上一章,我详细讲解了Eureka-Client全量拉取注册表的机制和原理。本章,我将讲解 增量拉取 注册表的原理,整体流程我用下面这张图表示。本章,读者应当重点掌握增量数据保存的设计思路,以及数据同步的 Hash比对 机制。
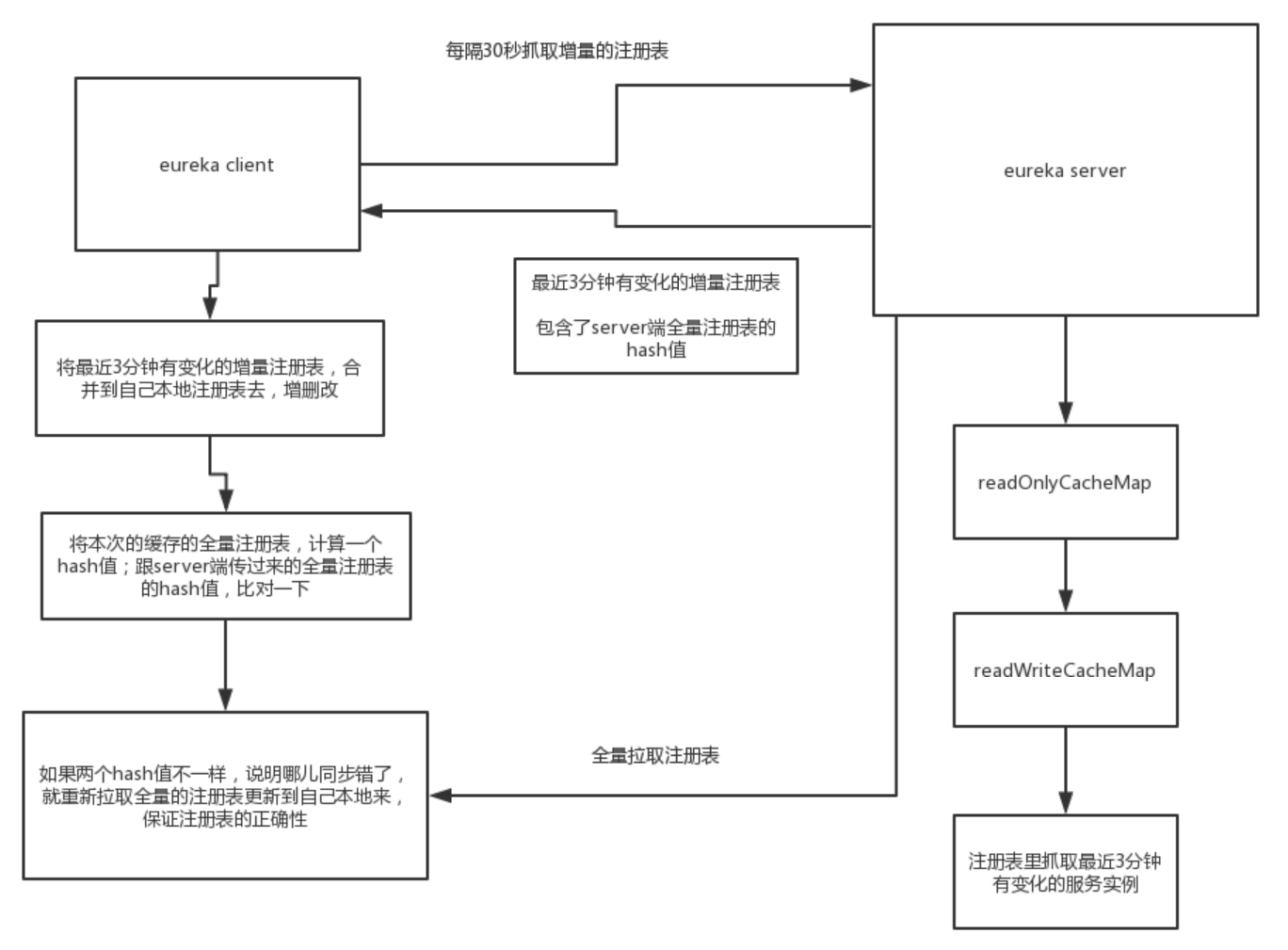
一、Eureka-Client拉取流程
1.1 定时调度任务
DiscoveryClient在构造时,会启动一个定时调度任务,默认每隔 30秒 发送一次请求到Eureka-Server,拉取 增量 的注册表信息:
DiscoveryClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs args, Provider<BackupRegistry> backupRegistryProvider) {
//...
