经过上一章的讲解,各位应该对Eureka Server启动的整体流程有了一个初步的了解。本章,我们来看下整体流程中的配置加载部分。在整个启动流程中,与配置相关的主要有四个类:
- ConfigurationManager: 配置管理器
- EurekaServerConfig: Eureka-Server注册中心配置
- EurekaInstanceConfig: Eureka应用实例配置
- EurekaClientConfig: Eureka-Client客户端配置
注意,这里一定要理解一个概念:对于一个Eureka-Server来说,它既是一个Server,又是一个Eureka-Client,还是一个EurekaInstance。
一、ConfigurationManager
ConfigurationManager,是一个配置管理器,管理着当前Eureka应用实例的所有配置:
protected void initEurekaEnvironment() throws Exception {
logger.info("Setting the eureka configuration..");
// 使用ConfigurationManager获取配置
String dataCenter = ConfigurationManager.getConfigInstance().getString(EUREKA_DATACENTER);
if (dataCenter == null) {
logger.info("Eureka data center value eureka.datacenter is not set, defaulting to default");
ConfigurationManager.getConfigInstance().setProperty(ARCHAIUS_DEPLOYMENT_DATACENTER, DEFAULT);
} else {
ConfigurationManager.getConfigInstance().setProperty(ARCHAIUS_DEPLOYMENT_DATACENTER, dataCenter);
}
String environment = ConfigurationManager.getConfigInstance().getString(EUREKA_ENVIRONMENT);
if (environment == null) {
ConfigurationManager.getConfigInstance().setProperty(ARCHAIUS_DEPLOYMENT_ENVIRONMENT, TEST);
logger.info("Eureka environment value eureka.environment is not set, defaulting to test");
}
}
ConfigurationManager是一个单例类,用了经典的 double check + volatile 模式。ConfigurationManager.getConfigInstance()方法,其实就是初始化ConfigurationManager的实例:
public class ConfigurationManager {
static volatile AbstractConfiguration instance = null;
//...
// 双重锁检查实现单例模式
public static AbstractConfiguration getConfigInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (ConfigurationManager.class) {
if (instance == null) {
instance = getConfigInstance(Boolean.getBoolean(DynamicPropertyFactory.DISABLE_DEFAULT_CONFIG));
}
}
}
return instance;
}
}
// ConfigurationManager#getConfigInstance
private static AbstractConfiguration getConfigInstance(boolean defaultConfigDisabled) {
if (instance == null && !defaultConfigDisabled) {
instance = createDefaultConfigInstance();
registerConfigBean();
}
return instance;
}
// ConfigurationManager#createDefaultConfigInstance
private static AbstractConfiguration createDefaultConfigInstance() {
ConcurrentCompositeConfiguration config = new ConcurrentCompositeConfiguration();
//...
return config;
}
二、EurekaServerConfig
EurekaBootStrap在启动过程中,会创建Eureka-Server需要的配置——EurekaServerConfig:
protected void initEurekaServerContext() throws Exception {
EurekaServerConfig eurekaServerConfig = new DefaultEurekaServerConfig();
//...
