UnpooledHeapByteBuf
引用计数缓冲区的子类,非池化的堆缓冲区,也就是内存在java堆里,内部其实就是分配了一个数组。这里还有个字节序的概念,也就是说字节是放在地址的高低位的区别。简单的说下,主要分两种,一种是小端字节序,也就是一般内存存放数据的,高字节放在高位地址,低地址放低位地址,而大端刚好是相反,一般用于网络通信获取的字节数据。比如16位数据是0xf123放在字长为2个字节的地址里,如果小端就是高位放f1低位放23,如果是大端就是高位放23低位放f1 。好像挺麻烦的,不就是个存放么,为什么不统一呢,这个貌似是历史遗留原因。
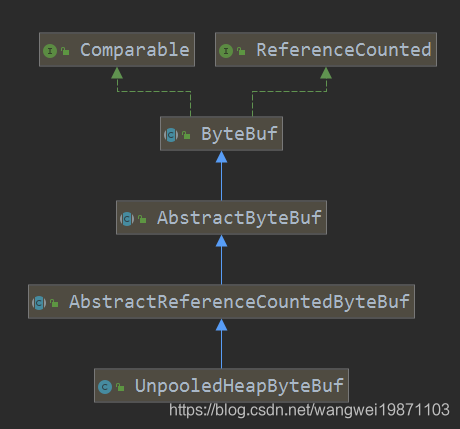
我们再来看看他的继承情况:
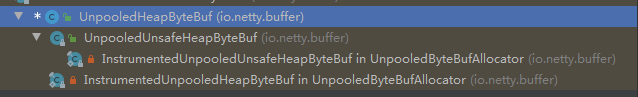
主要属性
可以看到,内部是一个数组,然后包装成ByteBuffer 。
private final ByteBufAllocator alloc;//缓冲区分配器
byte[] array;//内部是字节数组
private ByteBuffer tmpNioBuf;//用ByteBuffer来包装array数组
构造方法
可以看到,这个构造方法就是会创建一个initialCapacity大小的数组。
public UnpooledHeapByteBuf(ByteBufAllocator alloc, int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
super(maxCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > maxCapacity) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format(
"initialCapacity(%d) > maxCapacity(%d)", initialCapacity, maxCapacity));
}
this.alloc = checkNotNull(alloc, "alloc");
setArray(allocateArray(initialCapacity));
setIndex(0, 0);
}
//申请字节数组空间
protected byte[] allocateArray(int initialCapacity) {
return new byte[initialCapacity];
}
而这个方法是直接设置数组。
protected UnpooledHeapByteBuf(ByteBufAllocator alloc, byte[] initialArray, int maxCapacity) {
super(maxCapacity);
checkNotNull(alloc, "alloc");
checkNotNull(initialArray, "initialArray");
if (initialArray.length > maxCapacity) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format(
"initialCapacity(%d) > maxCapacity(%d)", initialArray.length, maxCapacity));
}
this.alloc = alloc;
setArray(initialArray);
setIndex(0, initialArray.length);
}
//设置数组
private void setArray(byte[] initialArray) {
array = initialArray;
tmpNioBuf = null;
}
字节序
从网络里面获取的字节系默认是大端的。
//大端字节序
@Override
public ByteOrder order() {
return ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN;
}
比如以int的类型去读取数组:
@Override
public int getInt(int index) {
ensureAccessible();
return _getInt(index);
}
@Override
protected int _getInt(int index) {
return HeapByteBufUtil.getInt(array, index);
}
至于字节序怎么转换的,有个辅助类HeapByteBufUtil,里面默认是大端的,但是也可以用小端的方法,后面是LE结尾的,比如下面的,用int类型来取数据,默认大端取。
//大端取 低位地址取出来的方法高位
static int getInt(byte[] memory, int index) {
