Spring 是如何解决循环依赖的?
循环依赖:
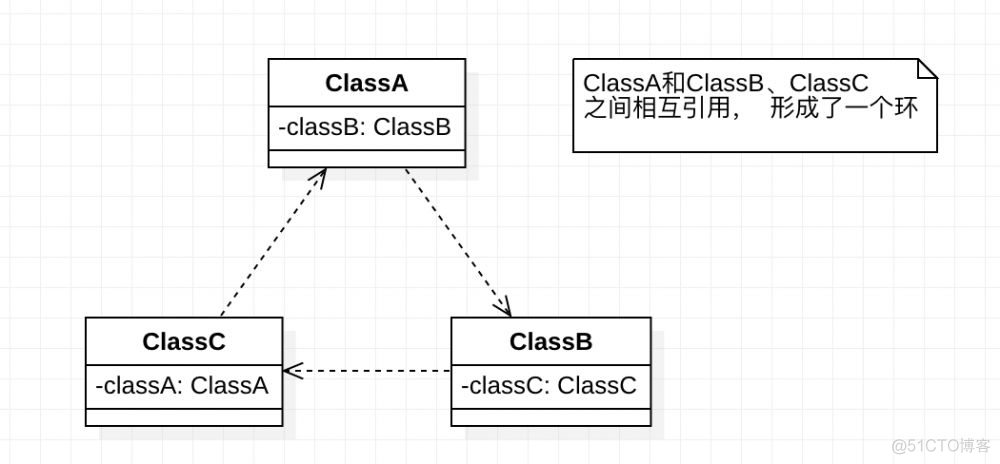
Spring 循环依赖有三种情况:
- 构造器的循环依赖,这种依赖 Spring 无法处理,直接抛出 BeanCurrentlyInCreationException 异常
- 单例模式下的 setter 循环依赖,可以通过三级缓存处理
- 非单例循环依赖,无法处理,BeanCurrentlyInCreationException 异常
构造器循环依赖
正要创建的 bean 记录在缓存中,Spring 容器架构一个正在创建的 bean 标识符放在一个 “当前创建 bean 池”中国, 因此如果在创建 Bean 过程中,如果发现已经在当前创建的 Bean 池中,则抛出 BeanCurrentlyInCreationException 异常表示循环依赖,对于创建完毕的 Bean 将从“当前创建 Bean 池”中清除。 先看个例子:
// StudentA
public class StudentA {
private StudentB studentB ;
public void setStudentB(StudentB studentB) {
this.studentB = studentB;
}
public StudentA() {
}
public StudentA(StudentB studentB) {
this.studentB = studentB;
}
}
// StudentB
public class StudentB {
private StudentC studentC ;
public void setStudentC(StudentC studentC) {
this.studentC = studentC;
}
public StudentB() {
}
public StudentB(StudentC studentC) {
this.studentC = studentC;
}
}
// StudentC
public class StudentC {
private StudentA studentA ;
public void setStudentA(StudentA studentA) {
this.studentA = studentA;
}
public StudentC() {
}
public StudentC(StudentA studentA) {
this.studentA = studentA;
}
}
xml 配置
<bean id="a" class="com.student.StudentA">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="b"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="b" class="com.student.StudentB">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="c"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="c" class="com.student.StudentC">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="a"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
测试代码
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//System.out.println(context.getBean("a", StudentA.class));
}
}
报错如下:
caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCurrentlyInCreationException:
Error creating bean with name 'a': Requested bean is currently in creation: Is there an unresolvable circular reference?
Setter 注入(单例)
<!--scope="singleton"(默认就是单例方式) -->
<bean id="a" class="com.student.StudentA" scope="singleton">
<property name="studentB" ref="b"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="b" class="com.student.StudentB" scope="singleton">
<property name="studentC" ref="c"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="c" class="com.student.StudentC" scope="singleton">
<property name="studentA" ref="a"></property>
</bean>
测试代码
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
System.out.println(context.getBean("a", StudentA.class));
}
}
运行时不会报错的.
