可扩展,分布式系统的一个基本要求。业务系统在从单体架构向集群架构演进的过程中,需要通过负载均衡技术,将流量尽可能均摊到集群中的每台机器上,以此克服单台机器硬件资源的限制,做到横向扩展。
Apache Dubbo就是一款高性能、轻量级的开源 Java RPC 框架,提供了以下核心能力:
- 面向接口的远程方法调用;
- 可靠、智能的容错和负载均衡;
- 服务自动注册和发现能力。
从本系列开始,我将对阿里巴巴开源的这款分布式RPC框架进行深入分析,具体来说,我会:
- 首先,我会从整体到局部的方式,介绍Dubbo的整体架构、核心知识点;
- 接着,我会自底向上剖析 Dubbo 源码,深入分析 Dubbo 的工作原理及核心实现;
- 在此期间,我会实现一个RPC框架的demo,帮助大家更好的理解。
Apache Dubbo 目前刚刚发布了3.0 Preview版本,还没有被业界公司运用,所以,本系列我基于Dubbo 2.7.7 版本对其源码进行分析。RPC 框架的核心原理和设计都是相通的,阅读过 Dubbo 2.X源码之后,你再去阅读3.X版本或其他 RPC 框架的代码,就是触类旁通而已。
一、整体架构
我们先来看看Dubbo的基本架构:
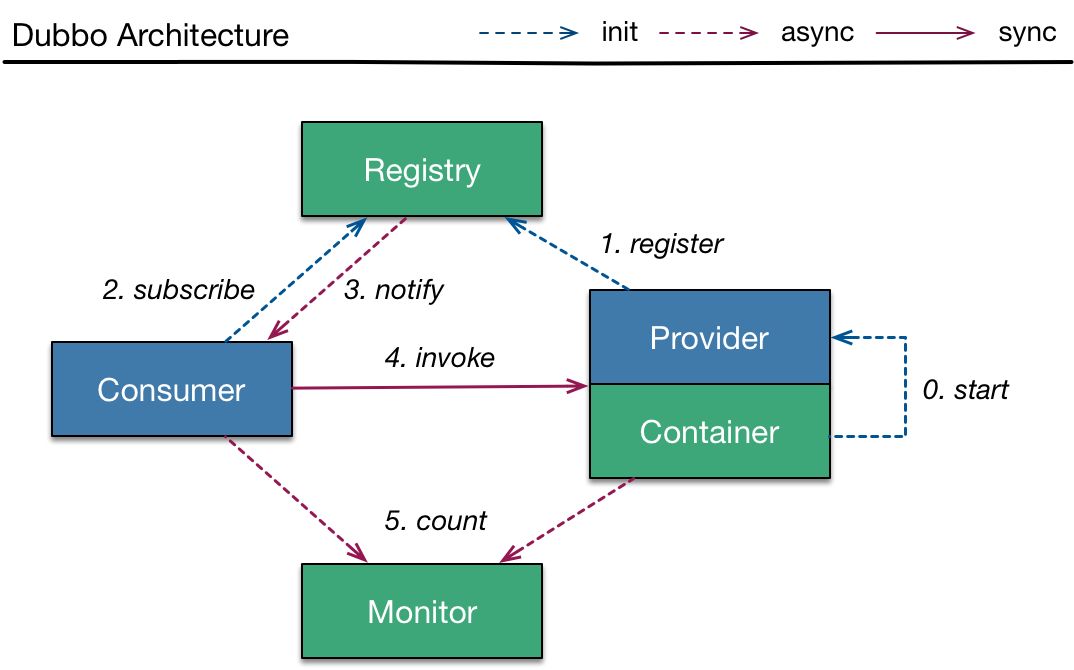
- Registry:注册中心。 负责服务注册与查找,服务提供者 Provider 和服务消费者 Consumer 只在启动时与注册中心交互。注册中心通过长连接感知 Provider 的存在,当 Provider 宕机时,注册中心会立即推送相关事件通知 Consumer;
- Provider:服务提供者。 启动时,会向 Registry 进行注册,将自己的服务地址和配置信息封装成 URL 添加到 ZooKeeper 中;
- Consumer:服务消费者。 启动时,会向 Registry 进行订阅操作。订阅操作会从注册中心获取 Provider 注册的 URL,并在注册中心中添加相应的监听器。获取到 Provider URL 之后,Consumer 会根据负载均衡算法从多个 Provider 中选择一个并与其建立连接,最后发起对 Provider 的 RPC 调用。 如果 Provider URL 发生变更,Consumer 将会通过之前订阅过程中在注册中心添加的监听器,获取到最新的 Provider URL 信息,进行相应的调整,比如断开与宕机 Provider 的连接,并与新的 Provider 建立连接。Consumer 与 Provider 建立的是长连接,且 Consumer 会缓存 Provider 信息,所以一旦连接建立,即使注册中心宕机,也不会影响已运行的 Provider 和 Consumer;
- Monitor:监控中心。 用于统计服务的调用次数和调用时间。Provider 和 Consumer 在运行过程中,会在内存中统计调用次数和调用时间,每分钟发送一次统计数据到监控中心。监控中心并不是必要角色,宕机只会丢失监控数据而已。
1.1 连通性
- 注册中心负责服务地址的注册与查找,相当于目录服务,服务提供者和消费者只在启动时与注册中心交互,注册中心不转发请求,压力较小;
- 监控中心负责统计各服务调用次数,调用时间等,统计先在内存汇总后每分钟一次发送到监控中心服务器,并以报表展示;
- 服务提供者向注册中心注册其提供的服务,并汇报调用时间到监控中心,此时间不包含网络开销;
- 服务消费者向注册中心获取服务提供者地址列表,并根据负载算法直接调用提供者,同时汇报调用时间到监控中心,此时间包含网络开销;
- 注册中心,服务提供者,服务消费者三者之间均为 长连接 ,监控中心除外;
- 注册中心通过长连接感知服务提供者的存在,服务提供者宕机,注册中心将立即推送事件通知消费者;
- 注册中心和监控中心全部宕机,不影响已运行的提供者和消费者,消费者在本地缓存了提供者列表;
- 注册中心和监控中心都是可选的,服务消费者可以直连服务提供者。
1.2 高可用
- 监控中心宕掉不影响使用,只是丢失部分采样数据;
- 注册中心对等集群,任意一台宕掉后,将自动切换到另一台;
- 注册中心全部宕掉后,服务提供者和服务消费者仍能通过本地缓存通讯;
- 服务提供者无状态,任意一台宕掉后,不影响使用;
- 服务提供者全部宕掉后,服务消费者应用将无法使用,并无限次重连等待服务提供者恢复。
1.3 可扩展
- 注册中心为对等集群,可动态增加机器部署实例,所有客户端将自动发现新的注册中心;
- 服务提供者无状态,可动态增加机器部署实例,注册中心将推送新的服务提供者信息给消费者。
关于Apache Dubbo的整体架构我不作其它赘述了,因为本专栏并不是讲解Dubbo的入门使用,关于这方面的内容,建议读者直接参考Apache Dubbo的官方文档:https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docsv2.7/user/preface/architecture/。
