一个bean定义扫描程序类,它检测类路径上的bean候选者,使用给定的注册表(BeanFactory或ApplicationContext)注册相应的bean定义。
通过可配置的类型过滤器检测候选类。 默认过滤器包括使用Spring的@Component,@Repository,@Service或@Controller构造型注释的类。还支持Java EE 6的javax.annotation.ManagedBean和JSR-330的javax.inject.Named注释(如果可用)。
public ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean useDefaultFilters,
Environment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
// 默认true 使用new AnnotationTypeFilter(Component.class)扫描指定类型
if (useDefaultFilters) {
registerDefaultFilters();
}
setEnvironment(environment);
setResourceLoader(resourceLoader);
}
protected void registerDefaultFilters() {
// includeFilters中是允许过滤的条件
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(Component.class));
ClassLoader cl = ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.class.getClassLoader();
try {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(
((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.annotation.ManagedBean", cl)), false));
logger.debug("JSR-250 'javax.annotation.ManagedBean' found and supported for component scanning");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-250 1.1 API (as included in Java EE 6) not available - simply skip.
}
try {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(
((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Named", cl)), false));
logger.debug("JSR-330 'javax.inject.Named' annotation found and supported for component scanning");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-330 API not available - simply skip.
}
}
复制代码添加AnnotationTypeFilter到includeFilters,代表只有被includeFilters内匹配的注解才可以被扫描解析,这里默认会对标有@Component,@ManagedBean,@Named注解的类进行解析。
setResourceLoader()被定义在父类ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider中,除了设置resourceLoader外还新建了两个对象。
@Override
public void setResourceLoader(@Nullable ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
// 默认PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver
this.resourcePatternResolver = ResourcePatternUtils.getResourcePatternResolver(resourceLoader);
this.metadataReaderFactory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory(resourceLoader);
this.componentsIndex = CandidateComponentsIndexLoader.loadIndex(this.resourcePatternResolver.getClassLoader());
}
复制代码如果想弄清楚ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner的工作原理的前提,还需要弄清楚几个类。
1、ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner涉及的核心组件
1.1、SimpleMetadataReader
基于ASM ClassReader的MetadataReader实现。MetadataReader定义了三个方法:
public interface MetadataReader {
//Resource代表类文件的引用对象
Resource getResource();
//ClassMetadata代表类的信息封装
ClassMetadata getClassMetadata();
//AnnotationMetadata代表类上的注解信息
AnnotationMetadata getAnnotationMetadata();
}
复制代码在SimpleMetadataReader的构造方法中,实例化了一个AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor对象,此对象是ClassMetadata和AnnotationMetadata的实现者。
SimpleMetadataReader(Resource resource, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) throws IOException {
InputStream is = new BufferedInputStream(resource.getInputStream());
ClassReader classReader;
try {
classReader = new ClassReader(is);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new NestedIOException("ASM ClassReader failed to parse class file - " +
"probably due to a new Java class file version that isn't supported yet: " + resource, ex);
}
finally {
is.close();
}
AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor visitor = new AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor(classLoader);
classReader.accept(visitor, ClassReader.SKIP_DEBUG);
this.annotationMetadata = visitor;
// (since AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor extends ClassMetadataReadingVisitor)
this.classMetadata = visitor;
this.resource = resource;
}
复制代码ClassReader是一个可以使ClassVisitor访问Java虚拟机规范中定义的ClassFile结构的解析器。 此类解析ClassFile内容,并针对遇到的每个字段、方法和字节码指令调用给定ClassVisitor的适当visit方法。AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor也继承于ClassVisitor,在AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor相应的visit方法内部会将相应的元数据信息保存起来,然后在通过AnnotationMetadata接口的方法暴露出去。
当上面代码中ClassVisitor调用accept()方法解析类结构时遇到的注解信息将会调用AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor的visitAnnotation()方法:
@Override
