14.5 带外部状态的解决方案
Sunny软件公司开发人员通过对围棋棋子进行进一步分析,发现虽然黑色棋子和白色棋子可以共享,但是它们将显示在棋盘的不同位置,如何让相同的黑子或者白子能够多次重复显示且位于一个棋盘的不同地方?解决方法就是将棋子的位置定义为棋子的一个外部状态,在需要时再进行设置。因此,我们在图14-4中增加了一个新的类Coordinates(坐标类),用于存储每一个棋子的位置,修改之后的结构图如图14-5所示:
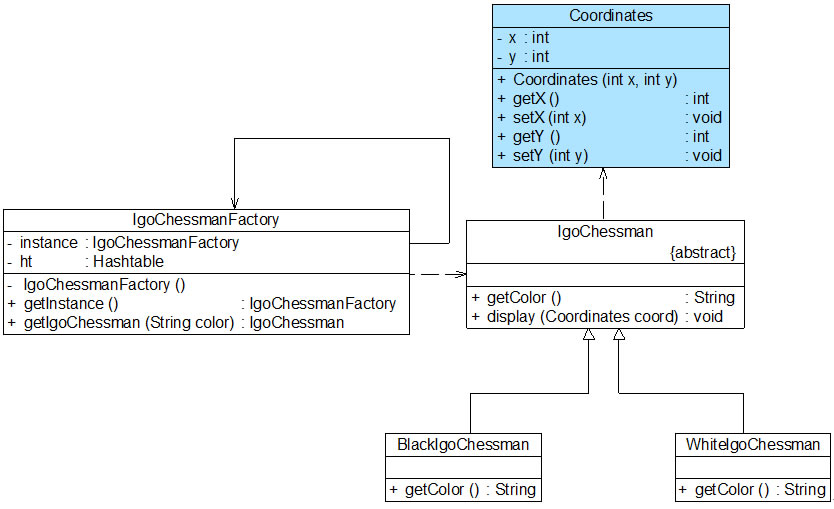
图14-5 引入外部状态之后的围棋棋子结构图
在图14-5中,除了增加一个坐标类Coordinates以外,抽象享元类IgoChessman中的display()方法也将对应增加一个Coordinates类型的参数,用于在显示棋子时指定其坐标,Coordinates类和修改之后的IgoChessman类的代码如下所示:
//坐标类:外部状态类
class Coordinates {
private int x;
private int y;
public Coordinates(int x,int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int getX() {
return this.x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getY() {
return this.y;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
}
//围棋棋子类:抽象享元类
abstract class IgoChessman {
public abstract String getColor();
public void display(Coordinates coord){
System.out.println("棋子颜色:" + this.getColor() + ",棋子位置:" + coord.getX() + "," + coord.getY() );
}
}
客户端测试代码修改如下:
class Client {
public static void main(String args[]) {
IgoChessman black1,black2,black3,white1,white2;
IgoChessmanFactory factory;
//获取享元工厂对象
factory = IgoChessmanFactory.getInstance();
//通过享元工厂获取三颗黑子
black1 = factory.getIgoChessman("b");
black2 = factory.getIgoChessman("b");
black3 = factory.getIgoChessman("b");
System.out.println("判断两颗黑子是否相同:" + (black1==black2));
//通过享元工厂获取两颗白子
white1 = factory.getIgoChessman("w");
white2 = factory.getIgoChessman("w");
System.out.println("判断两颗白子是否相同:" + (white1==white2));
//显示棋子,同时设置棋子的坐标位置
black1.display(new Coordinates(1,2));
black2.display(new Coordinates(3,4));
black3.display(new Coordinates(1,3));
white1.display(new Coordinates(2,5));
white2.display(new Coordinates(2,4));
}
}
编译并运行程序,输出结果如下:
判断两颗黑子是否相同:true
判断两颗白子是否相同:true
棋子颜色:黑色,棋子位置:1,2
棋子颜色:黑色,棋子位置:3,4
棋子颜色:黑色,棋子位置:1,3
棋子颜色:白色,棋子位置:2,5
棋子颜色:白色,棋子位置:2,4
从输出结果可以看到,在每次调用display()方法时,都设置了不同的外部状态——坐标值,因此相同的棋子对象虽然具有相同的颜色,但是它们的坐标值不同,将显示在棋盘的不同位置。
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

