小知识,大挑战!本文正在参与“程序员必备小知识”创作活动。
我们项目中经常使用Spring的BeanUtils.copyProperties()方法,进行对象之间属性的拷贝,来替换繁琐的get()、set()方法。但是稍加不注意,使用此方法就会出现意向不到的问题。今天就聊聊常见的坑,并从源码角度分析问题出现的原因。
常见的「坑」
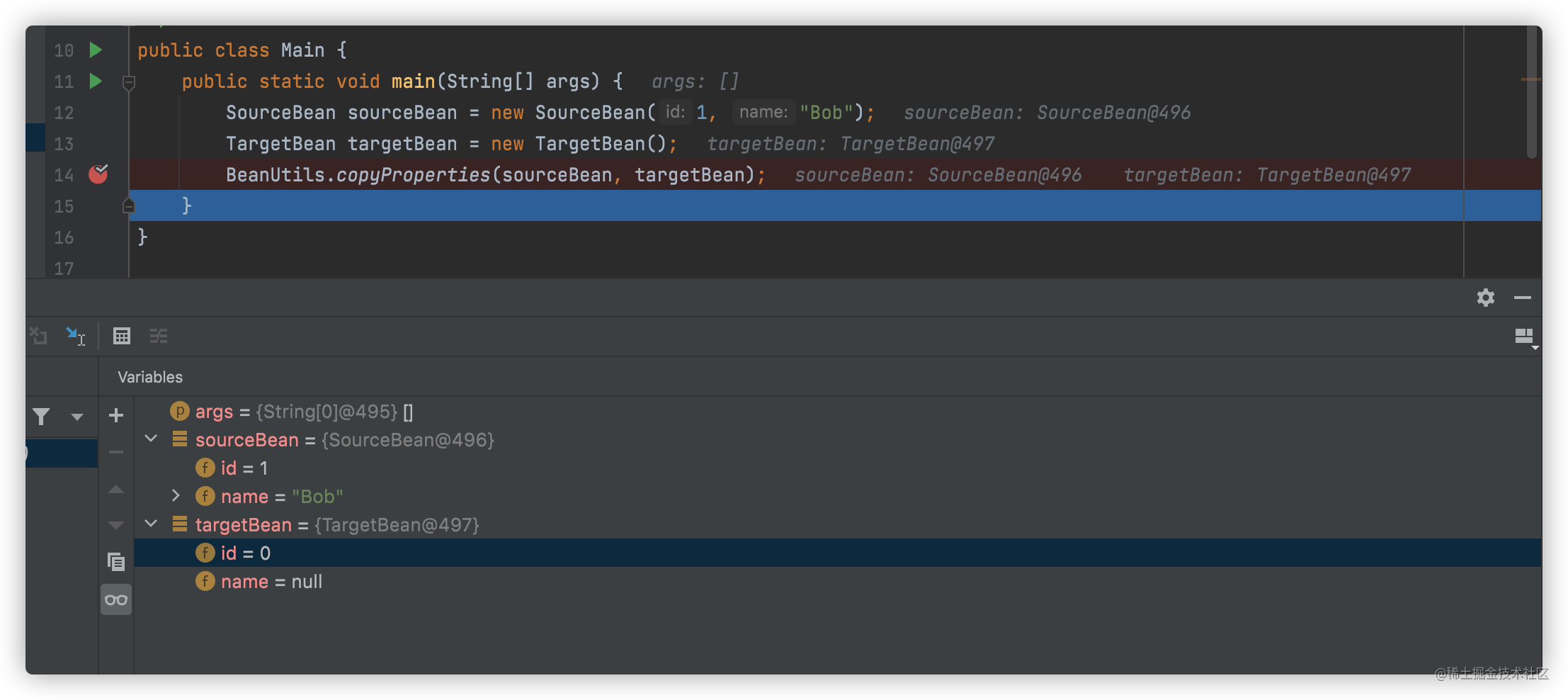
1. 不声明属性的get、set方法,属性将copy失败
实际项目中通常使用Lombok插件的@Data注解以省略get、set方法
public class SourceBean {
private int id;
private String name;
public SourceBean() {
}
public SourceBean(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
}
public class TargetBean {
private int id;
private String name;
public TargetBean() {
}
public TargetBean(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
}
从调试情况看,target属性并未拷贝成功。
2. copy为浅拷贝(拷贝对象的引用)
@Data
public class SourceBean {
private int id;
private String name;
private Map<String, String> content;
}
@Data
public class TargetBean {
private int id;
private String name;
private Map<String, String> content;
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SourceBean sourceBean = new SourceBean();
Map<String, String> sourceContent = new HashMap<>();