Setter 注入(非单例模式)
对于 prototype 作用域的 Bean ,Spring 容器无法完成依赖注入,因为 Prototype 作用域的bean ,sring 不进行缓冲,无法提提前暴露一个创建中的Bean。会抛出异常。
<bean id="a" class="com.student.StudentA" scope="prototype">
<property name="studentB" ref="b"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="b" class="com.student.StudentB" scope="prototype">
<property name="studentC" ref="c"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="c" class="com.student.StudentC" scope="prototype">
<property name="studentA" ref="a"></property>
</bean>
测试代码
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//System.out.println(context.getBean("a", StudentA.class));
}
}
报错
Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCurrentlyInCreationException:
Error creating bean with name 'a': Requested bean is currently in creation: Is there an unresolvable circular reference?
Spring Bean 创建过程
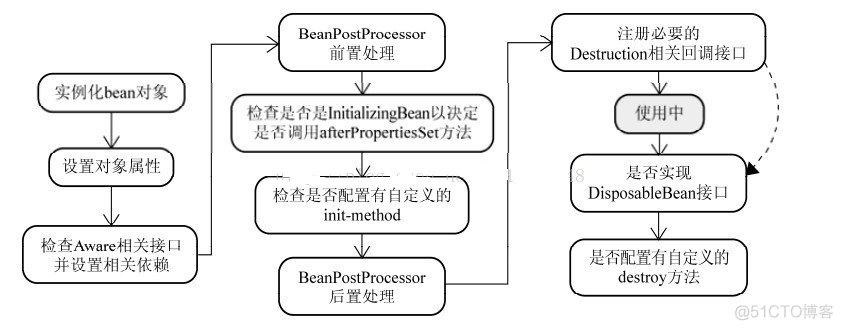
- 实例化 Bean 对象,createBeanInstance 实例化
- 设置 Bean 属性,populateBean 填充属性
- 通过 各种 Aware 接口声明了依赖关系,则会注入 Bean 对容器基础设施层面的依赖,包括 BeanNameAware、BeanFactoryAware 和 ApplicationContextAware 分别注入 BeanID, BeanFactory 或者 ApplicationContext。
- 调用 BeanPostProcessor 的前置初始化方法 postProcessBeforeInitialization
- 如果实现了 InitializingBean 接口,会调用 afterProperties 方法。
- 调用 Bean 自定义的 init 方法,initializeBean 调用 xml 的 init方法
- 调用 BeanPostprocessor 的后缀初始方法 postProcessAfterInitialization。
- 创建过程完毕。
Spring 是如何解决单例的循环依赖问题的呢?
Spring 采用的三级缓存解决了单例的循环依赖问题。
三级缓存:
Spring 源码 DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java 中:
/** Cache of singleton objects: bean name --> bean instance */
一级缓存:维护着所有创建完成的Bean
private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>(256);
/** Cache of early singleton objects: bean name --> bean instance */
二级缓存:维护早期暴露的Bean(只进行了实例化,并未进行属性注入)
private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new HashMap<String, Object>(16);
/** Cache of singleton factories: bean name --> ObjectFactory */
三级缓存:维护创建中Bean的ObjectFactory(解决循环依赖的关键)
private final Map<String, ObjectFactory<?>> singletonFactories = new HashMap<String, ObjectFactory<?>>(16);
public void registerSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) throws IllegalStateException {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "'beanName' must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
Object oldObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (oldObject != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not register object [" + singletonObject +
"] under bean name '" + beanName + "': there is already object [" + oldObject + "] bound");
}
// 如果是新的bean 也会调用这个方法,这个方法是往一级缓存中set 值的 getSingleton()中也会调用
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
}
/**
* 添加单例实例
* 解决循环引用的问题
* Add the given singleton factory for building the specified singleton
* if necessary.