try {
// 定时调度线程池
scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2,
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build());
//...
// 线程池,用来执行刷新本地缓存注册表的任务
cacheRefreshExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1, clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-CacheRefreshExecutor-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build()
);
//...
// 初始化调度任务
initScheduledTasks();
//...
}
private void initScheduledTasks() {
if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry()) {
// 参数eureka.client.refresh.interval可以设置注册表刷新间隔,默认30s
int registryFetchIntervalSeconds = clientConfig.getRegistryFetchIntervalSeconds();
// 重试延迟因子
int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();
scheduler.schedule(
new TimedSupervisorTask(
"cacheRefresh",
scheduler,
cacheRefreshExecutor,
registryFetchIntervalSeconds,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
// 关键看这个任务
new CacheRefreshThread()
),
registryFetchIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
//...
}
真正执行任务的逻辑是在任务类CacheRefreshThread中:
/**
* DiscoveryClient.java
*/
class CacheRefreshThread implements Runnable {
public void run() {
refreshRegistry();
}
}
void refreshRegistry() {
try {
//...
// 拉取注册表
boolean success = fetchRegistry(remoteRegionsModified);
//...
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("Cannot fetch registry from server", e);
}
}
最后,还是调用了DiscoveryClient#fetchRegistry(),此时本地缓存的注册表Applications不为null,最终会走 增量拉取 的逻辑DiscoveryClient.getAndUpdateDelta()。
/**
* DiscoveryClient.java
*/
private boolean fetchRegistry(boolean forceFullRegistryFetch) {
Stopwatch tracer = FETCH_REGISTRY_TIMER.start();
try {
// 1.获取本地缓存的注册表
Applications applications = getApplications();
if (clientConfig.shouldDisableDelta() // 如果禁用增量拉取注册表
|| (!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress()))
|| forceFullRegistryFetch
|| (applications == null)
|| (applications.getRegisteredApplications().size() == 0)
|| (applications.getVersion() == -1))
{
logger.info("Disable delta property : {}", clientConfig.shouldDisableDelta());
logger.info("Single vip registry refresh property : {}", clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress());
logger.info("Force full registry fetch : {}", forceFullRegistryFetch);
logger.info("Application is null : {}", (applications == null));
logger.info("Registered Applications size is zero : {}",
(applications.getRegisteredApplications().size() == 0));
logger.info("Application version is -1: {}", (applications.getVersion() == -1));
// 2.执行全量拉取并缓存
getAndStoreFullRegistry();
} else {
// 3.执行增量拉取
getAndUpdateDelta(applications);
}
// 4.设置应用集合hashcode
applications.setAppsHashCode(applications.getReconcileHashCode());
// 打印本地缓存的注册应用实例数量
logTotalInstances();
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error(PREFIX + appPathIdentifier + " - was unable to refresh its cache! status = " + e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
} finally {
if (tracer != null) {
tracer.stop();
}
}
// ...