sourceContent.put("name", "Bob");
sourceBean.setContent(sourceContent);
TargetBean targetBean = new TargetBean();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(sourceBean, targetBean);
// targetBean内容
System.out.println(targetBean.getContent().get("name"));
// 只修改sourceBean内容
sourceBean.getContent().put("name", "Peter");
// targetBean内容同时被修改
System.out.println(targetBean.getContent().get("name"));
}
}
// 控制台输出结果
Bob
Peter
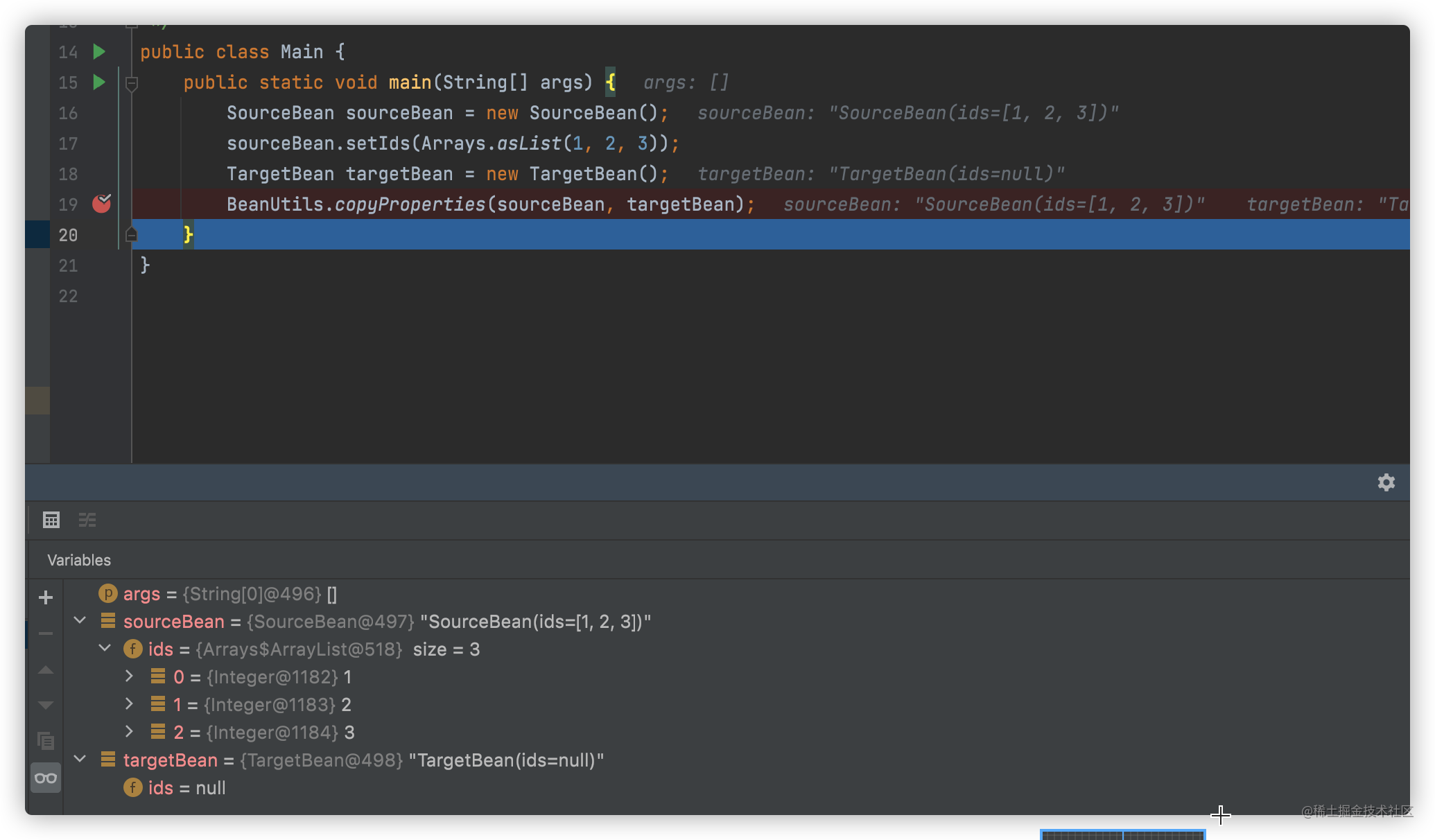
3. Spring不同版本对属性泛型处理方式不同
Spring5.3之后,匹配源对象和目标对象中的属性时遵循泛型类型信息,意思是copy属性时,会判断属性的泛型是否一致,如不一致,直接忽略属性的拷贝。
@Data
public class SourceBean {
private List<Integer> ids;
}
@Data
public class TargetBean {
private List<String> ids;
}
5.3.8版本运行情况:targetBean的ids依旧为null
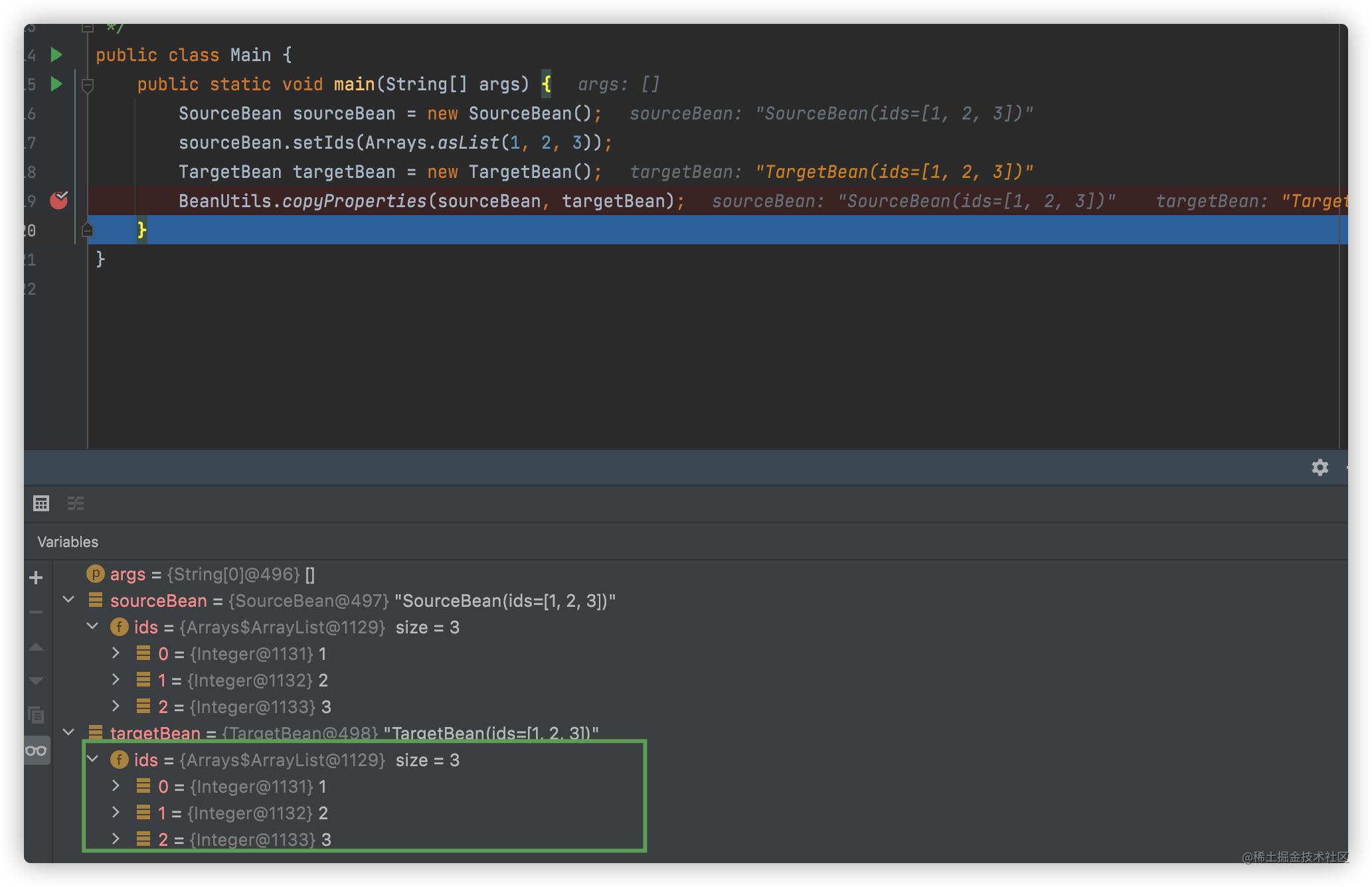
5.2.10版本运行情况:targetBean的ids拷贝了sourceBean的ids
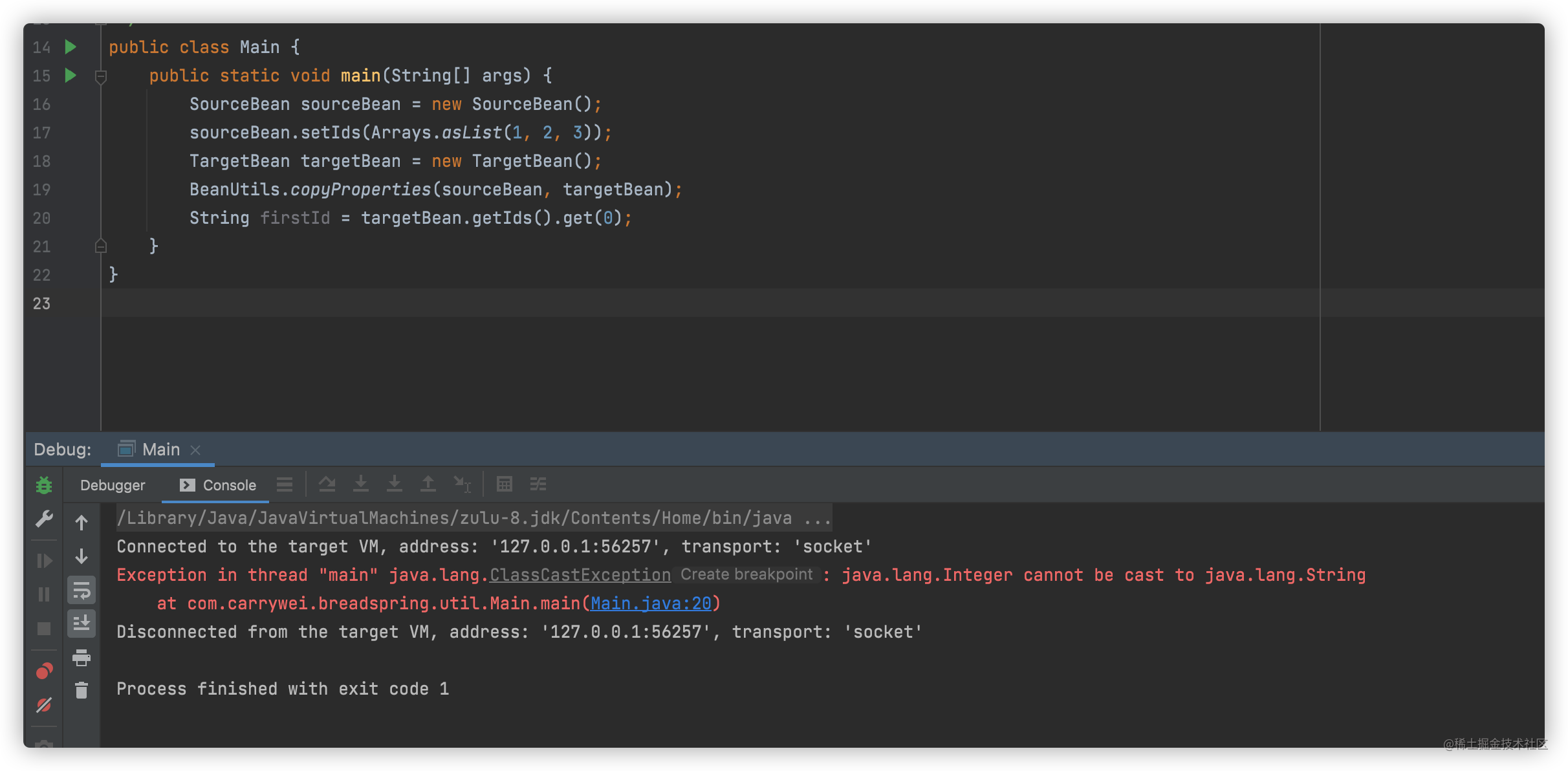
4. TargetBean拷贝的成员属性实际类型可能跟声明不一致
属性有泛型时会发生,可能会导致运行出错。 还是上面的Bean,执行以下代码,运行时将会抛出异常
public static void main(String[] args) {
SourceBean sourceBean = new SourceBean();
