环境准备
1.Bean定义
@Component
public class LagouBean {
public void tech(){
System.out.println("java learning......");
}
}
2.Aspect定义
@Component
@Aspect
public class LagouAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.lagou.*.*(..))")
public void pointcut(){
}
@Before("pointcut()")
public void before() {
System.out.println("before method ......");
}
}
3.测试类如下:
/**
* 测试⽤例:Aop 代理对象创建
*/
@Test
public void testAopProxyBuild(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = newAnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
LagouBean lagouBean = applicationContext.getBean(LagouBean.class);
lagouBean.tech();
}
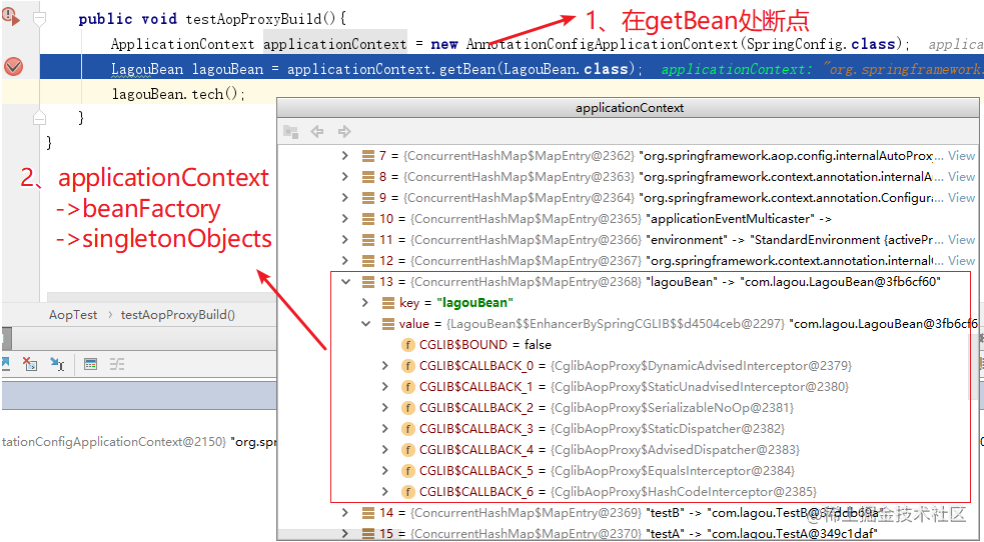 我们发现在 getBean 之前,LagouBean对象已经产⽣(即在第⼀⾏初始化代码中完成),⽽且该对象是⼀个代理对象(Cglib代理对象),我们断定,容器初始化过程中⽬标Ban已经完成了代理,返回了代理对象。
我们发现在 getBean 之前,LagouBean对象已经产⽣(即在第⼀⾏初始化代码中完成),⽽且该对象是⼀个代理对象(Cglib代理对象),我们断定,容器初始化过程中⽬标Ban已经完成了代理,返回了代理对象。
代理对象创建流程
入口:在bean实例化之后,并且填充完属性, 准备初始化 的时候。
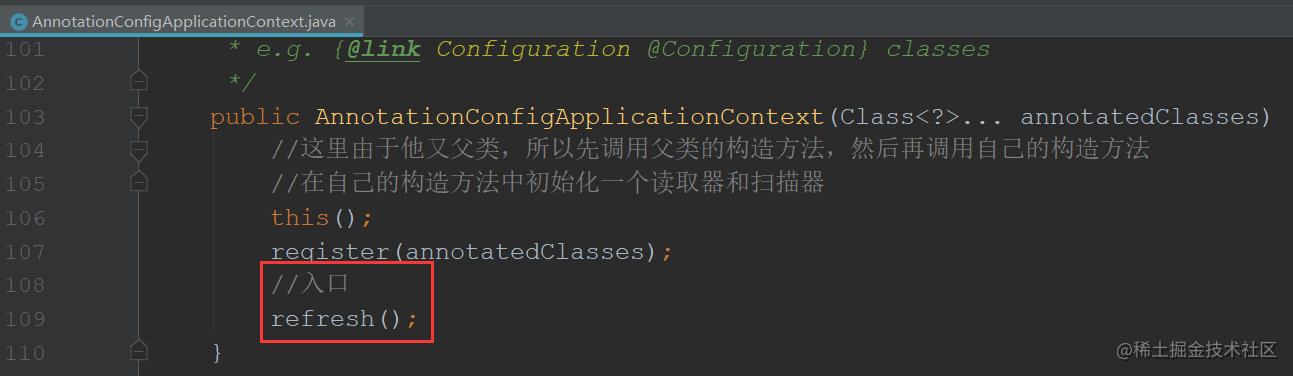
/**
* 该方法完成IOC容器创建以及初始化工作
* 该方法中最重要的是第二步和第十一步
*
*/
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
// STEP 1: 刷新预处理
//准备工作包括设置启动时间,是否激活标识位,初始化属性源(property,source)配置
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
//用DefaultListableBeanFactory的子类得到的是DefaultListableBeanFactory
//可以理解为初始化bean工厂
// STEP 2:
// a) 创建IoC容器(DefaultListableBeanFactory)
// b) 加载解析XML文件(最终存储到Document对象中)
// c) 读取Document对象,并完成BeanDefinition的加载和注册工作
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
//最重要的方法,准备bean工厂
// STEP 3: 对IoC容器进行一些预处理(设置一些公共属性)
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
//这个方法在当前版本的spring是没有任何代码的,可能spring期待在后面的版本中进行扩展
//空壳方法
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
//比较重要的方法
//在spring的环境中去执行已经被注册的factory processors
//设置执行自定义的ProcessorFactory和spring内部自己定义的(ConfigutationClassPoetProcessor)
//ConfigurationClassPostProcessor就是spring内部自己维护的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
//下面的方法主要执行ConfigurationClassPostProcessor中的方法
// STEP 5: 调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor后置处理器对BeanDefinition处理
/**
* BeanFactoryPostProcessor是spring的扩展点之一
* 实现该接口,可以在spring的bean创建之前修改bean的定义属性
* spring允许BeanFactoryPostProcessor在容器实例化任何其他bean之前读取它配置的元数据
* 并可以根据需要进行修改,例如可以把bean的scope从singleton改为prototype,也可以把property的值给修改
* 可以同时配置多个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,并且通过设置'order'属性来控制各个BeanFactoryPostProcessor
* BeanFactoryPostProcessor是在spring容器加载了bean的定义文件之后,在bean实例化之前执行的
* 可以写一个例子来测试以下这个功能
*/
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
//上一行的代码已经将一些后置处理器放到bdMap中了,包括自定义的BeanPostProcessor
// 注册BeanPostProcessor,即后置处理器,一共是7个
//把bdMap中的所有后置处理器拿出来,
// 再直接new另外一些后置处理器,一起放到工厂的list中
// STEP 6: 注册BeanPostProcessor后置处理器
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
//不重要,国际化的处理
// STEP 7: 初始化一些消息源(比如处理国际化的i18n等消息源)
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
//事件处理,用的比较少,不重要
// STEP 8: 初始化应用事件广播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
//这是一个空壳方法,里面没有代码
// STEP 9: 初始化一些特殊的bean
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
//对一些监听器的注册,先放一放
// STEP 10: 注册一些监听器
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//重点,重点
//完成bean的实例化
// STEP 11: 实例化剩余的单例bean(非懒加载方式)
// 注意事项:Bean的IoC、DI和AOP都是发生在此步骤
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// STEP 12: 完成刷新时,需要发布对应的事件
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
查看finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);,如下:
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
//省略不重要的代码
//最重要的代码
//这里调用的DefaultListableBeanFactory中的preInstantiateSingletons
//实例化所有的单例对象
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
接着:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons
//真正调用这里,重点
