前言
由于项目中某些特殊场景需要对k8s中的单个pod进行外部的调用,但是使用http的方式是没法调用的,所以想到了直接使用tcp/ip的方式做一个长连接,然后外部与 pod内部就能直接通信了。所以就想到了netty。
什么是netty
这里就不详细介绍了,网上应该有很多的介绍。例如:什么是netty。
思路
分为两个部分,一个是服务端,一个是客户端。
服务端
想法是跟使用springmvc一样的方式标记自己本地的方法,然后在netty的handle里边反射调用被标记的方法。
客户端
跟服务端类似,也是使用注解反射调用本地写的方法。
配置类
@Data
@Slf4j
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(value = RpcConfigProperties.class)
public class RpcAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "com.github.zy.netty.rpc.server", name = "enable", havingValue = "true")
public RpcServerRunner serverBootstrap(RpcConfigProperties rpcConfigProperties, ServerHandler serverHandler) {
return new RpcServerRunner(rpcConfigProperties, serverHandler);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "com.github.zy.netty.rpc.client", name = "enable", havingValue = "true")
public RpcClientRunner clientBootstrap(ClientHandler clientHandler, RpcClient client, RpcConfigProperties configProperties) {
return new RpcClientRunner(clientHandler, client, configProperties);
}
}
RpcServerRunner
这里的思路是实现CommandLineRunner,在springboot启动后,会去调用该接口的实现,所以,netty的初始化可以放在这里。
@Slf4j
public class RpcServerRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
private final RpcConfigProperties rpcConfigProperties;
private final ServerHandler serverHandler;
public RpcServerRunner(RpcConfigProperties rpcConfigProperties, ServerHandler serverHandler){
this.rpcConfigProperties = rpcConfigProperties;
this.serverHandler = serverHandler;
}
public void startServer() {
if (rpcConfigProperties.getServer().isEnable()) {
log.info("开始启动NettyServer...");
int port = rpcConfigProperties.getServer().getPort();
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(2048, 0, 4, 0, 4));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LengthFieldPrepender(4));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new MessagePacketDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new MessagePacketEncoder(FastJsonSerializer.INSTANCE));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new IdleStateHandler(0,0,rpcConfigProperties.getServer().getDisconnectInterval()));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ValidatePacketHandler());
ch.pipeline().addLast(serverHandler);
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
log.info("启动NettyServer[{}]成功...", port);
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("启动NettyServer[" + port + "]失败...", e);
} finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
new Thread(this::startServer).start();
}
}
RpcClientRunner
客户端这里在我使用的业务中,需要手动去调用初始化,所以这里多出来了一个start方法,里边去阻塞,等到和服务端完成连接后线程才继续走下去。 如果使用场景允许异步的话,那么可以改造下,直接就像RpcServerRunner 一样放到子线程里边去启动就行了。
@Slf4j
public class RpcClientRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
private final ClientHandler clientHandler;
private final RpcClient client;
