetType;
public ConvertiblePair(Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType) {
Assert.notNull(sourceType, "Source type must not be null");
Assert.notNull(targetType, "Target type must not be null");
this.sourceType = sourceType;
this.targetType = targetType;
}
public Class<?> getSourceType() {
return this.sourceType;
}
public Class<?> getTargetType() {
return this.targetType;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(@Nullable Object other) {
if (this == other) {
return true;
}
if (other == null || other.getClass() != ConvertiblePair.class) {
return false;
}
ConvertiblePair otherPair = (ConvertiblePair) other;
return (this.sourceType == otherPair.sourceType && this.targetType == otherPair.targetType);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return (this.sourceType.hashCode() * 31 + this.targetType.hashCode());
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return (this.sourceType.getName() + " -> " + this.targetType.getName());
}
}
}
getConvertibleTypes()方法用于返回这个 GenericConverter 能够转换的原类型和目标类型的一个组合,convert 方法则是用于进行类型转换。这个方法就复杂在TypeDescriptor这个参数类型上了,我们以后再介绍这个类。
有时我们只想要一个在特定条件成立的Converter,ConditionalGenericConverter接口可以满足这个需要,它集成了GenericConverter与ConditionalConverter。
public interface ConditionalConverter {
boolean matches(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);
}
public interface ConditionalGenericConverter
extends GenericConverter, ConditionalConverter {
}
我们看一个ConditionalGenericConverter的例子StringToArrayConverter:
final class StringToArrayConverter implements ConditionalGenericConverter {
private final ConversionService conversionService;
public StringToArrayConverter(ConversionService conversionService) {
this.conversionService = conversionService;
}
@Override
public Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes() {
return Collections.singleton(new ConvertiblePair(String.class, Object[].class));//可以将String转换为Object[]类型
}
@Override
public boolean matches(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {//返回为true,代表可以转换
return ConversionUtils.canConvertElements(sourceType, targetType.getElementTypeDescriptor(),
this.conversionService);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object convert(@Nullable Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {//具体转换逻辑
if (source == null) {
return null;
}
String string = (String) source;
String[] fields = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(string);
TypeDescriptor targetElementType = targetType.getElementTypeDescriptor();
Assert.state(targetElementType != null, "No target element type");
Object target = Array.newInstance(targetElementType.getType(), fields.length);
for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) {
String sourceElement = fields[i];
Object targetElement = this.conversionService.convert(sourceElement.trim(), sourceType, targetElementType);
Array.set(target, i, targetElement);
}
return target;
}
}
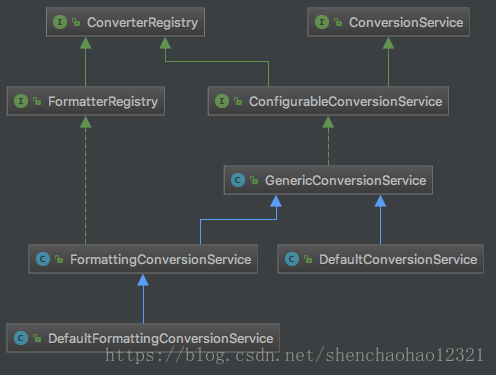
ConversionService是一个类型转换的方便接口,可以通过convert()方法的参数自动选取合适的转换器来进行转换,因为它的实现类都实现了ConverterRegistry接口,该接口的addConverter()方法用来注册转换器,DefaultConversionService使用的就是addConverter()方法加入的转换器。
public interface ConverterRegistry {
void addConverter(Converter<?, ?> converter);
<S, T> void addConverter(Class<S> sourceType, Class<T> targetType, Converter<? super S, ? extends T> converter);
void addConverter(GenericConverter converter);
void addConverterFactory(ConverterFactory<?, ?> factory);
void removeConvertible(Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType);
}
public interface ConversionService {
boolean canConvert(@Nullable Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType);
boolean canConvert(@Nullable TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);
@Nullable
<T> T convert(@Nullable Object source, Class<T> targetType);
@Nullable
Object convert(@Nullable Object source, @Nullable TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);
}
public interface ConfigurableConversionService extends ConversionService, ConverterRegistry {}
GenericConversionService类实现了ConfigurableConversionService接口,具备转换器注册与类型转换功能。该类有一个成员变量converters是Converters类型,通过addConverter()方法加入的转换器都会放入converters中。
@Override
public void addConverter(Converter<?, ?> converter) {
ResolvableType[] typeInfo = getRequiredTypeInfo(converter.getClass(), Converter.class);
if (typeInfo == null && converter instanceof DecoratingProxy) {
typeInfo = getRequiredTypeInfo(((DecoratingProxy) converter).getDecoratedClass(), Converter.class);
}
if (typeInfo == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to determine source type <S> and target type <T> for your " +
"Converter [" + converter.getClass().getName() + "]; does the class parameterize those types?");
}
addConverter(new ConverterAdapter(converter, typeInfo[0], typeInfo[1]));
}
@Override
public <S, T> void addConverter(Class<S> sourceType, Class<T> targetType, Converter<? super S, ? extends T> converter) {
addConverter(new ConverterAdapter(
converter, ResolvableType.forClass(sourceType), ResolvableType.forClass(targetType)));
}
@Override
public void addConverter(GenericConverter converter) {
this.converters.add(converter);
invalidateCache();
}
@Override
public void addConverterFactory(ConverterFactory<?, ?> factory) {
ResolvableType[] typeInfo = getRequiredTypeInfo(factory.getClass(), ConverterFactory.class);
if (typeInfo == null && factory instanceof DecoratingProxy) {
typeInfo = getRequiredTypeInfo(((DecoratingProxy) factory).getDecoratedClass(), ConverterFactory.class);
}
if (typeInfo == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to determine source type <S> and target type <T> for your " +
"ConverterFactory [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]; does the class parameterize those types?");
}
addConverter(new ConverterFactoryAdapter(factory,
new ConvertiblePair(typeInfo[0].resolve(Object.class), typeInfo[1].resolve(Object.class))));
}