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
//从bdMap拿到所有需要初始化的类
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
//这行代码不重要,合并父类的bd,这种应用很少用
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
//肯定会进到if中
//如果bean不是抽象的,而且是单例的,同时还不是懒加载的,则进行下面的操作
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
//这里判断是不是FactoryBean
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Boolean>)
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
//重点
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
}
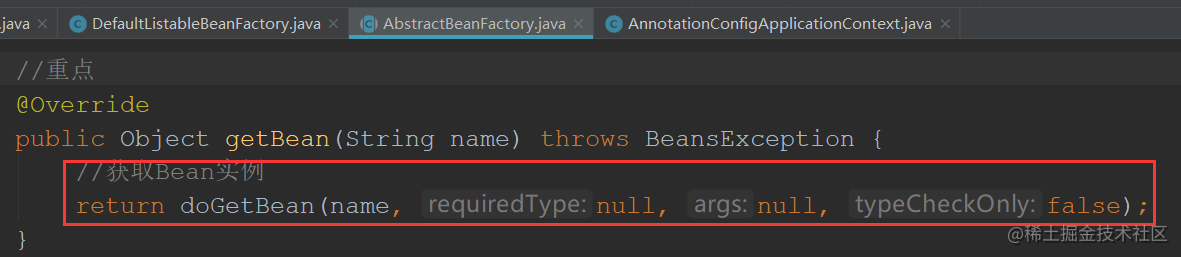
protected <T> T doGetBean(final String name, @Nullable final Class<T> requiredType,
@Nullable final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException {
// 省略不重要代码
//重点重点
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
/**
* getSingleton相当于从缓存中根据beanName取出对象,
* 如果取不到,就回调下面的匿名内部类的createBean方法
*/
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
//重点
//真正调用AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory中的createBean方法
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
}
return (T) bean;
}
接着查看org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean方法
@Override
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
//省略不重要代码
try {
//真正实例化bean(还有填充属性,初始化)的方法在这一行
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
return beanInstance;
}
}
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
//BeanWrapper把真实对象包装了一层,该类中的getWrappedInstance返回真实对象
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
//开始创建真实对象的包装类,利用反射
//默认调用无参构造实例化bean
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
//这里从包装类中拿出的是原生对象,而不是代理对象,接着下面的操作把原生对象变成代理对象
final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
//重要,牛逼
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
/**
* 解决循环依赖的关键步骤
*/
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
//如果要提前暴露单理bean,则将该bean加入到三级缓存中
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
//重要,一定要进去看看
//把创建出来的对象放入相应的map中
//将刚创建的bean放入到三级缓存中 singleFactories(key是besnName,value是FactoryBean)
//singletonFactory是通过lamda表达式获取得到的
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
//赋值属性的,重要
//主要借助Common和Autowired两个后置处理器来填充属性
//bean初始化第二步:填充属性(DI依赖注入发生在此步骤)
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
/**
* 重点,这里就是把原生对象变成代理对象的地方
* bean初始化第三步:调用初始化方法,完成bean的初始化,aop发生在此步骤
* 例如<besn init-method=""></besn>中的init-method方法就是在这里调用的
*/
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
return exposedObject;
}
创建代理对象在上述代码中的exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);这一行代码。
/**
* 重点,该方法就是把原生对象变成代理对象的
*/
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//重点
/**
* 前置处理器
* 执行BeanPostProcessor的Beforexxx方法,执行完before方法后还是原生对象
* 还没完成代理,执行完Afterxxx方法,就完成代理
* 执行BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
* 即该部分在初始化方法执行之前调用
*/
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
//重点:执行初始化方法(先调用InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet,再调用init-method属性指定的初始化方法)
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//后置处理器
//该部分在初始化方法执行之后调用
//重点
//aop在这里完成
//执行完后置处理器的Afterxxx方法,把原生对象变成代理对象
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
接着上述代码中的wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);这一行代码。
//重点重点,该方法就是把原生对象变成代理对象的
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
//下面会有很多的后置处理器,但是是通过AnnotationAutoProxyCreator完成代理的
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
//但是AnnotationAutoProxyCreator中没有这个方法
//具体调用AbstractAutoProxyCreator中的postProcessAfterInitialization方法
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
创建代理对象的后置处理器 AbstractAutoProxyCreator #postProcessAfterInitialization中,因为 AbstractAutoProxyCreator 也实现了 BeanPostProcessor 接口。
/**
