回答
Executor执行器是 Mybatis 核心组件,它负责执行 SQL 语句并处理数据库的交互,主要包括 SQL 语句的生成、参数绑定、执行、缓存处理以及结果集的映射等。
Mybatis 内置了三种基本的Executor。
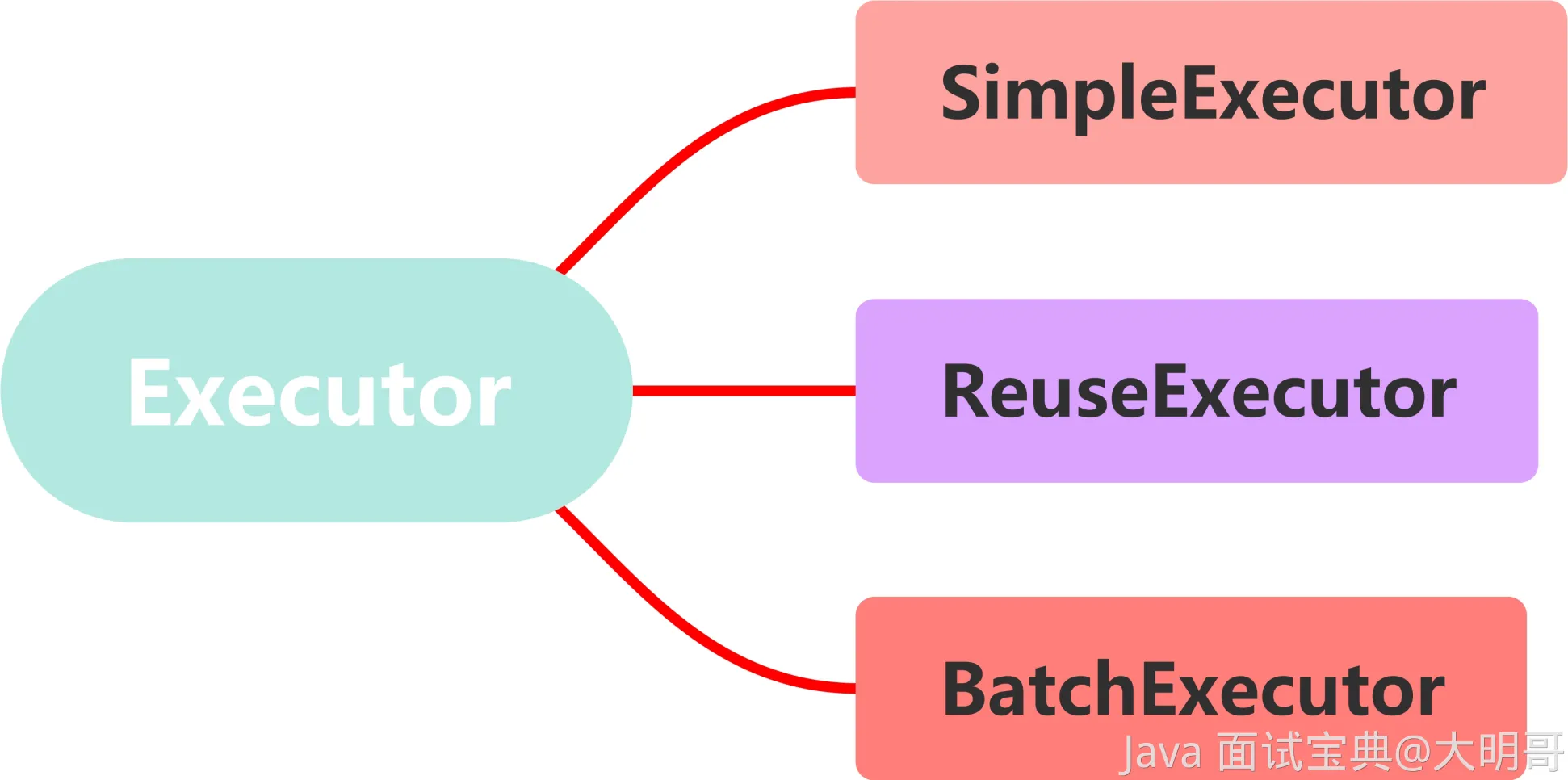
SimpleExecutor:每执行一次 update 或 select,就开启一个Statement对象,用完立刻关闭 Statement 对象。ReuseExecutor:执行 update 或 select,以 sql 作为 key 查找Statement对象,存在就使用,不存在就创建,用完后,不关闭 Statement 对象,而是放置于 Map<String, Statement>内,供下一次使用。BatchExecutor:支持批处理的执行器,支持批量更新操作,依赖 JDBC 的批处理。
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
// ExecutorType.SIMPLE 为默认执行器
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
// 批量执行器
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
// 复用执行器
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
// 简答执行器
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
// 缓存执行器
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
Executor 工作原理
- 获取 MappedStatement,每个 Mapper 方法在 MyBatis 配置中都有对应的
MappedStatement,它包含了 SQL 语句和配置信息。
// Map 缓存所有的 MappedStatement
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<MappedStatement>("Mapped Statements collection")
.conflictMessageProducer((savedValue, targetValue) ->
". please check " + savedValue.getResource() + " and " + targetValue.getResource());
// 根据全限定名得到 MappedStatement
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statementId);
- 生成 BoundSql:基于
MappedStatement生成BoundSql,包含了实际执行的 SQL 语句和参数。
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 从SqlSource得到BoundSql
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 获取 ParameterMapping
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings == null || parameterMappings.isEmpty()) {
boundSql = new BoundSql(configuration, boundSql.getSql(), parameterMap.getParameterMappings(), parameterObject);
}
// check for nested result maps in parameter mappings (issue #30)
for (ParameterMapping pm : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {
String rmId = pm.getResultMapId();
if (rmId != null) {
ResultMap rm = configuration.getResultMap(rmId);
if (rm != null) {
hasNestedResultMaps |= rm.hasNestedResultMaps();
}
}
}
return boundSql;
}
- 创建 ParameterHandler:负责将方法参数绑定到 SQL 语句的占位符中。
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = configuration.newParameterHandler(ms, parameterObject, boundSql);
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
// 创建 ParameterHandler 对象
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
// 插件执行
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
public class DefaultParameterHandler implements ParameterHandler {
@Override
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
// BoundSql 的参数映射列表
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
// 自定义 TypeHandler
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
// 参数设置
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException | SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
