一、ConcurrentSkipListSet简介
ConcurrentSkipListSet ,是JDK1.6时J.U.C新增的一个集合工具类,顾名思义,它是一种 SET 类型。
SET类型,在数学上称为“集合”,具有互异性、无序性的特点,也就是说SET中的任意两个元素均不相同(即不包含重复元素),且元素是无序的。
是不是感觉和HashMap有点类似?HashMap中的Key也是不能重复,且是无序的。
事实上,JDK提供的默认SET实现——HashSet,其实就是采用“组合”的方式——内部引用了一个HashMap对象,以此实现SET的功能。
我们来看下 ConcurrentSkipListSet 的类继承图:
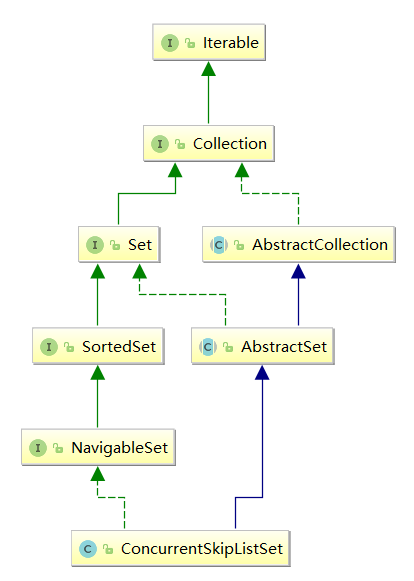
可以看到,ConcurrentSkipListSet实现了NavigableSet接口,在Java多线程进阶(二五)—— J.U.C之collections框架:ConcurrentSkipListMap中,我们提到过ConcurrentSkipListMap实现了NavigableMap接口,以提供和排序相关的功能,维持元素的有序性,所以 ConcurrentSkipListSet 就是一种为并发环境设计的有序SET工具类。
NavigableSet 的功能和 NavigableMap 几乎是完全一样的,提供了根据指定Key返回最接近项、按升序/降序返回所有键的视图等功能。唯一的区别是NavigableSet针对的仅仅是键值,NavigableMap针对键值对进行操作。
二、ConcurrentSkipListSet原理
2.1 内部结构
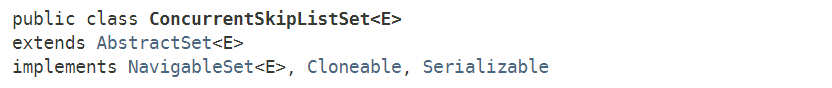
ConcurrentSkipListSet 的实现非常简单,其内部引用了一个ConcurrentSkipListMap对象,所有API方法均委托ConcurrentSkipListMap对象完成:
public class ConcurrentSkipListSet<E> extends AbstractSet<E>
implements NavigableSet<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
/**
* The underlying map. Uses Boolean.TRUE as value for each
* element. This field is declared final for the sake of thread
* safety, which entails some ugliness in clone().
*/
private final ConcurrentNavigableMap<E, Object> m;
public ConcurrentSkipListSet() {
m = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<E, Object>();
}
public ConcurrentSkipListSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
m = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<E, Object>(comparator);
}
public ConcurrentSkipListSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
m = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<E, Object>();
addAll(c);
}
public ConcurrentSkipListSet(SortedSet<E> s) {
m = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<E, Object>(s.comparator());
addAll(s);
}
ConcurrentSkipListSet(ConcurrentNavigableMap<E, Object> m) {
this.m = m;
}
// ...
}
复制代码从上述代码可以看出, ConcurrentSkipListSet 在构造时创建了一个ConcurrentSkipListMap对象,并由字段m引用,所以其实ConcurrentSkipListSet就是一种 跳表类型 的数据结构,其平均增删改查的时间复杂度均为O(logn)。
2.2 核心方法
我们来看下ConcurrentSkipListSet是如何实现API方法的:
public int size() {
return m.size();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return m.isEmpty();
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return m.containsKey(o);
}
public boolean add(E e) {
return m.putIfAbsent(e, Boolean.TRUE) == null;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return m.remove(o, Boolean.TRUE);
}
public void clear() {
m.clear();
}
//...
复制代码从上述代码可以看出,所有操作均是委托ConcurrentSkipListMap对象完成的。重点看下add方法:
public boolean add(E e) {
return m.putIfAbsent(e, Boolean.TRUE) == null;
}
复制代码我们知道 ConcurrentSkipListMap 对键值对的要求是均不能为null,所以ConcurrentSkipListSet在插入元素的时候,用一个Boolean.TRUE对象(相当于一个值为true的Boolean型对象)作为value,同时putIfAbsent可以保证不会存在相同的Key。
所以,最终跳表中的所有Node结点的Key均不会相同,且值都是Boolean.True。
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