return (memory[index] & 0xff) << 24 |
(memory[index + 1] & 0xff) << 16 |
(memory[index + 2] & 0xff) << 8 |
memory[index + 3] & 0xff;
}
//小端取 低位地址取出来的放低位
static int getIntLE(byte[] memory, int index) {
return memory[index] & 0xff |
(memory[index + 1] & 0xff) << 8 |
(memory[index + 2] & 0xff) << 16 |
(memory[index + 3] & 0xff) << 24;
}
//大端设置 高位数据放低位
static void setInt(byte[] memory, int index, int value) {
memory[index] = (byte) (value >>> 24);
memory[index + 1] = (byte) (value >>> 16);
memory[index + 2] = (byte) (value >>> 8);
memory[index + 3] = (byte) value;
}
//小端设置 低位数据放低位
static void setIntLE(byte[] memory, int index, int value) {
memory[index] = (byte) value;
memory[index + 1] = (byte) (value >>> 8);
memory[index + 2] = (byte) (value >>> 16);
memory[index + 3] = (byte) (value >>> 24);
}
internalNioBuffer
这个就是将数据包装成ByteBuffer。
private ByteBuffer internalNioBuffer() {
ByteBuffer tmpNioBuf = this.tmpNioBuf;
if (tmpNioBuf == null) {
this.tmpNioBuf = tmpNioBuf = ByteBuffer.wrap(array);
}
return tmpNioBuf;
}
capacity
可以看到,扩容的话可能会做数组的拷贝。
@Override
public ByteBuf capacity(int newCapacity) {
checkNewCapacity(newCapacity);
byte[] oldArray = array;
int oldCapacity = oldArray.length;
if (newCapacity == oldCapacity) {
return this;
}
int bytesToCopy;
if (newCapacity > oldCapacity) {//增加容量
bytesToCopy = oldCapacity;
} else {//减少容量
trimIndicesToCapacity(newCapacity);
bytesToCopy = newCapacity;
}
byte[] newArray = allocateArray(newCapacity);
System.arraycopy(oldArray, 0, newArray, 0, bytesToCopy);//数组拷贝
setArray(newArray);
freeArray(oldArray);//空方法,gc去释放
return this;
}
其他方法都比较好理解就不多说了,只要知道这个缓冲区内部是数组,由java虚拟机来管理内存,默认存取都是大端字节序。
UnpooledUnsafeHeapByteBuf
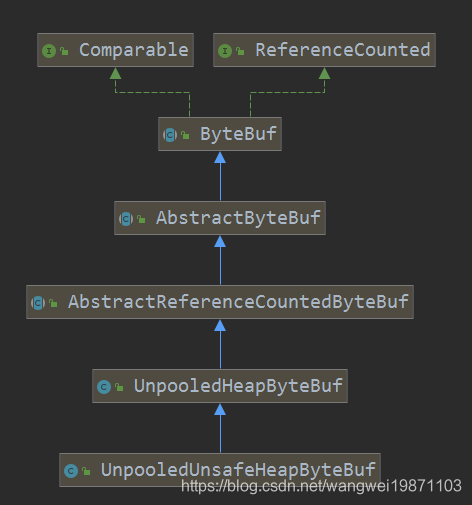
这个继承了上面的就比上面的多了一个Unsafe,也就是说好多操作应该是unsafe类做的。
allocateArray
比如这个分配内存的方法,用到了PlatformDependent平台相关的类,最后是用反射做的,因为unsafe只能java内部自己用,外面要用可以用反射。
@Override
protected byte[] allocateArray(int initialCapacity) {
return PlatformDependent.allocateUninitializedArray(initialCapacity);
}
public static byte[] allocateUninitializedArray(int size) {
return UNINITIALIZED_ARRAY_ALLOCATION_THRESHOLD < 0 || UNINITIALIZED_ARRAY_ALLOCATION_THRESHOLD > size ?