// 5.以拉取到的注册表为准,更新本地缓存中当前应用实例的状态(只更新缓存)
updateInstanceRemoteStatus();
return true;
}
1.2 getAndUpdateDelta增量拉取
增量拉取注册表的逻辑是在getAndUpdateDelta中,底层还是调用了AbstractJerseyEurekaHttpClient发送HTTP/GET请求到Eureka-Server,请求的URL形式类似http://localhost:8080/v2/apps/delta:
/**
* DiscoveryClient.java
*/
private void getAndUpdateDelta(Applications applications) throws Throwable {
long currentUpdateGeneration = fetchRegistryGeneration.get();
// 1.发送HTTP/GET请求增量拉取注册表(例如:http://localhost:8080/v2/apps/delta)
Applications delta = null;
EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> httpResponse = eurekaTransport.queryClient.getDelta(remoteRegionsRef.get());
if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode()) {
delta = httpResponse.getEntity();
}
// 2.增量拉取结果为空,则全量拉取
if (delta == null) {
logger.warn("The server does not allow the delta revision to be applied because it is not safe. " + "Hence got the full registry.");
getAndStoreFullRegistry();
} else if (fetchRegistryGeneration.compareAndSet(currentUpdateGeneration, currentUpdateGeneration + 1)) {
logger.debug("Got delta update with apps hashcode {}", delta.getAppsHashCode());
String reconcileHashCode = "";
if (fetchRegistryUpdateLock.tryLock()) {
try {
// 3.将增量获取到的应用集合和本地缓存的应用集合进行合并
updateDelta(delta);
// 4.计算本地的应用集合一致性哈希码
reconcileHashCode = getReconcileHashCode(applications);
} finally {
fetchRegistryUpdateLock.unlock();
}
} else {
logger.warn("Cannot acquire update lock, aborting getAndUpdateDelta");
}
// There is a diff in number of instances for some reason
if (!reconcileHashCode.equals(delta.getAppsHashCode()) || clientConfig.shouldLogDeltaDiff()) {
// 一致性哈希值不相等,则全量拉取一次并记日志
reconcileAndLogDifference(delta, reconcileHashCode); // this makes a remoteCall
}
} else {
logger.warn("Not updating application delta as another thread is updating it already");
logger.debug("Ignoring delta update with apps hashcode {}, as another thread is updating it already", delta.getAppsHashCode());
}
}
1.3 合并本地缓存
拉取到结果后,会调用updateDelta(delta);将结果与本地注册表缓存合并:
/**
* DiscoveryClient.java
*/
private void updateDelta(Applications delta) {
int deltaCount = 0;
// 循环增量(变化)应用集合
for (Application app : delta.getRegisteredApplications()) {
// 遍历每一个应用的所有实例
for (InstanceInfo instance : app.getInstances()) {
Applications applications = getApplications();
//...
++deltaCount;
// 添加
if (ActionType.ADDED.equals(instance.getActionType())) {
Application existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName());
if (existingApp == null) {
applications.addApplication(app);
}
logger.debug("Added instance {} to the existing apps in region {}", instance.getId(), instanceRegion);
applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()).addInstance(instance);
}
// 修改
else if (ActionType.MODIFIED.equals(instance.getActionType())) {
Application existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName());
if (existingApp == null) {
applications.addApplication(app);
}
logger.debug("Modified instance {} to the existing apps ", instance.getId());
applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()).addInstance(instance);
}
// 删除
else if (ActionType.DELETED.equals(instance.getActionType())) {
Application existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName());
if (existingApp == null) {
applications.addApplication(app);
}
logger.debug("Deleted instance {} to the existing apps ", instance.getId());
applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()).removeInstance(instance);
}
}
}
logger.debug("The total number of instances fetched by the delta processor : {}", deltaCount);
getApplications().setVersion(delta.getVersion());
// 过滤并打乱应用集合的顺序
getApplications().shuffleInstances(clientConfig.shouldFilterOnlyUpInstances());
//...
