[TOC]
前言
- 多路复用
单线程可以配合 Selector 完成对多个 Channel 可读写事件的监控,这称之为多路复用
-
多路复用仅针对网络 IO、普通文件 IO 没法利用多路复用
-
如果不用 Selector 的非阻塞模式,线程大部分时间都在做无用功,而 Selector 能够保证
-
有可连接事件时才去连接
-
有可读事件才去读取
-
有可写事件才去写入
- 限于网络传输能力,Channel 未必时时可写,一旦 Channel 可写,会触发 Selector 的可写事件
-
一、处理accept事件
- 服务器端代码
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* @author lilinchao
* @date 2022/6/2
* @description Accept事件
**/
@Slf4j
public class AcceptServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建Selector,可以管理多个channel
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
//2.建立channel和selector之间的联系(注册)
//SelectionKey:事件发生后通过这个可以获取到相应事件,以及对应事件发生的channel
SelectionKey sscKey = ssc.register(selector, 0, null);
//表名这个key只关注accept事件
sscKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
log.debug("register key:{}",sscKey);
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
while (true){
//3. selector.select()方法,没有事件就阻塞,有事件发送就恢复运行继续向下处理
selector.select();
//4.处理事件,selectionKeys内部包含了所有发生的事件
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
//注意,如果事件不调用accept进行处理,那么不会阻塞,因为事件没被处理,就不能阻塞
//也就是说事件要么处理要么取消,不能不管
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
log.debug("key:{}",key);
//拿到触发事件的channel
ServerSocketChannel channel = (ServerSocketChannel)key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = channel.accept();
log.debug("{}",sc);
}
}
}
}
- 客户端代码
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* @author lilinchao
* @date 2022/6/2
* @description 1.0
**/
public class AcceptClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", 8080)) {
System.out.println(socket);
socket.getOutputStream().write("world".getBytes());
System.in.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 运行
(1)启动服务端程序
(2)通过Debug模式启动客户端程序
(3)通过Debug模式再启动一个客户端程序
- 客户端启动项,选择【Edit Configurations】
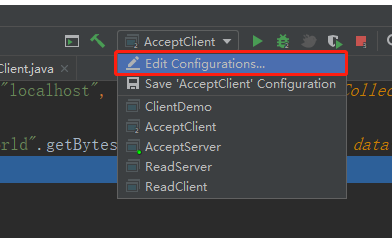
- 选择【Allow parallel run】,再点击【OK】
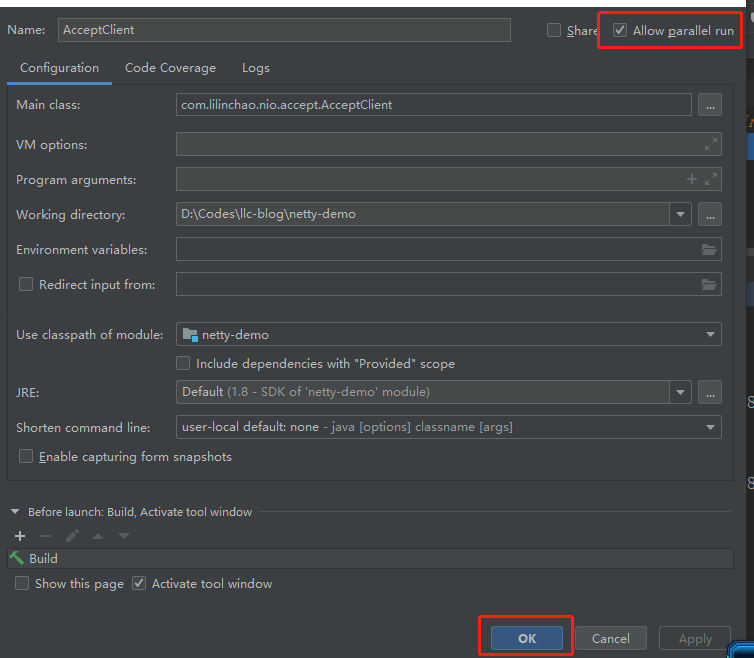
- 再通过Debug模式启动一个客户端
- 服务端程序输出结果
17:05:25.304 [main] DEBUG com.lilinchao.nio.accept.AcceptServer - register key:sun.nio.ch.SelectionKeyImpl@3b764bce
17:05:38.141 [main] DEBUG com.lilinchao.nio.accept.AcceptServer - key:sun.nio.ch.SelectionKeyImpl@3b764bce
17:05:38.142 [main] DEBUG com.lilinchao.nio.accept.AcceptServer - java.nio.channels.SocketChannel[connected local=/127.0.0.1:8080 remote=/127.0.0.1:51904]
17:05:55.911 [main] DEBUG com.lilinchao.nio.accept.AcceptServer - key:sun.nio.ch.SelectionKeyImpl@3b764bce
17:05:55.912 [main] DEBUG com.lilinchao.nio.accept.AcceptServer - java.nio.channels.SocketChannel[connected local=/127.0.0.1:8080 remote=/127.0.0.1:51919]
从打印结果可以看出有两个客户端向服务端发送了连接请求。
问题:事件发生后能否不处理?