sourceBean.setIds(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));
TargetBean targetBean = new TargetBean();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(sourceBean, targetBean);
String firstId = targetBean.getIds().get(0);
}
BeanUtils.copyProperties()源码解析
上面所说的常见的「坑」,翻看Spring的BeanUtils.copyProperties()方法源码,就很容易发现问题出现的原因。
源码核心部分(5.3.8版本):
private static void copyProperties(Object source, Object target, @Nullable Class<?> editable,
@Nullable String... ignoreProperties) throws BeansException {
// ... 其他
Class<?> actualEditable = target.getClass();
//... 其他
// 获取目标类的所有属性描述(PropertyDescriptor,主要包括属性名称和其相关的读写方法即set、get方法)
PropertyDescriptor[] targetPds = getPropertyDescriptors(actualEditable);
// ... 其他
// 遍历所有属性,为每个属性赋值
for (PropertyDescriptor targetPd : targetPds) {
// 获取属性的set方法
Method writeMethod = targetPd.getWriteMethod();
if (writeMethod != null && (ignoreList == null || !ignoreList.contains(targetPd.getName()))) {
// 获取targetBean属性对应sourceBean的属性描述
PropertyDescriptor sourcePd = getPropertyDescriptor(source.getClass(), targetPd.getName());
if (sourcePd != null) {
// sourceBean属性的读方法,即get方法
Method readMethod = sourcePd.getReadMethod();
if(readMethod != null) {
ResolvableType sourceResolvableType = ResolvableType.forMethodReturnType(readMethod);
ResolvableType targetResolvableType = ResolvableType.forMethodParameter(writeMethod, 0);
// 判断属性类型是否一致,包括泛型是否一致
boolean isAssignable =
(sourceResolvableType.hasUnresolvableGenerics() || targetResolvableType.hasUnresolvableGenerics() ?
ClassUtils.isAssignable(writeMethod.getParameterTypes()[0], readMethod.getReturnType()) :
targetResolvableType.isAssignableFrom(sourceResolvableType));
if (isAssignable) {
try {
if (!Modifier.isPublic(readMethod.getDeclaringClass().getModifiers())) {
readMethod.setAccessible(true);
}
// 通过反射,调用get方法,获取source属性的值
Object value = readMethod.invoke(source);
if (!Modifier.isPublic(writeMethod.getDeclaringClass().getModifiers())) {
writeMethod.setAccessible(true);
}