}
EurekaServerConfig是一个接口,定义了各种获取配置的GET方法,它对应的具体实现是DefaultEurekaServerConfig:
2.1 核心方法
我这里列举下EurekaServerConfig的核心方法:
// --------------------------- 请求认证相关 ---------------------------
// 打印访问的客户端名和版本号,配合 Netflix Servo 实现监控信息采集
shouldLogIdentityHeaders();
// --------------------------- 请求限流相关 ---------------------------
// 是否开启请求限流
isRateLimiterEnabled();
// 是否对标准客户端限流。标准客户端通过请求头( header )的 "DiscoveryIdentity-Name" 来判断,是否在标准客户端名集合里
isRateLimiterThrottleStandardClients();
// 标准客户端名集合。默认包含"DefaultClient" 和 "DefaultServer"
getRateLimiterPrivilegedClients();
// 速率限制的 burst size ,使用令牌桶算法
getRateLimiterBurstSize();
// 增量拉取注册信息的速率限制
getRateLimiterRegistryFetchAverageRate();
// 全量拉取注册信息的速率限制
getRateLimiterFullFetchAverageRate();
// --------------------------- 获取注册信息请求相关 ---------------------------
// 是否开启只读请求响应缓存。
// 响应缓存 ( ResponseCache ) 机制目前使用两层缓存策略。优先读取只读缓存,读取不到后读取固定过期的读写缓存
shouldUseReadOnlyResponseCache();
// 只读缓存更新频率,单位:毫秒。
// 只读缓存定时更新任务只更新读取过请求 (com.netflix.eureka.registry.Key),因此虽然永不过期,也会存在读取不到的情况
getResponseCacheUpdateIntervalMs();
// 读写缓存写入后过期时间,单位:秒
getResponseCacheAutoExpirationInSeconds();
// 租约变更记录过期时长,单位:毫秒。默认值:3 * 60 * 1000 毫秒
getRetentionTimeInMSInDeltaQueue();
// 移除队列里过期的租约变更记录的定时任务执行频率,单位:毫秒。默认值:30 * 1000 毫秒
DeltaRetentionTimerIntervalInMs();
// --------------------------- 自我保护机制相关 ---------------------------
// 是否开启自我保护模式
shouldEnableSelfPreservation();
// 心跳丢失比例,超过该比例后开启自我保护模式
getRenewalPercentThreshold();
// 自我保护模式比例更新定时任务的执行频率,单位:毫秒
getRenewalThresholdUpdateIntervalMs();
// --------------------------- 注册的应用实例的租约过期相关 ---------------------------
// 租约过期定时任务执行频率,单位:毫秒
getEvictionIntervalTimerInMs();
// --------------------------- Eureka-Server远程节点( 非集群 )读取相关 ---------------------------
// Eureka-Server 启动时,从远程 Eureka-Server 读取失败重试次数
getRegistrySyncRetries();
// Eureka-Server 启动时,从远程 Eureka-Server 读取失败等待( sleep )间隔,单位:毫秒
getRegistrySyncRetryWaitMs();
// 是否禁用本地读取不到注册信息,从远程Eureka-Server读取
disableTransparentFallbackToOtherRegion();
// --------------------------- Eureka-Server 集群同步相关 ---------------------------
// 同步应用实例信息最大线程数
getMaxThreadsForPeerReplication();
// 待执行同步应用实例信息事件缓冲最大数量
getMaxElementsInPeerReplicationPool();
// 执行单个同步应用实例信息状态任务最大时间
getMaxTimeForReplication();
// 是否同步应用实例信息,当应用实例信息最后更新时间戳( lastDirtyTimestamp )发生改变
shouldSyncWhenTimestampDiffers();
// Eureka-Server启动时,从远程 Eureka-Server 读取不到注册信息时,多长时间不允许 Eureka-Client 访问
getWaitTimeInMsWhenSyncEmpty();
// Eureka-Server集群节点更新频率,单位:毫秒
getPeerEurekaNodesUpdateIntervalMs() ;
2.2 构造流程
DefaultEurekaServerConfig类默认会读取eureka-server.properties文件中的配置,如果包含环境配置(比如eureka-server-test.properties),则会读取并覆盖同名配置项:

DefaultEurekaServerConfig在构造时会进行初始化,其实就是去加载配置文件:
private static final String ARCHAIUS_DEPLOYMENT_ENVIRONMENT = "archaius.deployment.environment";
private static final String TEST = "test";
private static final String EUREKA_ENVIRONMENT = "eureka.environment";
// 配置文件对象
private static final DynamicPropertyFactory configInstance = com.netflix.config.DynamicPropertyFactory
.getInstance();
// 加载配置文件
private static final DynamicStringProperty EUREKA_PROPS_FILE = DynamicPropertyFactory
.getInstance().getStringProperty("eureka.server.props","eureka-server");
//...
public DefaultEurekaServerConfig() {
init();
}
// DefaultEurekaServerConfig#init
private void init() {
// 环境信息
String env = ConfigurationManager.getConfigInstance().getString(EUREKA_ENVIRONMENT, TEST);
ConfigurationManager.getConfigInstance().setProperty(ARCHAIUS_DEPLOYMENT_ENVIRONMENT, env);
// 配置文件名
String eurekaPropsFile = EUREKA_PROPS_FILE.get();
try {
// 加载配置并保存到内存中
ConfigurationManager.loadCascadedPropertiesFromResources(eurekaPropsFile);
} catch (IOException e) {
// ...