}
1.4 Hash比对
最后,会将Eureka-Client端的合并完的注册表的hash值,跟Eureka-Server端的全量注册表的hash值进行一个比对:
reconcileHashCode = getReconcileHashCode(applications);
if (!reconcileHashCode.equals(delta.getAppsHashCode()) || clientConfig.shouldLogDeltaDiff()) {
// 一致性哈希值不相等,则全量拉取一次并记日志
reconcileAndLogDifference(delta, reconcileHashCode); // this makes a remoteCall
}
如果不一样的话,说明本地注册表跟Server端不一致,此时就会重新从Eureka-Server拉取全量注册表并更新到本地缓存。
二、Eureka-Server处理流程
接着,我们来看下Eureka-Server接受并处理增量拉取的流程。Eureka-Client发送的拉取注册表的HTTP/GET请求是类似这样的:http://localhost:8080/v2/apps/delta。
2.1 整体流程
在Eureka-Server端,由ApplicationsResource#getContainerDifferential()负责处理注册表拉取请求,可以看到注册表是从一个ResponseCache对象中获取的,所以整个Server端的处理流程核心就是ResponseCache:
/**
* ApplicationsResource.java
*/
@Path("delta")
@GET
public Response getContainerDifferential(
@PathParam("version") String version,
@HeaderParam(HEADER_ACCEPT) String acceptHeader,
@HeaderParam(HEADER_ACCEPT_ENCODING) String acceptEncoding,
@HeaderParam(EurekaAccept.HTTP_X_EUREKA_ACCEPT) String eurekaAccept,
@Context UriInfo uriInfo, @Nullable @QueryParam("regions") String regionsStr) {
boolean isRemoteRegionRequested = null != regionsStr && !regionsStr.isEmpty();
// 是否禁用增量访问
if ((serverConfig.shouldDisableDelta()) || (!registry.shouldAllowAccess(isRemoteRegionRequested))) {
return Response.status(Status.FORBIDDEN).build();
}
//...
// 创建响应缓存(ResponseCache) 的键
// 注意这里的缓存Key是ALL_APPS_DELTA
Key cacheKey = new Key(Key.EntityType.Application,
ResponseCacheImpl.ALL_APPS_DELTA,
keyType, CurrentRequestVersion.get(), EurekaAccept.fromString(eurekaAccept), regions
);
// 从响应缓存(ResponseCache)读取增量注册信息
if (acceptEncoding != null
&& acceptEncoding.contains(HEADER_GZIP_VALUE)) {
// 关键是responseCache.getGZIP(cacheKey)
return Response.ok(responseCache.getGZIP(cacheKey))
.header(HEADER_CONTENT_ENCODING, HEADER_GZIP_VALUE)
.header(HEADER_CONTENT_TYPE, returnMediaType)
.build();
} else {
return Response.ok(responseCache.get(cacheKey))
.build();
}
}
ResponseCache的原理在上一章已经讲解过了,我就不赘述了。重点来看下ResponseCacheImpl.generatePayload(Key key),这个方法会根据缓存Key获取注册表数据:
/**
* ResponseCacheImpl.java
*/
private final AbstractInstanceRegistry registry;
private Value generatePayload(Key key) {
Stopwatch tracer = null;
try {
String payload;
switch (key.getEntityType()) {
case Application:
boolean isRemoteRegionRequested = key.hasRegions();
// 1.全量拉取,略,上一章已讲解过
if (ALL_APPS.equals(key.getName())) {
//...
}
// 2.增量拉取
else if (ALL_APPS_DELTA.equals(key.getName())) {
//...
// 重点看这里: registry.getApplicationDeltasFromMultipleRegions(key.getRegions())
payload = getPayLoad(key,
registry.getApplicationDeltasFromMultipleRegions(key.getRegions()));
} else {
tracer = serializeOneApptimer.start();
payload = getPayLoad(key, registry.getApplication(key.getName()));
}
break;
//...
default:
logger.error("Unidentified entity type: " + key.getEntityType() + " found in the cache key.");
payload = "";
break;
}
return new Value(payload);
} finally {
if (tracer != null) {
tracer.stop();
}
}
}
// 将Applications转换成缓存值
private String getPayLoad(Key key, Applications apps) {
EncoderWrapper encoderWrapper = serverCodecs.getEncoder(key.getType(), key.getEurekaAccept());
String result;
try {
result = encoderWrapper.encode(apps);
} catch (Exception e) {
//...