}
- 执行 SQL 语句:根据
Executor的不同实现,执行 SQL 语句。
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 新建 StatementHandler
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 预编译
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 执行 SQL 查询
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 获取待执行 SQL
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
// SQL 执行
statement.execute(sql);
// 结果集处理
return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(statement);
}
- 处理结果集:通过
**ResultHandler**进行处理和映射,转换为相应的 Java 对象。
public class DefaultResultSetHandler implements ResultSetHandler {
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(mappedStatement.getId());
final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<>();
int resultSetCount = 0;
// 结果集包装器
ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt);
// Mapper结果映射
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
// ResultMap 映射校验
validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
// 遍历映射结果集
while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
// JDBC ResultSet 映射处理
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null);
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
String[] resultSets = mappedStatement.getResultSets();
if (resultSets != null) {
while (rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping = nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
}
return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}
}
扩展
除了上述三种执行器,Mybatis还内置了 CachingExecutor,它通过二级缓存机制实现对数据库查询结果的缓存,适用于频繁读取、数据相对静态的场景。
CachingExecutor
CachingExecutor 是 MyBatis 实现二级缓存的执行器。它通过装饰模式在 Executor 的基础上增加了缓存功能,在查询数据库之前先检查缓存,如果缓存中有数据,则直接返回缓存中的数据,否则执行查询并将结果存入缓存。
- 提升性能。使用二级缓存,显著减少对数据库的访问次数。当数据已经缓存在内存中时,直接从缓存中读取,无需再次访问数据库。
- 数据一致性。执行更新操作、提交和回滚事务时会清空相关缓存,以确保缓存中的数据与数据库中的数据保持一致。通过
flushCacheIfRequired方法来实现。 - 事务支持。事务提交时,将事务中的缓存操作应用到二级缓存中;在事务回滚时,撤销未提交的缓存操作。通过
TransactionalCacheManager管理事务中的缓存操作。
Java 面试宝典是大明哥全力打造的 Java 精品面试题,它是一份靠谱、强大、详细、经典的 Java 后端面试宝典。它不仅仅只是一道道面试题,而是一套完整的 Java 知识体系,一套你 Java 知识点的扫盲贴。
它的内容包括:
- 大厂真题:Java 面试宝典里面的题目都是最近几年的高频的大厂面试真题。
- 原创内容:Java 面试宝典内容全部都是大明哥原创,内容全面且通俗易懂,回答部分可以直接作为面试回答内容。
- 持续更新:一次购买,永久有效。大明哥会持续更新 3+ 年,累计更新 1000+,宝典会不断迭代更新,保证最新、最全面。
- 覆盖全面:本宝典累计更新 1000+,从 Java 入门到 Java 架构的高频面试题,实现 360° 全覆盖。
- 不止面试:内容包含面试题解析、内容详解、知识扩展,它不仅仅只是一份面试题,更是一套完整的 Java 知识体系。
- 宝典详情:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/xvlo920axlp7sf4k
- 宝典总览:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/yogsehzntzgp4ly1
- 宝典进展:https://www.yuque.com/chenssy/sike-java/en9ned7loo47z5aw
目前 Java 面试宝典累计更新 400+ 道,总字数 42w+。大明哥还在持续更新中,下图是大明哥在 2024-12 月份的更新情况:

想了解详情的小伙伴,扫描下面二维码加大明哥微信【daming091】咨询

同时,大明哥也整理一套目前市面最常见的热点面试题。微信搜[大明哥聊 Java]或扫描下方二维码关注大明哥的原创公众号[大明哥聊 Java] ,回复【面试题】 即可免费领取。