这四个加入转换器的方法最终都是调用public void addConverter(GenericConverter converter)这个方法,所以不论我们传入哪种类型(Converter或ConverterFactory)的转换器都会通过相应的适配器包装为ConditionalGenericConverter放入converters中。
public void addConverter(Converter converter):得到converter父接口Converter的两个泛型参数,传入ConverterAdapter作为ConditionalGenericConverter中getConvertibleTypes()方法的返回值,matches方法会用到。其余addConverter()方法类似。
下面看一下Converters类。
private final Set<GenericConverter> globalConverters = new LinkedHashSet<>();
private final Map<ConvertiblePair, ConvertersForPair> converters = new LinkedHashMap<>(36);
public void add(GenericConverter converter) {
Set<ConvertiblePair> convertibleTypes = converter.getConvertibleTypes();
if (convertibleTypes == null) {
Assert.state(converter instanceof ConditionalConverter,
"Only conditional converters may return null convertible types");
this.globalConverters.add(converter);
}
else {
for (ConvertiblePair convertiblePair : convertibleTypes) {
ConvertersForPair convertersForPair = getMatchableConverters(convertiblePair);
convertersForPair.add(converter);
}
}
}
private ConvertersForPair getMatchableConverters(ConvertiblePair convertiblePair) {
ConvertersForPair convertersForPair = this.converters.get(convertiblePair);
if (convertersForPair == null) {
convertersForPair = new ConvertersForPair();
this.converters.put(convertiblePair, convertersForPair);
}
return convertersForPair;
}
converters存储convertibleTypes不为空的GenericConverter,globalConverters存储实现了ConditionalConverter的转换器。
converters是一个Map<ConvertiblePair, ConvertersForPair>, ConvertersForPair可以保存多个转换器,因为add方法可能会注册多个ConvertiblePair相同的转换器,这时候选取转换器的优先级为如下。
public GenericConverter getConverter(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
for (GenericConverter converter : this.converters) {
if (!(converter instanceof ConditionalGenericConverter) ||
((ConditionalGenericConverter) converter).matches(sourceType, targetType)) {
return converter;
}
}
return null;
}
接下来再看一看GenericConversionService的convert()方法。
@Override
@Nullable
public Object convert(@Nullable Object source, @Nullable TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
Assert.notNull(targetType, "Target type to convert to cannot be null");
if (sourceType == null) {
Assert.isTrue(source == null, "Source must be [null] if source type == [null]");
return handleResult(null, targetType, convertNullSource(null, targetType));
}
if (source != null && !sourceType.getObjectType().isInstance(source)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Source to convert from must be an instance of [" +
sourceType + "]; instead it was a [" + source.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
GenericConverter converter = getConverter(sourceType, targetType);
if (converter != null) {
Object result = ConversionUtils.invokeConverter(converter, source, sourceType, targetType);
return handleResult(sourceType, targetType, result);
}
return handleConverterNotFound(source, sourceType, targetType);
}
首先调用getConverter()方法找到能转换sourceType到targetType的转换器。
protected GenericConverter getConverter(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
ConverterCacheKey key = new ConverterCacheKey(sourceType, targetType);
GenericConverter converter = this.converterCache.get(key);
if (converter != null) {
return (converter != NO_MATCH ? converter : null);
}
converter = this.converters.find(sourceType, targetType);
if (converter == null) {
converter = getDefaultConverter(sourceType, targetType);
}
if (converter != null) {
this.converterCache.put(key, converter);
return converter;
}
this.converterCache.put(key, NO_MATCH);
return null;
}
核心查找过程是由converters的find()方法,
public GenericConverter find(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
// Search the full type hierarchy
List<Class<?>> sourceCandidates = getClassHierarchy(sourceType.getType());
List<Class<?>> targetCandidates = getClassHierarchy(targetType.getType());
for (Class<?> sourceCandidate : sourceCandidates) {
for (Class<?> targetCandidate : targetCandidates) {
ConvertiblePair convertiblePair = new ConvertiblePair(sourceCandidate, targetCandidate);
GenericConverter converter = getRegisteredConverter(sourceType, targetType, convertiblePair);
if (converter != null) {
return converter;
}
}
}
return null;
}
沿着父类方向找出sourceType和targetType的所有Class,然后排列组作为getRegisteredConverter()方法的入参,直到返回一个转换器为止。
private GenericConverter getRegisteredConverter(TypeDescriptor sourceType,
TypeDescriptor targetType, ConvertiblePair convertiblePair) {
// Check specifically registered converters
ConvertersForPair convertersForPair = this.converters.get(convertiblePair);
if (convertersForPair != null) {
GenericConverter converter = convertersForPair.getConverter(sourceType, targetType);
if (converter != null) {
return converter;
}
}
// Check ConditionalConverters for a dynamic match
for (GenericConverter globalConverter : this.globalConverters) {
if (((ConditionalConverter) globalConverter).matches(sourceType, targetType)) {
return globalConverter;
}
}
return null;
}
得到转换器后调用ConversionUtils静态方法invokeConverter取得最终结果。
@Nullable
public static Object invokeConverter(GenericConverter converter, @Nullable Object source,
TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
try {
return converter.convert(source, sourceType, targetType);
}
catch (ConversionFailedException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ConversionFailedException(sourceType, targetType, source, ex);
}
}
默认情况下GenericConversionService自己不会注册任何转换器,需要我们调用addConverter()方法增加自定义的转换器,他的子类DefaultConversionService默认会注册一些常用的类型转换器供我们使用,所以我们平时不会直接使用GenericConversionService。
public class DefaultConversionService extends GenericConversionService {
@Nullable
private static volatile DefaultConversionService sharedInstance;
public DefaultConversionService() {
addDefaultConverters(this);
}
public static ConversionService getSharedInstance() {
DefaultConversionService cs = sharedInstance;
if (cs == null) {
synchronized (DefaultConversionService.class) {
cs = sharedInstance;
