instantiateBean调用默认构造方法
前一篇说了,如果是普通的实例创建,会去寻找可以用的构造方法,可能是多个,有重载的,也可能就只有默认构造方法,我们先来看下默认构造方法怎么做的,因为他相对简单。
其实里面就是获取实例化的策略,然后进行instantiate实例化,前面有说过策略是CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy的,但是只会在注入的时候起作用,一般的还是用父类SimpleInstantiationStrategy的instantiate。
protected BeanWrapper instantiateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
try {
Object beanInstance;
final BeanFactory parent = this;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
beanInstance = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () ->
getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent),
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
beanInstance = getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent);
}
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(beanInstance);//包装成BeanWrapper
initBeanWrapper(bw);
return bw;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
}
SimpleInstantiationStrategy的instantiate
如果发现是有方法重载的,就需要用CGLIB来动态代理,如果没有就直接获取默认构造方法实例化。因为前面已经发现是有无参构造方法的,所以这里可以直接获取他的构造方法,然后进行实例化。
@Override
public Object instantiate(RootBeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String beanName, BeanFactory owner) {
// Don't override the class with CGLIB if no overrides.
if (!bd.hasMethodOverrides()) {//无lookup重载的方法
Constructor<?> constructorToUse;
synchronized (bd.constructorArgumentLock) {
constructorToUse = (Constructor<?>) bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod;
if (constructorToUse == null) {
final Class<?> clazz = bd.getBeanClass();
if (clazz.isInterface()) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "Specified class is an interface");
}
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
constructorToUse = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedExceptionAction<Constructor<?>>) clazz::getDeclaredConstructor);
}
else {
constructorToUse = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor();
}
bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod = constructorToUse;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "No default constructor found", ex);
}
}
}
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse);
}
else {//有lookup重载的话要用CGLIB动态代理了
// Must generate CGLIB subclass.
return instantiateWithMethodInjection(bd, beanName, owner);
}
}
BeanUtils的instantiateClass
这里就是调用构造函数实例化了,不过会先看是不是Kotlin的,然后才是一般JAVA的构造方法实例化创建。
public static <T> T instantiateClass(Constructor<T> ctor, Object... args) throws BeanInstantiationException {
Assert.notNull(ctor, "Constructor must not be null");
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(ctor);
if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinReflectPresent() && KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(ctor.getDeclaringClass())) {
return KotlinDelegate.instantiateClass(ctor, args);
}
else {
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = ctor.getParameterTypes();
Assert.isTrue(args.length <= parameterTypes.length, "Can't specify more arguments than constructor parameters");
Object[] argsWithDefaultValues = new Object[args.length];
for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length; i++) {//获得参数
if (args[i] == null) {
Class<?> parameterType = parameterTypes[i];
argsWithDefaultValues[i] = (parameterType.isPrimitive() ? DEFAULT_TYPE_VALUES.get(parameterType) : null);
}
else {
argsWithDefaultValues[i] = args[i];
}
}
return ctor.newInstance(argsWithDefaultValues);
}
}
catch (InstantiationException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Is it an abstract class?", ex);
}
catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Is the constructor accessible?", ex);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Illegal arguments for constructor", ex);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Constructor threw exception", ex.getTargetException());
}
}
CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy的instantiateWithMethodInjection
如果发现有loolup注解的方法,就会调用这个方法。
@Override
protected Object instantiateWithMethodInjection(RootBeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String beanName, BeanFactory owner) {
return instantiateWithMethodInjection(bd, beanName, owner, null);
}
@Override
protected Object instantiateWithMethodInjection(RootBeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String beanName, BeanFactory owner,
@Nullable Constructor<?> ctor, Object... args) {
// Must generate CGLIB subclass...
return new CglibSubclassCreator(bd, owner).instantiate(ctor, args);
}
CglibSubclassCreator的instantiate
首先创建一个GCLIB的增强器子类,如果传入构造方法是空的话就用BeanUtils进行GCLIB子类的实例化,否则就用增强子类的构造方法直接实例化。然后设置方法拦截器,这样调用的时候就会进入拦截器里,就可以去容器里寻找,有就直接返回,没有就创建。
public Object instantiate(@Nullable Constructor<?> ctor, Object... args) {
Class<?> subclass = createEnhancedSubclass(this.beanDefinition);
Object instance;
if (ctor == null) {
instance = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(subclass);
}
else {
try {
Constructor<?> enhancedSubclassConstructor = subclass.getConstructor(ctor.getParameterTypes());
instance = enhancedSubclassConstructor.newInstance(args);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(this.beanDefinition.getBeanClass(),
"Failed to invoke constructor for CGLIB enhanced subclass [" + subclass.getName() + "]", ex);
}
}
// SPR-10785: set callbacks directly on the instance instead of in the
// enhanced class (via the Enhancer) in order to avoid memory leaks.
Factory factory = (Factory) instance;
factory.setCallbacks(new Callback[] {NoOp.INSTANCE,
new LookupOverrideMethodInterceptor(this.beanDefinition, this.owner),
new ReplaceOverrideMethodInterceptor(this.beanDefinition, this.owner)});
return instance;
}
实战LOOKUP注解
有时候你可能不想写在同一个文件写bean注解来进行实例化,这样对实现类是有依赖的,比如这样,其实对实现类是有依赖的:

但是我们可以想办法解耦,但是这样这个类又会依赖spring了,如果你要独立给其他框架用的话,估计这样就不可以了,还是得想起他办法,比如xml,或者自定义后置处理器处理。


这样就进行了解耦啦,然后执行的时候:

到LookupOverrideMethodInterceptor拦截器里来啦,可以看到最后是调用owner.getBean,传入一个你要的类型,这里就是UserDao:
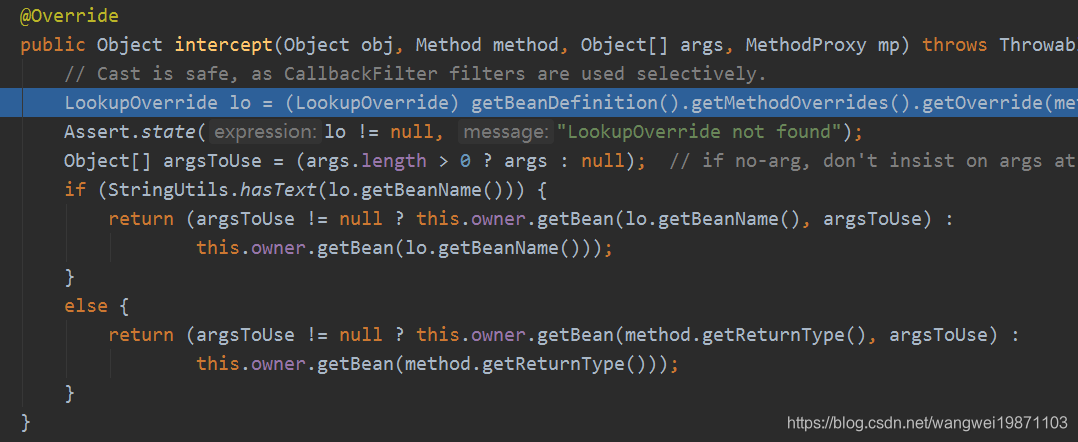
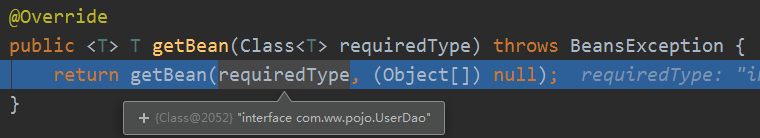
最后内部会封装成一个NamedBeanHolder返回,然后getBeanInstance可以取出你要的对象,当然里面还是调用getBean去获取的。可以看到就是容器里的单例:

注意点
不要存在两个同类型的实例,否则他不知道你要的是哪个,除非你指定名字,不然就报异常:

org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'com.ww.pojo.UserDao' available: expected single matching bean but found 2: testBean,userDao
你可以这样加名字:

或者这样:

好了,今天就到这里了,希望对学习理解有帮助,大神看见勿喷,仅为自己的学习理解,能力有限,请多包涵。
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