new byte[size] : PlatformDependent0.allocateUninitializedArray(size);
}
static byte[] allocateUninitializedArray(int size) {
try {
return (byte[]) ALLOCATE_ARRAY_METHOD.invoke(INTERNAL_UNSAFE, byte.class, size);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new Error(e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
UnsafeByteBufUtil
当然他也是大端字节序,用的是这个工具类。
@Override
public int getInt(int index) {
checkIndex(index, 4);
return _getInt(index);
}
@Override
protected int _getInt(int index) {
return UnsafeByteBufUtil.getInt(array, index);
}
内部也是PlatformDependent类。
static int getInt(byte[] array, int index) {
if (UNALIGNED) {
int v = PlatformDependent.getInt(array, index);
return BIG_ENDIAN_NATIVE_ORDER ? v : Integer.reverseBytes(v);
}
return PlatformDependent.getByte(array, index) << 24 |
(PlatformDependent.getByte(array, index + 1) & 0xff) << 16 |
(PlatformDependent.getByte(array, index + 2) & 0xff) << 8 |
PlatformDependent.getByte(array, index + 3) & 0xff;
}
static int getIntLE(byte[] array, int index) {
if (UNALIGNED) {
int v = PlatformDependent.getInt(array, index);
return BIG_ENDIAN_NATIVE_ORDER ? Integer.reverseBytes(v) : v;
}
return PlatformDependent.getByte(array, index) & 0xff |
(PlatformDependent.getByte(array, index + 1) & 0xff) << 8 |
(PlatformDependent.getByte(array, index + 2) & 0xff) << 16 |
PlatformDependent.getByte(array, index + 3) << 24;
}
底层也是调用unsafe的方法,UNSAFE就是unsafe,只是通过反射来获取的:
static int getInt(byte[] data, int index) {
return UNSAFE.getInt(data, BYTE_ARRAY_BASE_OFFSET + index);
}
InstrumentedUnpooledHeapByteBuf
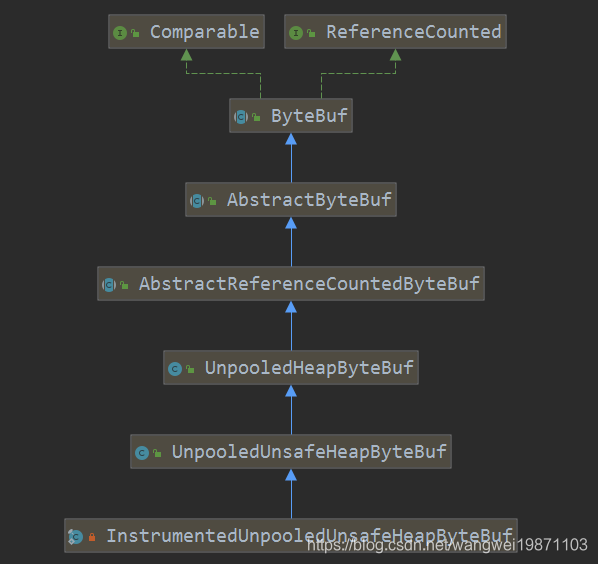
这个前面又加了形容词,其实就是记录了申请和释放的时候记录字节数,InstrumentedUnpooledUnsafeHeapByteBuf也是类似的,就不多说了:
//仪表化的无池化的堆缓冲区
private static final class InstrumentedUnpooledHeapByteBuf extends UnpooledHeapByteBuf {
InstrumentedUnpooledHeapByteBuf(UnpooledByteBufAllocator alloc, int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
super(alloc, initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
}
@Override
protected byte[] allocateArray(int initialCapacity) {
byte[] bytes = super.allocateArray(initialCapacity);//申请了字节数组
((UnpooledByteBufAllocator) alloc()).incrementHeap(bytes.length);//增加堆字节
return bytes;
}
//实现了释放内部字节数组
@Override
protected void freeArray(byte[] array) {
int length = array.length;
super.freeArray(array);
((UnpooledByteBufAllocator) alloc()).decrementHeap(length);//减少堆字节
}
}
总结
这次我们讲了堆内缓冲区,讲了字节序,讲了是否用unsafe方法操作的,还有一些子类。这个还是比较简单的,后面一篇我们讲堆外的就有点复杂啦。不过可以先看看我前面的一篇文章,有个预备知识比较好。
好了,今天就到这里了,希望对学习理解有帮助,大神看见勿喷,仅为自己的学习理解,能力有限,请多包涵。
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