* 具体调用该方法完成代AOP理
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
//重点,具体调用该方法
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
接着查看wrapIfNecessary方法
/**
* 真正调用该方法完成代理
*/
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
//拦截器器作用跟切面一样,通过解析拿出所有的切面
/**
* 然后查看你的bean是否符合切面的切点表达式,即execution.....,如果符合就就行理
* 否则不景行代理
*/
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
//最重要的这行代码中的createProxy方法完成代理
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
接着createProxy方法
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
//创建代理工厂对象,用于产生代理对象
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
//如果没有使用CGLIB代理
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
//比较重要
//获取所有关联的Advisor集合
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
//该方法完成代理
//proxyFactory中加入了拦截器或者切面
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
接着:org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory#getProxy方法,
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
//1.创建JDK方式的AOP代理或者CGLIB方式的AOP代理
//2.调用具体的AopProxy来创建Proxy代理对象
return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader);
}
1.先查看org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyCreatorSupport#createAopProxy方法
protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() {
if (!this.active) {
activate();
}
//具体调用DefaultAopProxyFactory中的createAopProxy方法
return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this);
}
接着org.springframework.aop.framework.DefaultAopProxyFactory#createAopProxy方法
//重点
@Override
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
//config.isProxyTargetClass()是判断是jdk还是cglib,ProxyTargetClass=true就是cglib
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
//如果该类是接口的话,走jdk动态代理
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
//该类没有实现接口走cglib动态代理
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
//这里是jdk动态代理
//重点,真正调用JdkDynamicAopProxy中的getProxy方法
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}
因为当前咱们演示的bean没有实现接口,所以走Cglib动态代理,所以最终执行return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);这行代码创建出AopProxy对象。
2.回到上面的getProxy方法,由于走的Cglib动态代理,所以执行org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy#getProxy方法,如下;
@Override
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating CGLIB proxy: target source is " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
try {
Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");
Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;
if (ClassUtils.isCglibProxyClass(rootClass)) {
proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();
Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {
this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);
}
}
// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.
validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);
// Configure CGLIB Enhancer...
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
if (classLoader != null) {
enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&
((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
}
}
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareUndeclaredThrowableStrategy(classLoader));
Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
// fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call above
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(
this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.
return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
}
catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() +
": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// TargetSource.getTarget() failed
throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);
}
}
看到了Enhancer类就知道了这底层确实是通过Cglib动态代理来创建代理对象的。