}
}
上述整个构造流程如下:
- 将
eureka-server.properties中的配置加载到一个Properties对象中,然后将Properties对象中的配置放到ConfigurationManager中去,此时ConfigurationManager就有了所有server配置; - DefaultEurekaServerConfig获取配置项的方法,都是硬编码配置项名称,从
DynamicPropertyFactory中获取配置项值,DynamicPropertyFactory是从ConfigurationManager那儿来的,所以也包含了所有配置项的值; - DynamicPropertyFactory在获取配置项值时,如果没有配置,就采用默认值。
上述代码的核心就是通过ConfigurationManager.loadCascadedPropertiesFromResources()加载配置文件到内存中,我这里省略掉了一些无关代码:
// ConfigurationManager#loadCascadedPropertiesFromResources
public static void loadCascadedPropertiesFromResources(String configName) throws IOException {
Properties props = loadCascadedProperties(configName);
//...
ConfigurationUtils.loadProperties(props, instance);
}
可以看到,其实是将配置读取到一个内部的Properties对象里,通过Properties去加载KV配置文件是一种非常常见的方式:
private static Properties loadCascadedProperties(String configName) throws IOException {
// eureka-server.properties
String defaultConfigFileName = configName + ".properties";
if (instance == null) {
instance = getConfigInstance();
}
ClassLoader loader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
URL url = loader.getResource(defaultConfigFileName);
if (url == null) {
throw new IOException("Cannot locate " + defaultConfigFileName + " as a classpath resource.");
}
// 加载到Properties对象中
Properties props = getPropertiesFromFile(url);
// 加载对应的环境配置,覆盖之前加载的同名属性配置
String environment = getDeploymentContext().getDeploymentEnvironment();
if (environment != null && environment.length() > 0) {
// 默认为eureka-server-test.properties
String envConfigFileName = configName + "-" + environment + ".properties";
url = loader.getResource(envConfigFileName);
if (url != null) {
Properties envProps = getPropertiesFromFile(url);
if (envProps != null) {
props.putAll(envProps);
}
}
}
return props;
}
三、EurekaInstanceConfig
EurekaInstanceConfig代表着当前Eureka应用实例的配置,例如应用名、应用端口等等,这里的应用指的是Application Consumer 和 Application Provider。
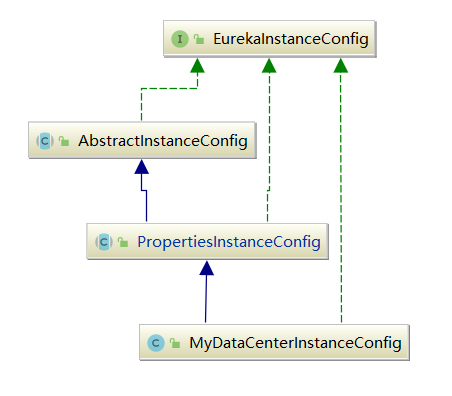
EurekaInstanceConfig也是一个接口,提供了各种获取应用实例配置的GET方法。它的具体实现类是MyDataCenterInstanceConfig:
3.1 核心方法
我这里列举下EurekaInstanceConfig的核心方法:
// 对象编号,需要保证在相同应用名下唯一
String getInstanceId();
// 应用名
String getAppname();
// 应用分组
String getAppGroupName();
// 应用实例是否一注册上就可以开始接收请求,默认false
boolean isInstanceEnabledOnit();
// 应用 http 端口
int getNonSecurePort();
// 应用 https 端口
int getSecurePort();
// 心跳(续约)频率,单位:秒;
// 应用不断按照该频率发送心跳给 Eureka-Server 以达到续约的作用
int getLeaseRenewalIntervalInSeconds();
// 租约过期时间,单位:秒
int getLeaseExpirationDurationInSeconds();
// 虚拟主机名。也可以叫做VIPAddress。
String getVirtualHostName();
// 虚拟安全主机名。也可以叫做 SecureVIPAddress
String getSecureVirtualHostName();
// 元数据( Metadata )集合
Map<String, String> getMetadataMap();
// IP 地址
String getIpAddress();
// 配置命名空间,默认使用eureka
String getNamespace();
3.2 构造流程
EurekaInstanceConfig的构造其实就是子类MyDataCenterInstanceConfig的构造,而MyDataCenterInstanceConfig又调用了父类PropertiesInstanceConfig的构造器:
public class MyDataCenterInstanceConfig extends PropertiesInstanceConfig implements EurekaInstanceConfig {
public MyDataCenterInstanceConfig() {
}
//...