private final RpcConfigProperties configProperties;
public RpcClientRunner(ClientHandler clientHandler, RpcClient client, RpcConfigProperties configProperties) {
this.clientHandler = clientHandler;
this.client = client;
this.configProperties = configProperties;
}
public void doStart() {
client.startClient(clientHandler);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
new Thread(this::doStart).start();
}
/**
* todo 手动触发, 异步监听关闭,这里在建立了连接通道后,返回future,使用者根据future.isSuccess来判断是否已经启动成功(阻塞线程)
*/
public void start() {
//防止多次调用该方法,去多次启动
if (client.getChannelFuture() == null || !client.getChannelFuture().isSuccess()) {
doStart();
waitStart();
//异步监听关闭
syncClose();
}
}
private void syncClose() {
//异步监听关闭
new Thread(() -> {
try {
client.getChannelFuture().channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("客户端链接发生异常", e);
}
});
}
private void waitStart() {
//最大等待阻塞时间
long startWaitTime = configProperties.getClient().getStartWaitTime();
//开始计数时间
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (; ; ) {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
//如果当前时间已经大于开始计数的时间,那么就跳出本次等待
if(currentTime > startWaitTime){
break;
}
boolean startSuccess = false;
if (client.getChannelFuture() != null) {
startSuccess = client.getChannelFuture().isSuccess();
}
if (startSuccess) {
log.debug("连接netty服务端成功,退出等待.");
break;
} else {
log.debug("连接还未准备就绪,线程阻塞.");
}
try {
Thread.sleep(configProperties.getClient().getStartWaitIntervalTime());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
}
核心点
1:服务端如何接受消息
- 定义@RpcService注解,用于标记本地的业务类,类似springmvc的@Controller.该注解主要是为了确定业务类。
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface RpcService {
}
- 定义@RpcMapping注解,用于标记业务类中的业务方法,类似springmvc的@RequestMapping。
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RpcMapping {
String url();
}
- 在netty的handle中将接受到的消息反射调用本地被标记的方法。
@Slf4j
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class ServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<DefaultMessagePacket> {
private final SessionManager sessionManager;
private final ServerMessageHandle serverMessageHandle;
private final RpcConfigProperties configProperties;
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, DefaultMessagePacket msg) throws Exception {
serverMessageHandle.handle(ctx, msg);
}
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) {
IdleState state = ((IdleStateEvent) evt).state();
if(IdleState.READER_IDLE == state){
//规定时间未收到客户端数据(如果有心跳交互的话就不会走到这来)那么就关闭客户端的channel
ctx.close();
}
}
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ChannelHandlerContextUtil contextUtil = ChannelHandlerContextUtil.INSTANCE;
String ip = contextUtil.getIp(ctx);
int port = contextUtil.getPort(ctx);
log.debug("和客户端建立连接,目标 ip : {}, port : {}", ip, port);
}
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
//断开连接的时候可以去将session清理掉