}
//...
return result;
}
上述获取增量注册表信息的逻辑的重点在与方法registry.getApplicationDeltasFromMultipleRegions(),registery就是Server端的注册表 PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl 。
2.2 获取增量注册表
我们来看下AbstractInstanceRegistry.getApplicationDeltasFromMultipleRegions()。重点是它从一个recentlyChangedQueue队列中遍历出所有应用信息,然后返回:
/**
* AbstractInstanceRegistry.java
*/
//最近租约变更记录队列
private ConcurrentLinkedQueue<RecentlyChangedItem> recentlyChangedQueue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<RecentlyChangedItem>();
public Applications getApplicationDeltasFromMultipleRegions(String[] remoteRegions) {
//...
Applications apps = new Applications();
apps.setVersion(responseCache.getVersionDeltaWithRegions().get());
Map<String, Application> applicationInstancesMap = new HashMap<String, Application>();
try {
write.lock();
// 遍历【最近租约变更记录队列】
Iterator<RecentlyChangedItem> iter = this.recentlyChangedQueue.iterator();
logger.debug("The number of elements in the delta queue is :" + this.recentlyChangedQueue.size());
while (iter.hasNext()) {
// 租约
Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = iter.next().getLeaseInfo();
// 应用实例
InstanceInfo instanceInfo = lease.getHolder();
Object[] args = {instanceInfo.getId(),
instanceInfo.getStatus().name(),
instanceInfo.getActionType().name()};
logger.debug("The instance id %s is found with status %s and actiontype %s", args);
// 应用信息
Application app = applicationInstancesMap.get(instanceInfo.getAppName());
if (app == null) {
app = new Application(instanceInfo.getAppName());
applicationInstancesMap.put(instanceInfo.getAppName(), app);
// 添加到结果集
apps.addApplication(app);
}
app.addInstance(decorateInstanceInfo(lease));
}
//...
// 获取全量应用集合,计算全量集合的hash值
Applications allApps = getApplications(!disableTransparentFallback);
// 保存这个hash值,注意这里apps本身保存的是增量注册表
apps.setAppsHashCode(allApps.getReconcileHashCode());
return apps;
} finally {
write.unlock();
}
}
2.3 recentlyChangedQueue
上述的recentlyChangedQueue,本质是一个ConcurrentLinkedQueue(底层基于单链表实现的无锁并发队列),里面保存着 最近有变化的应用实例 。
也就是说Eureka-Server发现有应用实例注册、下线、状态变更时,它会创建一个 RecentlyChangedItem对象并入队:
/**
* AbstractInstanceRegistry.java
*/
private ConcurrentLinkedQueue<RecentlyChangedItem> recentlyChangedQueue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<RecentlyChangedItem>();
private static final class RecentlyChangedItem {
/**
* 最后更新时间戳
*/
private long lastUpdateTime;
/**
* 租约
*/
private Lease<InstanceInfo> leaseInfo;
public RecentlyChangedItem(Lease<InstanceInfo> lease) {
this.leaseInfo = lease;
lastUpdateTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public long getLastUpdateTime() {
return this.lastUpdateTime;
}
public Lease<InstanceInfo> getLeaseInfo() {
return this.leaseInfo;
}
}
然后, PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl在构造时,会创建一个定时调度任务,这个任务默认 每隔30秒 扫描一下 `recentlyChangedQueue队列,当发现有Item在队列里的停留时间超过一定时长(默认 180秒 )后,就把它移除。
也就是说: 这个recentlyChangedQueue,就保留了最近3分钟的应用实例变更记录 。