}
PropertiesInstanceConfig会将eureka-client.properties文件中的配置加载到ConfigurationManager中去,然后基于EurekaInstanceConfig对外暴露的接口来进行配置项的读取,同时也提供了所有配置项的默认值:
public abstract class PropertiesInstanceConfig extends AbstractInstanceConfig implements EurekaInstanceConfig {
public PropertiesInstanceConfig(String namespace, DataCenterInfo info) {
super(info);
this.namespace = namespace.endsWith(".") ? namespace : namespace + ".";
appGrpNameFromEnv = ConfigurationManager.getConfigInstance()
.getString(FALLBACK_APP_GROUP_KEY, Values.UNKNOWN_APPLICATION);
// 这里会读取eureka-client.properties文件
this.configInstance = Archaius1Utils.initConfig(CommonConstants.CONFIG_FILE_NAME);
}
}
Archaius1Utils这个工具类内部真正执行了配置文件的读取:
public final class Archaius1Utils {
private static final String ARCHAIUS_DEPLOYMENT_ENVIRONMENT = "archaius.deployment.environment";
private static final String EUREKA_ENVIRONMENT = "eureka.environment";
public static DynamicPropertyFactory initConfig(String configName) {
// 配置文件对象
DynamicPropertyFactory configInstance = DynamicPropertyFactory.getInstance();
// 配置文件名
DynamicStringProperty EUREKA_PROPS_FILE = configInstance.getStringProperty("eureka.client.props", configName);
// 配置文件环境
String env = ConfigurationManager.getConfigInstance().getString(EUREKA_ENVIRONMENT, "test");
ConfigurationManager.getConfigInstance().setProperty(ARCHAIUS_DEPLOYMENT_ENVIRONMENT, env);
// 将配置文件加载到环境变量
String eurekaPropsFile = EUREKA_PROPS_FILE.get();
try {
ConfigurationManager.loadCascadedPropertiesFromResources(eurekaPropsFile);
} catch (IOException e) {
//...