事件发生后,要么处理,要么取消(cancel),不能什么都不做,否则下次该事件仍会触发,这是因为 nio 底层使用的是水平触发
二、处理read事件
- 服务端代码
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import static com.lilinchao.nio.util.ByteBufferUtil.debugAll;
/**
* @author lilinchao
* @date 2022/6/2
* @description Read事件 服务端
**/
@Slf4j
public class ReadServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建selector,管理多个channel
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
//2. 建立channel和selector之间的联系(注册)
SelectionKey sscKey = ssc.register(selector, 0, null);
sscKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
log.debug("register key:{}",sscKey);
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
while (true){
//3. selector.select()方法,没有事件就阻塞,有了事件发送了就恢复运行继续向下处理
selector.select();
//4. 处理事件,selectionKeys拿到所有发生的可读可写的事件
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
//多个key的时候,accept和read方法都会触发事件,所以要区分事件类型
while (iterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
//处理key的时候要从selectKeys中删除,否则会报错
iterator.remove();
log.debug("key:{}",key);
//5.区分事件类型
if(key.isAcceptable()){
//拿到触发事件的channel
ServerSocketChannel channel = (ServerSocketChannel)key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = channel.accept();
//设置为非阻塞
sc.configureBlocking(false);
//scKey管sc的channel
SelectionKey scKey = sc.register(selector, 0, null);
//scKey关注读事件,也就是说客户端的通道关注可读事件
scKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
log.debug("{}",sc);
}else if(key.isReadable()){
//客户端关闭之后也会引发read事件,这时需要从key中remove掉,否则拿不到channel,报错
try {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
//客户端正常断开,read返回值是-1
int read = channel.read(buffer1);
if(read == -1){
//正常断开
key.channel();
}
buffer1.flip();
debugAll(buffer1);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
key.cancel();//客户端断开,需要将key取消(从selector的key集合中真正删除)
}
}
}
}
}
}
- 客户端代码
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.SocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
/**
* @author lilinchao
* @date 2022/6/2
* @description Read事件 客户端
**/
public class ReadClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
SocketAddress localAddress = sc.getLocalAddress();
System.out.println("waiting...");
}
}
- 运行
(1)启动服务端程序
(2)Debug启动客户端程序
- 选择【Evalute Expression】
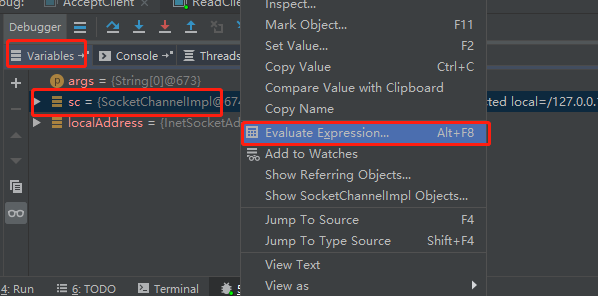
- 输入如下内容
sc.write(Charset.defaultCharset().encode("hello!"));
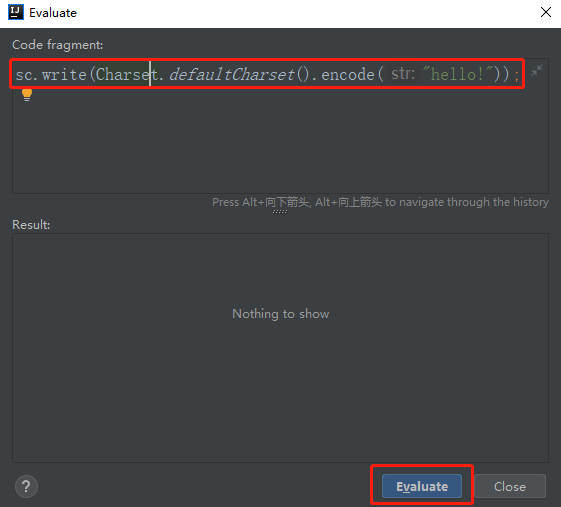
- 点击【Evaluate】提交
- 服务端输出结果
17:20:50.713 [main] DEBUG com.lilinchao.nio.read.ReadServer - register key:sun.nio.ch.SelectionKeyImpl@3b764bce
17:21:11.373 [main] DEBUG com.lilinchao.nio.read.ReadServer - key:sun.nio.ch.SelectionKeyImpl@3b764bce
17:21:11.374 [main] DEBUG com.lilinchao.nio.read.ReadServer - java.nio.channels.SocketChannel[connected local=/127.0.0.1:8080 remote=/127.0.0.1:52466]
17:23:48.603 [main] DEBUG com.lilinchao.nio.read.ReadServer - key:sun.nio.ch.SelectionKeyImpl@368102c8
17:23:48.653 [main] DEBUG io.netty.util.internal.logging.InternalLoggerFactory - Using SLF4J as the default logging framework
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [0], limit: [6]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 68 65 6c 6c 6f 21 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |hello!..........|
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
服务端监听到客户端的连接,并读取打印客户端发送过来的数据。
问题:为何要 iter.remove()
因为 select 在事件发生后,就会将相关的 key 放入 selectedKeys 集合,但不会在处理完后从 selectedKeys 集合中移除,需要我们自己编码删除。例如 > > * 第一次触发了 ssckey 上的 accept 事件,没有移除 ssckey > * 第二次触发了 sckey 上的 read 事件,但这时 selectedKeys 中还有上次的 ssckey ,在处理时因为没有真正的 serverSocket 连上了,就会导致空指针异常
问题:cancel 的作用
cancel 会取消注册在 selector 上的 channel,并从 keys 集合中删除 key 后续不会再监听事件
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

