在上篇文章中,分析了启动的流程,遗留一个内部类ServerBootstrapAcceptor,
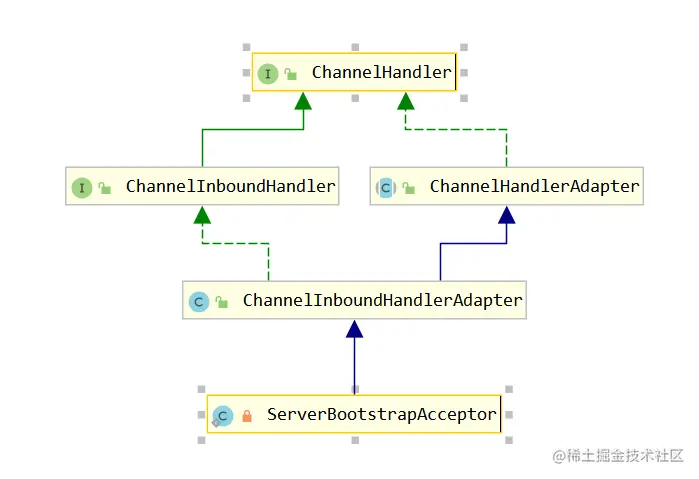
这个类其实是一个inBound,我们服务器启动的eveentloop线程会回调其channelRead方法
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
final Channel child = (Channel) msg;
child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler);
for (Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object> e: childOptions) {
try {
if (!child.config().setOption((ChannelOption<Object>) e.getKey(), e.getValue())) {
logger.warn("Unknown channel option: " + e);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Failed to set a channel option: " + child, t);
}
}
for (Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object> e: childAttrs) {
child.attr((AttributeKey<Object>) e.getKey()).set(e.getValue());
}
try {
//这里看到的代码和服务端注册异曲同工
//此处是按照顺序遍历获取eventloop,保证一个客户端channel对应一个eventloop
childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
forceClose(child, future.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
forceClose(child, t);
}
}
这部分代码得结合服务端启动的代码才更好理解,在服务端启动中,我们eventloop开启了一个线程,这个线程执行代码的关键逻辑如下,是个死循环:
@Override
protected void run() {
for (;;) {
try {
switch (selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) {
case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:
continue;
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:
select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false));
if (wakenUp.get()) {
selector.wakeup();
}
default:
// fallthrough
}
cancelledKeys = 0;
needsToSelectAgain = false;
final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;
//此处就是监听io和执行任务cpu分配时间占比
if (ioRatio == 100) {
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
// Ensure we always run tasks.
runAllTasks();
}
} else {
final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
// Ensure we always run tasks.
final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;
runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
// Always handle shutdown even if the loop processing threw an exception.
try {
if (isShuttingDown()) {
closeAll();
if (confirmShutdown()) {
return;
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
}
}
ioTime/taskTime = ioRatio/(100-ioRatio);
ioTime: 监听客户端io时间花费的时间 taskTime: 任务执行花费时间 ioRatio:监听客户端io时间占比 (100-ioRatio):任务执行时间占比
按照下面的流程一路追踪,就能找到ServerBootstrapAcceptor的channelRead被执行
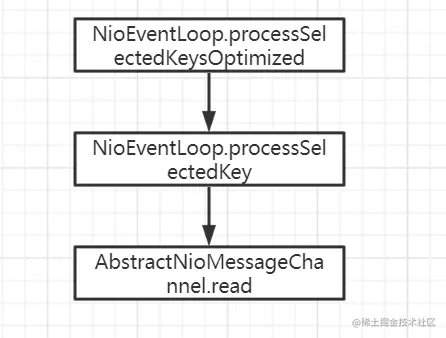
read方法如下:
@Override
public void read() {
assert eventLoop().inEventLoop();
final ChannelConfig config = config();
**//服务端pipeline**
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = unsafe().recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.reset(config);
boolean closed = false;
Throwable exception = null;
try {
try {
do {
int localRead = doReadMessages(readBuf);
if (localRead == 0) {
break;
}
if (localRead < 0) {
closed = true;
break;
}
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(localRead);
} while (allocHandle.continueReading());
} catch (Throwable t) {
exception = t;
}
int size = readBuf.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
readPending = false;
//此处是关键,会回调添加到pipechannel的handler,当前就剩ServerBootstrapAcceptor这一个自定义业务
pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i));
}
readBuf.clear();
allocHandle.readComplete();
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
if (exception != null) {
closed = closeOnReadError(exception);
pipeline.fireExceptionCaught(exception);
}
if (closed) {
inputShutdown = true;
if (isOpen()) {
close(voidPromise());
}
}
} finally {
// Check if there is a readPending which was not processed yet.
// This could be for two reasons:
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelRead(...) method
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelReadComplete(...) method
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2254
if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) {
removeReadOp();
}
}
}
}
在ServerBootstrapAcceptor的read方法中,和服务端注册差不多,只不过channel由服务端channel,即serverSocketChannel变为客户端channenl,即socketChannel
只不过这里的区别是, 会有多个线程池(exccutor)执行客户端socket的请求,每个线程池的就一个线程 , 可以理解我多线程,我理解,采用线程池,可以通知根据线程池状态来控制线程的创建,这里是通过CAS来防止并发。
SingleThreadEventExecutor
private void startThread() {
//此处根据状态决定是否重新创建新线程
if (STATE_UPDATER.get(this) == ST_NOT_STARTED) {
if (STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, ST_NOT_STARTED, ST_STARTED)) {
doStartThread();
}
}
}