二、源码环境
本节,我先搭建好Dubbo的源码环境,为后续源码阅读作铺垫。
首先,clone代码并切换到2.7.7分支:
git clone https://github.com/apache/dubbo.git
git checkout -b dubbo-2.7.7 dubbo-2.7.7
接着,执行Maven命令进行编译:
mvn clean -Dmaven.test.skip=true install
然后,执行下面的命令转换成 IDEA 项目:
mvn idea:idea
最后,使用Intellij Idea导入工程:
2.1 模块说明
我对上述Dubbo源码工程的几个核心模块进行说明:
-
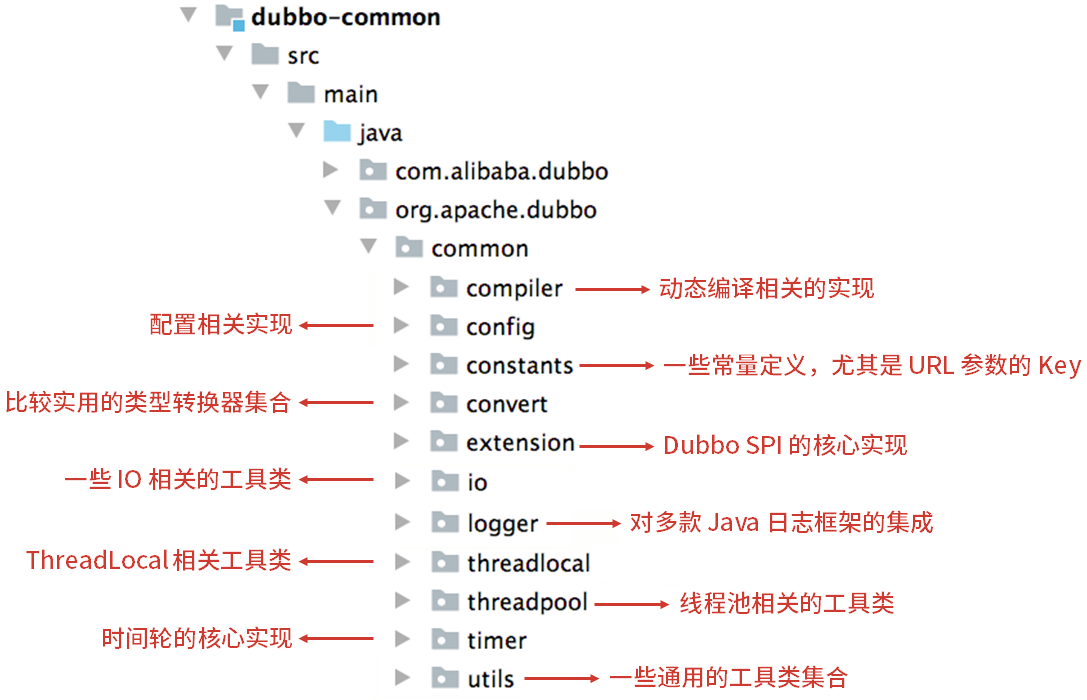
dubbo-common: 公共模块。包含很多工具类以及公共逻辑,例如Dubbo SPI 实现、时间轮、动态编译器等;
-
dubbo-remoting: 远程通信模块。其中的子模块依赖各种开源组件实现远程通信。在 dubbo-remoting-api 子模块中定义该模块的抽象概念,在其他子模块中依赖其他开源组件进行实现,例如dubbo-remoting-netty 子模块依赖 Netty 实现远程通信,dubbo-remoting-zookeeper 通过 Apache Curator 实现与 ZooKeeper 集群的交互;

-
dubbo-rpc: 远程调用协议模块。其中抽象了各种协议,依赖于 dubbo-remoting 模块的远程调用功能。dubbo-rpc-api 子模块是核心抽象,其他子模块是针对具体协议的实现,例如,dubbo-rpc-dubbo 子模块是对 Dubbo 协议的实现,依赖了 dubbo-remoting-netty 等 dubbo-remoting 子模块。 dubbo-rpc 模块的实现中只包含一对一的调用,不关心集群的相关内容;

-
dubbo-cluster: 集群管理模块。提供了负载均衡、容错、路由等一系列集群相关的功能,最终的目的是将多个 Provider 伪装为一个 Provider,这样 Consumer 就可以像调用一个 Provider 那样调用 Provider 集群了;
-
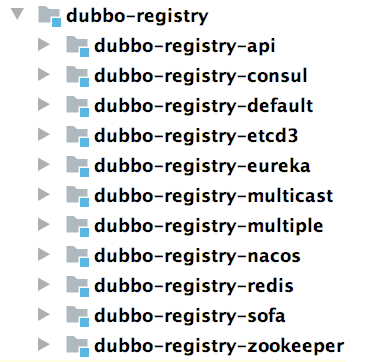
dubbo-registry: 注册中心模块。提供了注册中心的能力。其中, dubbo-registry-api 子模块是顶层抽象,其他子模块是针对具体开源注册中心组件的具体实现,例如,dubbo-registry-zookeeper 子模块是 Dubbo 接入 ZooKeeper 的具体实现;
-
dubbo-monitor : 监控模块。用于统计服务调用次数、调用时长以及实现调用链跟踪的服务;
-
dubbo-config: 配置模块。dubbo-config-api 子模块负责处理 API 方式使用时的相关配置,dubbo-config-spring 子模块负责处理与 Spring 集成使用时的相关配置方式。有了 dubbo-config 模块,用户只需要了解 Dubbo 配置的规则即可,无须了解 Dubbo 内部的细节;

-
dubbo-metadata: 元数据模块;

-
dubbo-configcenter: 配置中心模块。负责从配置中心动态获取配置,以及服务治理规则的存储与通知,提供了多个子模块用来接入多种开源配置中心;

2.2 源码示例
Dubbo 源码中的dubbo-demo模块,有三个Dubbo 示例项目:
- 使用Spring XML 配置的 Demo 示例;
- 使用 Spring 注解配置的 Demo 示例;
- 使用 非Spring 项目 的 Demo 示例。
接着来,我结合这三个示例,介绍 Dubbo 的基本使用。同时,将这三个项目作为后续分析和Debug Dubbo 源码的入口。
上述的
dubbo-demo-interface定义了服务提供方的接口存根。
dubbo-demo-xml
dubbo-demo-xml工程展示了如何通过Spring XML配置来使用Dubbo。
服务提供方
我们先来看服务提供方的使用,示例定义在子模块dubbo-demo-xml-provider中:
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 启动一个Spring容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring/dubbo-provider.xml");
context.start();
System.in.read();
}
}
Spring容器启动后,会去classpath加载dubbo配置文件dubbo-provider.xml:
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<dubbo:application metadata-type="remote" name="demo-provider"/>
<!-- 注册中心配置 -->
<dubbo:metadata-report address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"/>
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"/>
<!-- 请求协议配置 -->
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo"/>
<!-- 服务提供方定义 -->
<bean id="demoService" class="org.apache.dubbo.demo.provider.DemoServiceImpl"/>
<dubbo:service interface="org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService" ref="demoService"/>
</beans>
上面定义了一个DemoService服务提供方,并注入了Spring容器:
public interface DemoService {
String sayHello(String name);
}
@Service // 注意,这个是Dubbo的注解:org.apache.dubbo.config.annotation.Service
public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DemoServiceImpl.class);
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
logger.info("Hello " + name + ", request from consumer: " + RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteAddress());
return "Hello " + name + ", response from provider: " + RpcContext.getContext().getLocalAddress();
}
}
服务消费方
再来看服务消费方的使用,示例定义在子模块dubbo-demo-xml-consumer中:
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 启动一个Spring容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring/dubbo-consumer.xml");
context.start();
// RPC调用
DemoService demoService = context.getBean("demoService", DemoService.class);
CompletableFuture<String> hello = demoService.sayHelloAsync("world");
System.out.println("result: " + hello.get());
}
}
Spring容器启动后,会去classpath加载dubbo配置文件dubbo-consumer.xml:
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<dubbo:application name="demo-consumer"/>
<!-- 注册中心配置 -->
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"/>
<!-- 服务调用引用 -->
<dubbo:reference id="demoService" check="false" interface="org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService"/>
</beans>
dubbo-demo-annotation
dubbo-demo-annotation工程展示了如何通过Spring 注解来使用Dubbo。
服务提供方
我们先来看服务提供方的使用,示例定义在子模块dubbo-demo-annotation-provider中:
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 启动一个Spring容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ProviderConfiguration.class);
context.start();