/**
* AbstractInstanceRegistry.java
*/
this.deltaRetentionTimer.schedule(getDeltaRetentionTask(),
serverConfig.getDeltaRetentionTimerIntervalInMs(),
serverConfig.getDeltaRetentionTimerIntervalInMs());
private TimerTask getDeltaRetentionTask() {
return new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
Iterator<RecentlyChangedItem> it = recentlyChangedQueue.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
// 是否超时
if (it.next().getLastUpdateTime() < System.currentTimeMillis() - serverConfig.getRetentionTimeInMSInDeltaQueue()) {
it.remove();
} else {
break;
}
}
}
};
}
eureka.deltaRetentionTimerIntervalInMs: 定时任务执行频率,单位:毫秒,默认 :30 1000 毫秒。
eureka.retentionTimeInMSInDeltaQueue:队列中保存的应用实例有效期,单位:毫秒,默认:3 60 * 1000 毫秒。
三、Hash比对原理
了解增量拉取注册表的流程,本节我们来看下Hash比对的底层原理,首先回顾下整个增量拉取流程:
- Eureka-Server端,通过维护一个LinkedQueue队列,保存最近一段时间内变化的应用实例,这个就是增量注册表;
- Eureka-Server端,对保存的全量注册表计算一个hash值,然后在响应给Eureka-Client的增量注册表对象中设置这个hash值;
- Eureka-Client端,调用增量拉取注册表的接口获取到增量的应用实例信息,更新并合并本地缓存的注册表;
- Eureka-Client端,更新并合并完成后,计算本地注册表的hash值,与Server端的hash值进行比对,一致就OK,不一致就再进行一次全量拉取。
3.1 hash值计算
应用集合的hash值,就是Applications.appsHashCode 。它是如何计算的呢?我们来看下一下代码:
/**
* Applications.java
*/
public String getReconcileHashCode() {
// 计数集合 key:应用实例状态
TreeMap<String, AtomicInteger> instanceCountMap = new TreeMap<String, AtomicInteger>();
populateInstanceCountMap(instanceCountMap);
// 计算 hashcode
return getReconcileHashCode(instanceCountMap);
}
public void populateInstanceCountMap(Map<String, AtomicInteger> instanceCountMap) {
for (Application app : this.getRegisteredApplications()) {
for (InstanceInfo info : app.getInstancesAsIsFromEureka()) {
// 计数
AtomicInteger instanceCount = instanceCountMap.computeIfAbsent(info.getStatus().name(),
k -> new AtomicInteger(0));
instanceCount.incrementAndGet();
}
}
}
public List<Application> getRegisteredApplications() {
return new ArrayList<Application>(this.applications);
}
public static String getReconcileHashCode(Map<String, AtomicInteger> instanceCountMap) {
StringBuilder reconcileHashCode = new StringBuilder(75);
// 这里拼接字符串,把它作为hash值
for (Map.Entry<String, AtomicInteger> mapEntry : instanceCountMap.entrySet()) {
reconcileHashCode.append(mapEntry.getKey()).append(STATUS_DELIMITER) // status
.append(mapEntry.getValue().get()).append(STATUS_DELIMITER); // count
}
return reconcileHashCode.toString();
}
所以,Applications的hash值的计算公式就是:将每个应用实例状态( status ) 与 数量( count ) 进行拼接。若数量为0,则不进行拼接。 状态以字符串大小排序 。
appsHashCode = ${status}_${count}_
举个例子,假设现在一共有8个应用实例,其中8 个 UP ,0 个 DOWN ,则 :
appsHashCode = DOWN_2_UP_8_
四、总结
本章,我讲解了Eureka进行增量拉取注册表的核心流程及原理。Eureka在设计这块时,有两个地方比较值得我们借鉴:
- 增量数据的设计思路:如果你要保存一份增量的最新变更数据,可以基于LinkedQuueue,将最新变更的数据放入这个queue中,然后通过一个定时任务扫描队列,移除过期数据,这样就可以让这个队列只保存最近一段时间内变更的增量数据。
- 数据同步的Hash值比对机制:在一个分布式系统中,如果我们要进行数据同步,可以采用Hash值比对的思想,从源数据计算一个hash值,在目标数据再计算一个hash值,只要这两个hash值是一样的,就说明数据没有发生变动。
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