ChannelHandlerContextUtil contextUtil = ChannelHandlerContextUtil.INSTANCE;
String ip = contextUtil.getIp(ctx);
int port = contextUtil.getPort(ctx);
//sessionManager.delete(SessionHelper.getSessionId(configProperties.getClient().getSystemId(), ip));
ctx.close();
log.error("和客户端断开连接,目标 ip: {} , port : {}", ip, port);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
log.error("服务端的异常情况," , cause);
}
}
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class ServerMessageHandle {
private final List<ServerMessageResolverStrategy> strategies;
public void handle(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, DefaultMessagePacket msg) {
Optional<ServerMessageResolverStrategy> optional = strategies.stream().filter(strategie -> strategie.support(msg.getMessageType())).findFirst();
if (optional.isPresent()) {
optional.get().resolver(ctx, msg);
}
}
}
这里对serviceMessageHandle做了一个策略,具体有处理客户端的请求,ping,上报消息等。具体实现可以参考github上的代码。
2:客户端如何接受消息
- 定义@RpcClient注解,用于标记客户端的处理类。
- 使用@RpcMapping标记本地方法,在netty的handle中反射调用被标记的该方法即可。
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class ClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<DefaultMessagePacket> {
private final ClientMessageHandle clientMessageHandle;
private final RpcConfigProperties configProperties;
private final RpcClient client;
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, DefaultMessagePacket packet) throws Exception {
clientMessageHandle.handle(ctx, packet);
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ClientChannelHolder.CHANNEL_REFERENCE.set(ctx.channel());
//建立连接的时候就将自己的moduleId携带到服务端去
DefaultMessagePacket packet = MessagePacketBuilder.buildBasicReportModuleId().systemId(configProperties.getClient()
.getSystemId()).targetIp(IPUtil.getAddress()).build();
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(packet);
ChannelHandlerContextUtil contextUtil = ChannelHandlerContextUtil.INSTANCE;
String ip = contextUtil.getIp(ctx);
int port = contextUtil.getPort(ctx);
log.info("和服务端建立连接.... ip : {}, port : {}", ip, port);
}
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) {
if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) {
IdleState state = ((IdleStateEvent) evt).state();
switch (state) {
case READER_IDLE:
//规定时间没有读取操作的时候,这里可以当做没有收到服务端的回复,可能服务端挂了了啥的,这里去主动关闭连接,然后触发关闭的回调函数
ctx.close();
break;
case WRITER_IDLE:
//规定时间没有写入操作的时候
break;
case ALL_IDLE:
//在规定时间没有进行读写操作的话,就去向服务端发送一个心跳
sendHeartbeatPacket(ctx);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
//当连接关闭的时候会触发该方法,可以在这里进行对服务端的重连
ctx.channel().eventLoop().schedule(() -> {
client.startClient(this);
}, configProperties.getClient().getDisconnectRetryInterval(), TimeUnit.SECONDS);
log.error("与服务端断开连接。。。。");
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
log.error("出现未知异常....", cause);
}