if (cs == null) {
cs = new DefaultConversionService();
sharedInstance = cs;
}
}
}
return cs;
}
public static void addDefaultConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {
addScalarConverters(converterRegistry);
addCollectionConverters(converterRegistry);
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ByteBufferConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToTimeZoneConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ZoneIdToTimeZoneConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ZonedDateTimeToCalendarConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToObjectConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new IdToEntityConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new FallbackObjectToStringConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToOptionalConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
}
public static void addCollectionConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {
ConversionService conversionService = (ConversionService) converterRegistry;
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ArrayToCollectionConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new CollectionToArrayConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ArrayToArrayConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new CollectionToCollectionConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new MapToMapConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ArrayToStringConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToArrayConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ArrayToObjectConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToArrayConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new CollectionToStringConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToCollectionConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new CollectionToObjectConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToCollectionConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StreamConverter(conversionService));
}
private static void addScalarConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {
converterRegistry.addConverterFactory(new NumberToNumberConverterFactory());
converterRegistry.addConverterFactory(new StringToNumberConverterFactory());
converterRegistry.addConverter(Number.class, String.class, new ObjectToStringConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToCharacterConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(Character.class, String.class, new ObjectToStringConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new NumberToCharacterConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverterFactory(new CharacterToNumberFactory());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToBooleanConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(Boolean.class, String.class, new ObjectToStringConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverterFactory(new StringToEnumConverterFactory());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new EnumToStringConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
converterRegistry.addConverterFactory(new IntegerToEnumConverterFactory());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new EnumToIntegerConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToLocaleConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(Locale.class, String.class, new ObjectToStringConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToCharsetConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(Charset.class, String.class, new ObjectToStringConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToCurrencyConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(Currency.class, String.class, new ObjectToStringConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToPropertiesConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new PropertiesToStringConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToUUIDConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(UUID.class, String.class, new ObjectToStringConverter());
}
}
Spring还提供了一个FactoryBean用来配置ConversionService。
org.springframework.context.support.ConversionServiceFactoryBean内部默认使用DefaultConversionService,提供了一个 setConverters()方法来增加自定义转换器。
public class ConversionServiceFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<ConversionService>, InitializingBean {
@Nullable
private Set<?> converters;
@Nullable
private GenericConversionService conversionService;
public void setConverters(Set<?> converters) {
this.converters = converters;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
this.conversionService = createConversionService();
ConversionServiceFactory.registerConverters(this.converters, this.conversionService);
}
protected GenericConversionService createConversionService() {
return new DefaultConversionService();
}
@Override
@Nullable
public ConversionService getObject() {
return this.conversionService;
}
@Override
public Class<? extends ConversionService> getObjectType() {
return GenericConversionService.class;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
public abstract class ConversionServiceFactory {
public static void registerConverters(@Nullable Set<?> converters, ConverterRegistry registry) {
if (converters != null) {
for (Object converter : converters) {
if (converter instanceof GenericConverter) {
registry.addConverter((GenericConverter) converter);
}
else if (converter instanceof Converter<?, ?>) {
registry.addConverter((Converter<?, ?>) converter);
}
else if (converter instanceof ConverterFactory<?, ?>) {
registry.addConverterFactory((ConverterFactory<?, ?>) converter);
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Each converter object must implement one of the " +
"Converter, ConverterFactory, or GenericConverter interfaces");
}
}
}
}
}
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