public AnnotationVisitor visitAnnotation(String desc, boolean visible) {
String className = Type.getType(desc).getClassName();
this.annotationSet.add(className);
return new AnnotationAttributesReadingVisitor(
className, this.attributesMap, this.metaAnnotationMap, this.classLoader);
}
复制代码可以看到对注解的访问依靠的是AnnotationAttributesReadingVisitor,查看doc文档描述:
AnnotationAttributesReadingVisitor是ASM访问者,用于查找在类或方法上定义的注释,包括元注释。此访问者是完全递归的,并考虑了任何嵌套的注释或嵌套的注释数组。
说明AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor是支持类注解的派生注解的属性读取的。
1.2、CachingMetadataReaderFactory
在ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner中并不是直接通过new来直接创建MetadataReader对象的,而是在构造方法的执行过程中实例化了一个CachingMetadataReaderFactory。
CachingMetadataReaderFactory是MetadataReaderFactory接口缓存的实现,每个Spring Resource句柄(即每个“.class”文件)缓存一个MetadataReader实例。
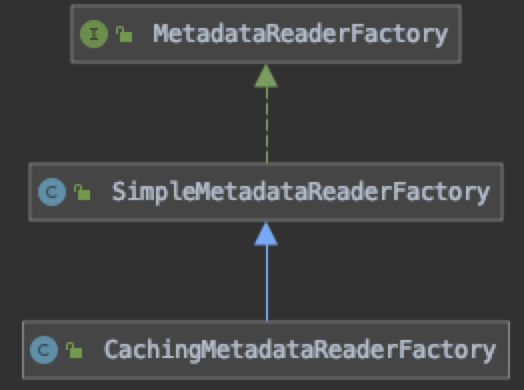
public interface MetadataReaderFactory {
MetadataReader getMetadataReader(String className) throws IOException;
MetadataReader getMetadataReader(Resource resource) throws IOException;
}
复制代码下面是SimpleMetadataReaderFactory的具体实现:
@Override
public MetadataReader getMetadataReader(String className) throws IOException {
try {
String resourcePath = ResourceLoader.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX +
ClassUtils.convertClassNameToResourcePath(className) + ClassUtils.CLASS_FILE_SUFFIX;
Resource resource = this.resourceLoader.getResource(resourcePath);
return getMetadataReader(resource);
}
catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
// Maybe an inner class name using the dot name syntax? Need to use the dollar syntax here...
// ClassUtils.forName has an equivalent check for resolution into Class references later on.
int lastDotIndex = className.lastIndexOf('.');
if (lastDotIndex != -1) {
String innerClassName =
className.substring(0, lastDotIndex) + '$' + className.substring(lastDotIndex + 1);
String innerClassResourcePath = ResourceLoader.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX +
ClassUtils.convertClassNameToResourcePath(innerClassName) + ClassUtils.CLASS_FILE_SUFFIX;
Resource innerClassResource = this.resourceLoader.getResource(innerClassResourcePath);
if (innerClassResource.exists()) {
return getMetadataReader(innerClassResource);
}
}
throw ex;
}
}
@Override
public MetadataReader getMetadataReader(Resource resource) throws IOException {
return new SimpleMetadataReader(resource, this.resourceLoader.getClassLoader());
}
复制代码1.3、CandidateComponentsIndex
Spring Framework 5 改进了扫描和识别组件的方法,使大型项目的性能得到提升。目前,扫描是在编译时执行的,而且向 META-INF/spring.components 文件中的索引文件添加了组件坐标。该索引是通过一个为项目定义的特定于平台的应用程序构建任务来生成的。标有来自 javax 包的注解的组件会添加到索引中,任何带 @Indexed 注解的类或接口都会添加到索引中。Spring 的传统类路径扫描方式没有删除,而是保留为一种后备选择。有许多针对大型代码库的明显性能优势,而托管许多 Spring 项目的服务器也会缩短启动时间。
@Nullable
private static CandidateComponentsIndex doLoadIndex(ClassLoader classLoader) {
//在spring.properties中或系统属性中配置spring.index.ignore=true,可忽略这一组件的作用
if (shouldIgnoreIndex) {
return null;
}
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader.getResources(COMPONENTS_RESOURCE_LOCATION);
if (!urls.hasMoreElements()) {
return null;
}
List<Properties> result = new ArrayList<>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(url));
result.add(properties);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + result.size() + "] index(es)");
}
int totalCount = result.stream().mapToInt(Properties::size).sum();
//将类路径下所有的META-INF/spring.components文件封装成List<Properties>传入构造方法中
return (totalCount > 0 ? new CandidateComponentsIndex(result) : null);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to load indexes from location [" +
COMPONENTS_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
复制代码CandidateComponentsIndex内部使用MultiValueMap<String, Entry>保存被标记@Indexed的注解与被此注解标记的类的映射,getCandidateTypes()方法从集合中取得指定包(包含子包)下面被stereotype注解标记的类。
public class CandidateComponentsIndex {
private final static AntPathMatcher pathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher(".");
private final MultiValueMap<String, Entry> index;
CandidateComponentsIndex(List<Properties> content) {
this.index = parseIndex(content);
}
/**
* Return the candidate types that are associated with the specified stereotype.