System.in.read();
}
@Configuration
@EnableDubbo(scanBasePackages = "org.apache.dubbo.demo.provider")
@PropertySource("classpath:/spring/dubbo-provider.properties")
static class ProviderConfiguration {
@Bean
public RegistryConfig registryConfig() {
RegistryConfig registryConfig = new RegistryConfig();
registryConfig.setAddress("zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181");
return registryConfig;
}
}
}
上述服务提供方应用启动后,会去扫描org.apache.dubbo.demo.provider包下的所有服务提供方,注入到容器中:
@Service
public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DemoServiceImpl.class);
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
logger.info("Hello " + name + ", request from consumer: " + RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteAddress());
return "Hello " + name + ", response from provider: " + RpcContext.getContext().getLocalAddress();
}
}
dubbo-provider.properties定义了Dubbo的服务提供方配置:
dubbo.application.name=dubbo-demo-annotation-provider
dubbo.protocol.name=dubbo
dubbo.protocol.port=20880
服务消费方
再来看服务消费方的使用,示例定义在子模块dubbo-demo-annotation-consumer中:
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 启动一个Spring容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConsumerConfiguration.class);
context.start();
// 发起RPC调用
DemoService service = context.getBean("demoServiceComponent", DemoServiceComponent.class);
String hello = service.sayHello("world");
System.out.println("result :" + hello);
}
@Configuration
@EnableDubbo(scanBasePackages = "org.apache.dubbo.demo.consumer.comp")
@PropertySource("classpath:/spring/dubbo-consumer.properties")
@ComponentScan(value = {"org.apache.dubbo.demo.consumer.comp"})
static class ConsumerConfiguration {
}
}
上述服务消费方应用启动后,会去扫描org.apache.dubbo.demo.consumer.comp包下的所有服务消费方,注入到容器中:
@Component("demoServiceComponent")
public class DemoServiceComponent implements DemoService {
@Reference
private DemoService demoService;
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
return demoService.sayHello(name);
}
}
dubbo-consumer.properties定义了Dubbo的服务消费方配置:
dubbo.application.name=dubbo-demo-annotation-consumer
dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
dubbo-demo-api