}
return configInstance;
}
}
四、EurekaClientConfig
EurekaClientConfig,包含了与EurekaClient相关的一些配置项,也是通过读取eureka-client.properties里的配置构造出来的。只不过它关注的跟之前的EurekaInstanceConfig是不一样的,主要关注EurekaClient的一些配置项:

4.1 核心方法
我这里列举下EurekaClientConfig的核心方法:
// 从 Eureka-Server 拉取注册表频率,单位:秒
int getRegistryFetchIntervalSeconds();
// 向 Eureka-Server 同步应用实例信息频率,单位:秒
int getInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds();
// 初始化后,首次向 Eureka-Server 同步应用实例信息的延迟,单位:秒
int getInitialInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds();
// 轮询获取 Eureka-Server 地址变更频率,单位:秒,默认300
int getEurekaServiceUrlPollIntervalSeconds();
// Eureka-Server 读取超时时间
int getEurekaServerReadTimeoutSeconds();
// Eureka-Server 连接超时时间
int getEurekaServerConnectTimeoutSeconds();
// 获取备份注册中心实现类
// 当 Eureka-Client 启动时,无法从 Eureka-Server 读取注册信息(可能挂了),从备份注册中心读取注册信息
// ps:目前 Eureka-Client 未提供合适的实现。
String getBackupRegistryImpl();
// 允许的所有 Eureka-Server 总连接数
int getEurekaServerTotalConnections();
// 允许的单个 Eureka-Server 总连接数
int getEurekaServerTotalConnectionsPerHost();
// Eureka-Server 的 Port
String getEurekaServerPort();
// Eureka-Server 的 DNS 名
String getEurekaServerDNSName();
// 是否使用 DNS 获取 Eureka-Server 地址集合
boolean shouldUseDnsForFetchingServiceUrls();
// 是否向 Eureka-Server 注册自身服务
boolean shouldRegisterWithEureka();
// 应用关闭时,是否向 Eureka-Server 取消注册自身服务
boolean shouldUnregisterOnShutdown();
// 优先使用相同 Zone 的 Eureka-Server
boolean shouldPreferSameZoneEureka();
// 是否允许被 Eureka-Server 重定向
boolean allowRedirects();
// 是否关闭增量获取注册表
boolean shouldDisableDelta();
// 所在区域Region
String getRegion();
// 获取 Eureka-Client 所在区域( Zone )的 Eureka-Server 服务地址
List<String> getEurekaServerServiceUrls(String myZone);
// 是否过滤,只获取状态为开启( Up )的应用实例集合
boolean shouldFilterOnlyUpInstances();
// Eureka-Server 连接的空闲关闭时间,单位:秒
int getEurekaConnectionIdleTimeoutSeconds();
// 是否从 Eureka-Server 拉取注册信息
boolean shouldFetchRegistry();
// 执行心跳的线程池大小
int getHeartbeatExecutorThreadPoolSize();
// 心跳超时后,延迟重试的时间
int getHeartbeatExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();
// 本地注册表缓存刷新的线程池大小
int getCacheRefreshExecutorThreadPoolSize();
// 本地注册表缓存刷新超时延迟重试的时间
int getCacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();
// 是否同步应用实例状态到 Eureka-Server
boolean shouldOnDemandUpdateStatusChange();
4.2 构造流程
EurekaClientConfig构造时,默认创建DefaultEurekaClientConfig对象:
EurekaClientConfig eurekaClientConfig = new DefaultEurekaClientConfig();
public DefaultEurekaClientConfig(String namespace) {
this.namespace = namespace.endsWith(".") ? namespace : namespace + ".";
// 这里读取eureka-client.properties配置
this.configInstance = Archaius1Utils.initConfig(CommonConstants.CONFIG_FILE_NAME);
// 构造客户端通信相关参数的对象
this.transportConfig = new DefaultEurekaTransportConfig(namespace, configInstance);
}
注意,在构造DefaultEurekaClientConfig时,还创建了一个DefaultEurekaTransportConfig对象,这个对象就是保存了一些网络通信相关的配置:
public class DefaultEurekaTransportConfig implements EurekaTransportConfig {
private static final String SUB_NAMESPACE = TRANSPORT_CONFIG_SUB_NAMESPACE + ".";
private final String namespace;
private final DynamicPropertyFactory configInstance;
public DefaultEurekaTransportConfig(String parentNamespace, DynamicPropertyFactory configInstance) {
this.namespace = parentNamespace == null ? SUB_NAMESPACE : (parentNamespace.endsWith(".")
? parentNamespace + SUB_NAMESPACE
: parentNamespace + "." + SUB_NAMESPACE);
this.configInstance = configInstance;
}
// ...
}
五、总结
本章,我介绍了Eureka启动过程中的几个核心配置对象。通过阅读源码可以看到,Eureka对这些配置对象的处理思路都是一致的:定义各种配置类接口,然后全部从配置文件读取后保存到内存中,最后统一交给ConfigurationManager管理。
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