* @param basePackage the package to check for candidates
* @param stereotype the stereotype to use
* @return the candidate types associated with the specified {@code stereotype}
* or an empty set if none has been found for the specified {@code basePackage}
*/
public Set<String> getCandidateTypes(String basePackage, String stereotype) {
List<Entry> candidates = this.index.get(stereotype);
if (candidates != null) {
return candidates.parallelStream()
.filter(t -> t.match(basePackage))
.map(t -> t.type)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
}
return Collections.emptySet();
}
private static MultiValueMap<String, Entry> parseIndex(List<Properties> content) {
MultiValueMap<String, Entry> index = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
for (Properties entry : content) {
entry.forEach((type, values) -> {
String[] stereotypes = ((String) values).split(",");
for (String stereotype : stereotypes) {
index.add(stereotype, new Entry((String) type));
}
});
}
return index;
}
private static class Entry {
private final String type;
private final String packageName;
Entry(String type) {
this.type = type;
this.packageName = ClassUtils.getPackageName(type);
}
public boolean match(String basePackage) {
if (pathMatcher.isPattern(basePackage)) {
return pathMatcher.match(basePackage, this.packageName);
}
else {
return this.type.startsWith(basePackage);
}
}
}
}
复制代码2、ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner的扫描过程
下面再看ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner的scan()方法,主要是调用了doScan()方法,找出指定包名下符合bean定义的BeanDefinition注册到容器中,具体下面看。
protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified");
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
// 扫描候选组件的类路径。
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) {
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate);
candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry);
if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName);
}
if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate);
}
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName);
definitionHolder =
AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder);
// 将扫描的候选类注册到bean factory
registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
复制代码findCandidateComponents()方法负责找出spring bean定义,if分支使用了上面讲到的CandidateComponentsIndex,else分支为包扫描方式。
public Set<BeanDefinition> findCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
if (this.componentsIndex != null && indexSupportsIncludeFilters()) {
return addCandidateComponentsFromIndex(this.componentsIndex, basePackage);
}
else {
return scanCandidateComponents(basePackage);
}
}
复制代码includeFilters中只要有一个AnnotationTypeFilter或AssignableTypeFilter的注解类型没有被@Indexed标记并且不属于包"javax."下面的都不会走if分支也就不会用到CandidateComponentsIndex。
private boolean indexSupportsIncludeFilters() {
for (TypeFilter includeFilter : this.includeFilters) {
if (!indexSupportsIncludeFilter(includeFilter)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean indexSupportsIncludeFilter(TypeFilter filter) {
if (filter instanceof AnnotationTypeFilter) {
Class<? extends Annotation> annotation = ((AnnotationTypeFilter) filter).getAnnotationType();
return (AnnotationUtils.isAnnotationDeclaredLocally(Indexed.class, annotation) ||
annotation.getName().startsWith("javax."));
}
if (filter instanceof AssignableTypeFilter) {
Class<?> target = ((AssignableTypeFilter) filter).getTargetType();
return AnnotationUtils.isAnnotationDeclaredLocally(Indexed.class, target);
}
return false;
}
复制代码if分支中就是从META/spring.components索引文件中取出basePackage包下标有includeFilters中注解的类,isCandidateComponent()方法用来过滤此类是否可以作为BeanDefinition。isCandidateComponent()方法接收一个MetadataReader对象,该对象是由CachingMetadataReaderFactory根据bean的类名创建的一个SimpleMetadataReader实例,在构造方法内部使用了ClassReader用来解析class文件获取类的元数据信息。
final class SimpleMetadataReader implements MetadataReader {
private final Resource resource;
private final ClassMetadata classMetadata;