dubbo-demo-api 工程展示了如何在那些未使用Spring框架的应用中,通过原生API的方式使用Dubbo。
服务提供方
我们先来看服务提供方的使用,示例定义在子模块dubbo-demo-api-provider中:
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
startWithBootstrap();
}
private static void startWithBootstrap() {
ServiceConfig<DemoServiceImpl> service = new ServiceConfig<>();
service.setInterface(DemoService.class);
service.setRef(new DemoServiceImpl());
DubboBootstrap bootstrap = DubboBootstrap.getInstance();
bootstrap.application(new ApplicationConfig("dubbo-demo-api-provider"))
.registry(new RegistryConfig("zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"))
.service(service)
.start()
.await();
}
}
public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DemoServiceImpl.class);
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
logger.info("Hello " + name + ", request from consumer: " + RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteAddress());
return "Hello " + name + ", response from provider: " + RpcContext.getContext().getLocalAddress();
}
}
服务消费方
再来看服务消费方的使用,示例定义在子模块dubbo-demo-api-consumer中:
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
runWithBootstrap();
}
private static void runWithBootstrap() {
ReferenceConfig<DemoService> reference = new ReferenceConfig<>();
reference.setInterface(DemoService.class);
reference.setGeneric("true");
DubboBootstrap bootstrap = DubboBootstrap.getInstance();
bootstrap.application(new ApplicationConfig("dubbo-demo-api-consumer"))
.registry(new RegistryConfig("zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"))
.reference(reference)
.start();
// 发起RPC调用
DemoService demoService = ReferenceConfigCache.getCache().get(reference);
String message = demoService.sayHello("dubbo");
System.out.println(message);
// 泛型调用
GenericService genericService = (GenericService) demoService;
Object genericInvokeResult = genericService.$invoke("sayHello", new String[] { String.class.getName() },
new Object[] { "dubbo generic invoke" });
System.out.println(genericInvokeResult);
}
}
三、总结
本章,我对Apache Dubbo的整体逻辑架构进行了简单分析,并搭建完了Dubbo源码研发环境,介绍了Dubbo的几种不同的使用方式。从下一章开始,我将对Dubbo的源码进行分析。
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