// 通过反射,调用set方法,将source属性的值赋值给target的属性
writeMethod.invoke(target, value);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new FatalBeanException(
"Could not copy property '" + targetPd.getName() + "' from source to target", ex);
}
}
}
}
}
}
从源码可以看出:
- sourceBean和targetBean的属性的拷贝,是通过反射中的Method完成的,所以如果Bean不声明属性的set和get方法,则不能属性间的copy。
- Method的invoke方法,只是把sourceBean的get方法获取的值通过targetBean的set方法设置,所以并不涉及深拷贝,只是拷贝属性的引用。
- 上面的源码,有一步:属性的泛型是否一致判断。
boolean isAssignable =
(sourceResolvableType.hasUnresolvableGenerics() || targetResolvableType.hasUnresolvableGenerics() ?
ClassUtils.isAssignable(writeMethod.getParameterTypes()[0], readMethod.getReturnType()) :
targetResolvableType.isAssignableFrom(sourceResolvableType));
而在Spring 5.3.0之前并没有这一步,其判断方式:
ClassUtils.isAssignable(writeMethod.getParameterTypes()[0], readMethod.getReturnType()))
- 在5.3.0之前没有泛型的判断,所以通过反射的方法赋值会出现实际的类型与声明的不一致。
总结
BeanUtils.copyProperties()更适合简单Bean之间拷贝,如果Bean属性复杂,很容易因为浅拷贝导致一系列的问题。而且copyProperties方法实现过程并不简单,相对于直接用get和set方法赋值,其性能开销更大。