private final AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata;
SimpleMetadataReader(Resource resource, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) throws IOException {
InputStream is = new BufferedInputStream(resource.getInputStream());
ClassReader classReader;
try {
classReader = new ClassReader(is);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new NestedIOException("ASM ClassReader failed to parse class file - " +
"probably due to a new Java class file version that isn't supported yet: " + resource, ex);
}
finally {
is.close();
}
AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor visitor = new AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor(classLoader);
classReader.accept(visitor, ClassReader.SKIP_DEBUG);
this.annotationMetadata = visitor;
// (since AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor extends ClassMetadataReadingVisitor)
this.classMetadata = visitor;
this.resource = resource;
}
@Override
public Resource getResource() {
return this.resource;
}
@Override
public ClassMetadata getClassMetadata() {
return this.classMetadata;
}
@Override
public AnnotationMetadata getAnnotationMetadata() {
return this.annotationMetadata;
}
}
复制代码excludeFilters优先级高于includeFilters,通过includeFilters还需要ConditionEvaluator对条件的校验。
protected boolean isCandidateComponent(MetadataReader metadataReader) throws IOException {
for (TypeFilter tf : this.excludeFilters) {
if (tf.match(metadataReader, getMetadataReaderFactory())) {
return false;
}
}
for (TypeFilter tf : this.includeFilters) {
if (tf.match(metadataReader, getMetadataReaderFactory())) {
return isConditionMatch(metadataReader);
}
}
return false;
}
复制代码之后创建一个AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition对象,使用isCandidateComponent()重载方法在次判断是否符合Bean定义。
protected boolean isCandidateComponent(AnnotatedBeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
AnnotationMetadata metadata = beanDefinition.getMetadata();
return (metadata.isIndependent() && (metadata.isConcrete() ||
(metadata.isAbstract() && metadata.hasAnnotatedMethods(Lookup.class.getName()))));
}
复制代码判断是一个class是独立的,有两种情况:一.他是top-level的 二.他是nested class也就是静态内部类。
else分支遍历指定包下的所有类文件转换为MetadataReader对象,默认有@Component注解则认为符合bean的定义。
private Set<BeanDefinition> scanCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>();
try {
String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX +
resolveBasePackage(basePackage) + '/' + this.resourcePattern;
// 所有类路径下的.class文件
Resource[] resources = getResourcePatternResolver().getResources(packageSearchPath);
boolean traceEnabled = logger.isTraceEnabled();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
for (Resource resource : resources) {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Scanning " + resource);
}
if (resource.isReadable()) {
try {
// 用于访问类元数据
MetadataReader metadataReader = getMetadataReaderFactory().getMetadataReader(resource);
// 使用includeFilters和excludeFilters过滤候选类
if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) {
ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(metadataReader);
sbd.setResource(resource);
sbd.setSource(resource);
// 确定给定的bean定义是否符合候选条件:独立类、(非抽象||带有@Lookup的抽象类)
if (isCandidateComponent(sbd)) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Identified candidate component class: " + resource);
}
candidates.add(sbd);
}
else {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Ignored because not a concrete top-level class: " + resource);
}
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not matching any filter: " + resource);
}
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to read candidate component class: " + resource, ex);
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not readable: " + resource);
}
}
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("I/O failure during classpath scanning", ex);
}
return candidates;
}
复制代码Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

