Spring是一个Java开发框架,核心内容包括spring-ioc、spring-aop等组件,支持对象的控制反转,依赖自动注入.
学习Spring是每一个Java开发者都要做的事,正所谓读万卷书不如行万里路,所以在此开始练习完善一个Spring框架,今天首先模拟一个简单的ioc容器实现过程.
Spring在进行ioc时,首先要确定容器包含类的范围,然后将此范围内的所有被标记的类加载到容器中,最后对这些类进行初始化,生成对象并存储在容器中.
步骤:
- 得到包扫描路径
- 扫描路径,将路径下所有class文件存储
- 初始化对象,存入容器
所有的系统都存在一个入口,Java程序中就是启动类的main方法,我们可以通过在启动类上增加注解, 利用注解记录包扫描的路径
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ComponentScan {
//包扫描路径
String value() default "";
}
首先,新建容器ApplicationContext,创建容器时将将启动类的class对象作为参数初始化容器
public class ApplicationContext {
private Class<?> clazz;
public ApplicationContext(Class<?> clazz) {
this.clazz = clazz;
}
public void run() {
//1.获取扫描路径
ComponentScan componentScan = clazz.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
String basePackage = componentScan.value();
}
}
在启动类上加上@Component,启动后检测该注解的value,解析为包路径
@ComponentScan(value = "com.spring")
public class SpringApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ApplicationContext(SpringApplication.class);
context.run();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
sc.next();
}
}
我们需要把该路径下的所有被标记的类加载到容器中,这里使用的标记是注解@Component
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Component {
//别名
String value() default "";
}
加载包路径下的class文件
public class ApplicationContext {
...
//存储bean的class对象
private final Map<String, Class<?>> beanClassMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//存储bean的容器
private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public void run() {
//扫描包文件
//1.获取扫描路径
ComponentScan componentScan = clazz.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
String basePackage = componentScan.value();
String path = basePackage.replace('.', '/');
try {
//获取该路径下的文件
Enumeration<URL> dirs = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResources(path);
while (dirs.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = dirs.nextElement();
String filePath = URLDecoder.decode(url.getFile(), "UTF-8");
//获取包路径的File对象
File file = new File(filePath);
File[] files = file.listFiles();
//这里转成List是为了使用广度优先遍历,需要add待扫描文件夹
List<File> fileList = new ArrayList<>();
for (File file1 : files) {
fileList.add(file1);
}
//广度优先遍历
for (int i = 0; i < fileList.size(); i++) {
File file1 = fileList.get(i);
if (file1.isDirectory()) {
File[] files1 = file1.listFiles();
if (files1==null) {
continue;
}
for (File file2 : files1) {
//存在子文件则直接加入遍历队列
fileList.add(file2);
}
continue;
}else {
//扫描.class文件
if (file1.getName().endsWith(".class")) {
String className = file1.getName().substring(0, file1.getName().length() - 6);
try {
String absolutePath = file1.getAbsolutePath();
int i1 = absolutePath.indexOf(path.replace("/", "\\"));
String substring = absolutePath.substring(i1);
substring = substring.replace('\\', '.').substring(0, substring.length() - 6);
//这里是因为发现在使用过程中会出现以$1结尾的.class文件,所以处理一下
if (substring.endsWith("$1")) {
continue;
}
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(substring);
beanClassMap.put(clazz.getCanonicalName(), clazz);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("包扫描error: ", e);
}
//将类注入进容器
Set<Map.Entry<String, Class<?>>> entries = beanClassMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Class<?>> entry : entries) {
String beanName = entry.getKey();
Class<?> beanClass = entry.getValue();
//检查是否包含@Component注解
if (beanClass.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
if (!singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) {
Object bean = null;
try {
//简单粗暴
bean = beanClass.newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
log.error("反射bean出现错误,beanName: {}", beanName, e);
}
singletonObjects.put(beanName, bean);
}
}
}
}
}
然后我们在com.spring目录下新建两个类,一个使用注解,一个不使用
@Component
public class Test1 {
}
public class Test2 {
}
运行后可以看到,beanClassMap扫描到了com.spring下的所有.class对象,然后将包含@Component注解的对象注入到容器中
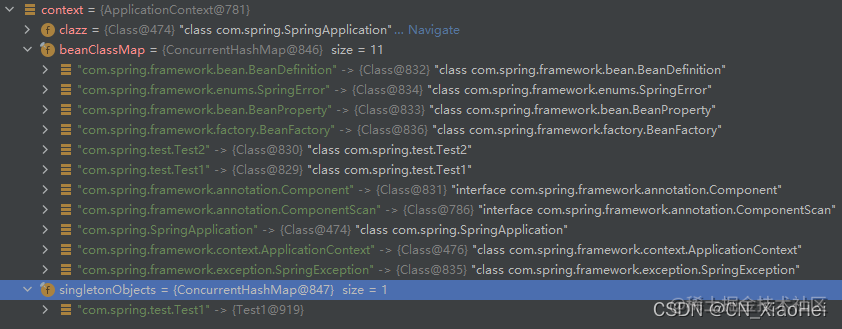 一个简易的ioc容器就完成啦.
一个简易的ioc容器就完成啦.