* <p>To be called for eager registration of singletons, e.g. to be able to
* resolve circular references.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param singletonFactory the factory for the singleton object
*/
protected void addSingletonFactory(String beanName, ObjectFactory singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(singletonFactory, "Singleton factory must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// 一级缓存实例化 bean 中不包含 正创建的 bean
if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) {
// 三级缓存中添加
this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory);
// 二级缓冲删除
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
}
AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean()
protected T doGetBean(final String name, @Nullable final Class requiredType,
@Nullable final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException {
// 尝试通过bean名称获取目标bean对象,比如这里的A对象
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
// 我们这里的目标对象都是单例的
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 这里就尝试创建目标对象,第二个参数传的就是一个ObjectFactory类型的对象,这里是使用Java8的lamada
// 表达式书写的,只要上面的getSingleton()方法返回值为空,则会调用这里的getSingleton()方法来创建
// 目标对象
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
// 尝试创建目标对象
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
} catch (BeansException ex) {
throw ex;
}
});
}
return (T) bean;
}
getSingleton 可以这样理解:
- 先从一级缓冲中看有没有创建好的 bean ,有就直接返回。
- 如果没有,那么从二级缓存中看有没有创建 半成品的 Bean,如果有,直接返回
- 如果没有,从三级缓存中看下有没有创建过程中的 bean,还没有 那么通过 singletonFactory.getObject 最后到 createBean 创建。
@Nullable
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// 尝试从缓存中获取成品的目标对象,如果存在,则直接返回
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
// 如果缓存中不存在目标对象,则判断当前对象是否已经处于创建过程中,在前面的讲解中,第一次尝试获取A对象
// 的实例之后,就会将A对象标记为正在创建中,因而最后再尝试获取A对象的时候,这里的if判断就会为true
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
// 这里的singletonFactories是一个Map,其key是bean的名称,而值是一个ObjectFactory类型的
// 对象,这里对于A和B而言,调用图其getObject()方法返回的就是A和B对象的实例,无论是否是半成品
ObjectFactory singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
// 获取目标对象的实例
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
Spring 是怎么解决单例setter注入循环依赖的?
- Spring是通过递归的方式获取目标bean及其所依赖的bean的;
- Spring实例化一个bean的时候,是分两步进行的,首先实例化目标bean,然后为其注入属性
setter 注入是属性注入和构造器注入不一样,spring初始化是先创建bean ,然后注入属性的。单例 的setter采用三级缓存各自拿到各自的属性引用,然后再属性注入,最后各自完成实例化,不存在循环等待死锁的问题。
场景:A 依赖 B,B 依赖 A。
假设创建 A 对象的时候进入 getSingleton 方法。创建 B 的时候进入了个 doCreateBean 方法,在创建 B 还没创建完过程中,会在三级缓存 singletonFactories 先放一个 B,此时,如果创建 A 对象时,一级缓存没有B,从二级缓存找,二级缓存没有,从三级别缓存中找到就可以直接返回,并将自身A放入一级缓存中。
此时 B 在初始化过程中,从一级缓存中取到了A,这样B就拿到了A的引用,这样也B也就在拿到A的过程中完成了初始化。
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// 实例化当前尝试获取的bean对象,比如A对象和B对象都是在这里实例化的
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// 判断Spring是否配置了支持提前暴露目标bean,也就是是否支持提前暴露半成品的bean
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences
&& isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
// 如果支持,这里就会将当前生成的半成品的bean放到singletonFactories中,这个singletonFactories
// 就是前面第一个getSingleton()方法中所使用到的singletonFactories属性,也就是说,这里就是
// 封装半成品的bean的地方。而这里的getEarlyBeanReference()本质上是直接将放入的第三个参数,也就是
// 目标bean直接返回
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
try {
// 在初始化实例之后,这里就是判断当前bean是否依赖了其他的bean,如果依赖了,
// 就会递归的调用getBean()方法尝试获取目标bean
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 省略...
}
return exposedObject;
}