private void sendHeartbeatPacket(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
DefaultMessagePacket packet = MessagePacketBuilder.buildBasicPing().build();
ctx.writeAndFlush(packet);
}
}
3:服务端如何发送消息
由于服务端与客户端的关系是一对多,可能同时有多个客户端连接上了服务端,所以这里就需要一个session来讲客户端与服务端的会话连接信息记录存起来 所以定义了一个SessionManage与SessionStorage
public interface SessionManager {
/**
* 根据sessionId得到一个session
*
* @param sessionId
* @return
*/
Session findOne(String sessionId);
/**
* 获取所有的session
*
* @return
*/
List<Session> findAll();
/**
* 移除某一个session
*
* @param sessionId
* @return
*/
void delete(String sessionId);
/**
* 移除某一批session
*
* @param sessionIds
* @return
*/
void delete(List<String> sessionIds);
/**
* 保存单个session
*
* @param session
*/
void save(Session session);
/**
* 保存一批session
*
* @param sessions
*/
void save(Iterable<Session> sessions);
}
/**
* session 存储策略
* @version 1.0 created by zy on 2020/4/26 14:50
*/
public interface SessionStorage {
/**
* 获取某个session
* @param sessionId systemId + ip
* @return
*/
Session findOne(String sessionId);
/**
* 获取所有的session
* @return
*/
List<Session> findAll();
/**
* 移除某一个session
* @param sessionId systemId + ip
* @return
*/
void delete(String sessionId);
/**
* 移除某一批session
* @param sessionIds systemId + ip
* @return
*/
void delete(List<String> sessionIds);
/**
* 保存单个session
* @param session
*/
void save(Session session);
/**
* 保存一批session
* @param sessions
*/
void save(Iterable<Session> sessions);
}
4:客户端如何发送消息
定义@RpcRequestClient注解标记接口,类似@FeginClient一样,只需要将url的映射与服务端的@RpcMapping映射一致就行
/**
* @version 1.0 created by zy on 2020/4/26 9:45
*/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RpcRequestClient {
RpcRequestClientType targetType() default RpcRequestClientType.SERVER;
}
/**
* @version 1.0 created by zy on 2020/5/24 17:37
*/
@RpcRequestClient
public interface ServerRequestClient {
@RpcMapping(url = "/hello-server")
ServerResponse helloServer(ClientRequest request);
}
使用
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private ServerSendTemplate serverSendTemplate;
@Autowired
private SessionManager sessionManager;
@Autowired
private ServerRequestClient serverRequestClient;
@GetMapping("/hello-client")
public ClientResponse helloClient(ServerRequest serverRequest) {
return serverSendTemplate.sendToClient(serverRequest.getSystemId(), serverRequest.getIp(), serverRequest.getUrlMapping(), serverRequest, ClientResponse.class);
}
@GetMapping("/hello-server")
public ServerResponse helloServer(ClientRequest clientRequest) {
return serverRequestClient.helloServer(clientRequest);
}
@GetMapping("/sessions")
public List<Session> sessions() {
return sessionManager.findAll();
}
}
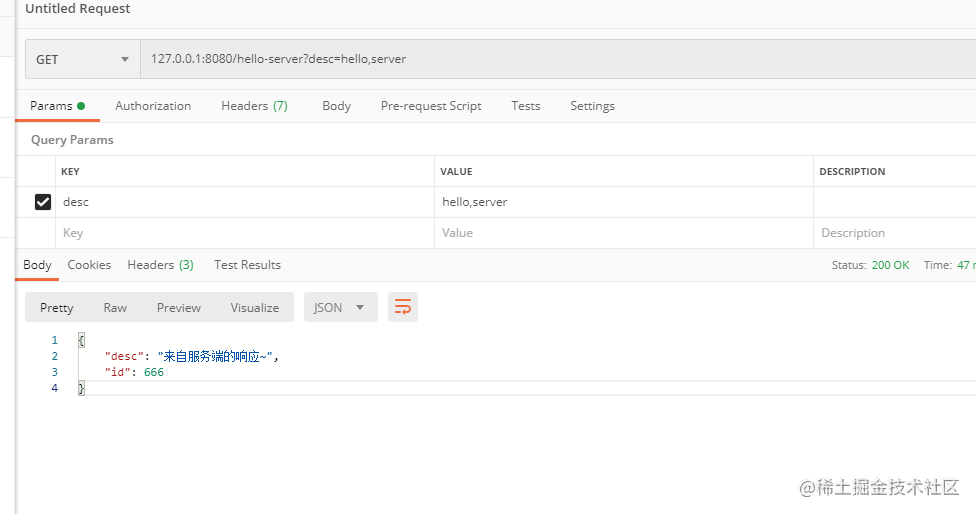
然后访问http://localhost:8080/hello-server,向服务端发送请求。
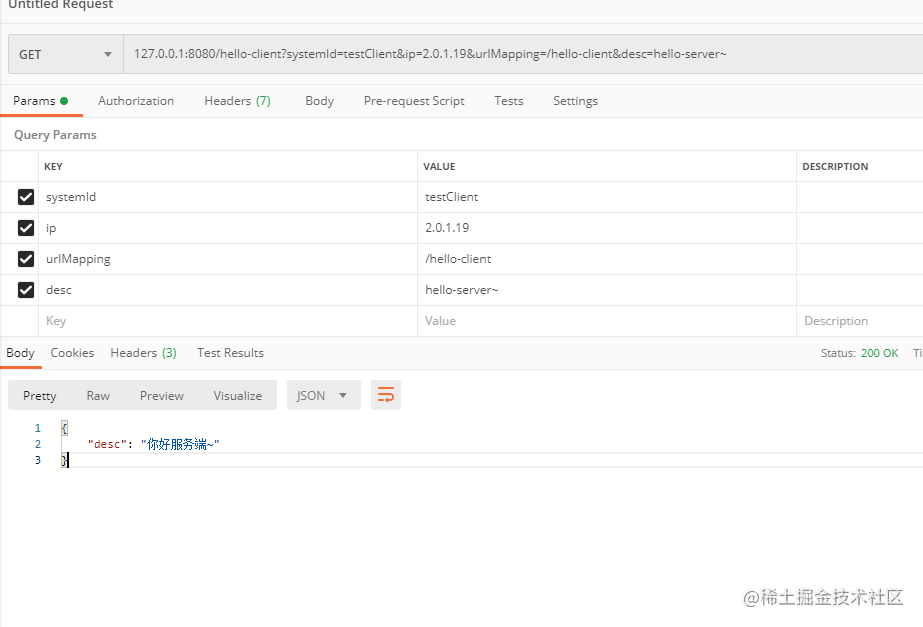
 访问http://localhost:8080/hello-client,向客户端发送请求
访问http://localhost:8080/hello-client,向客户端发送请求
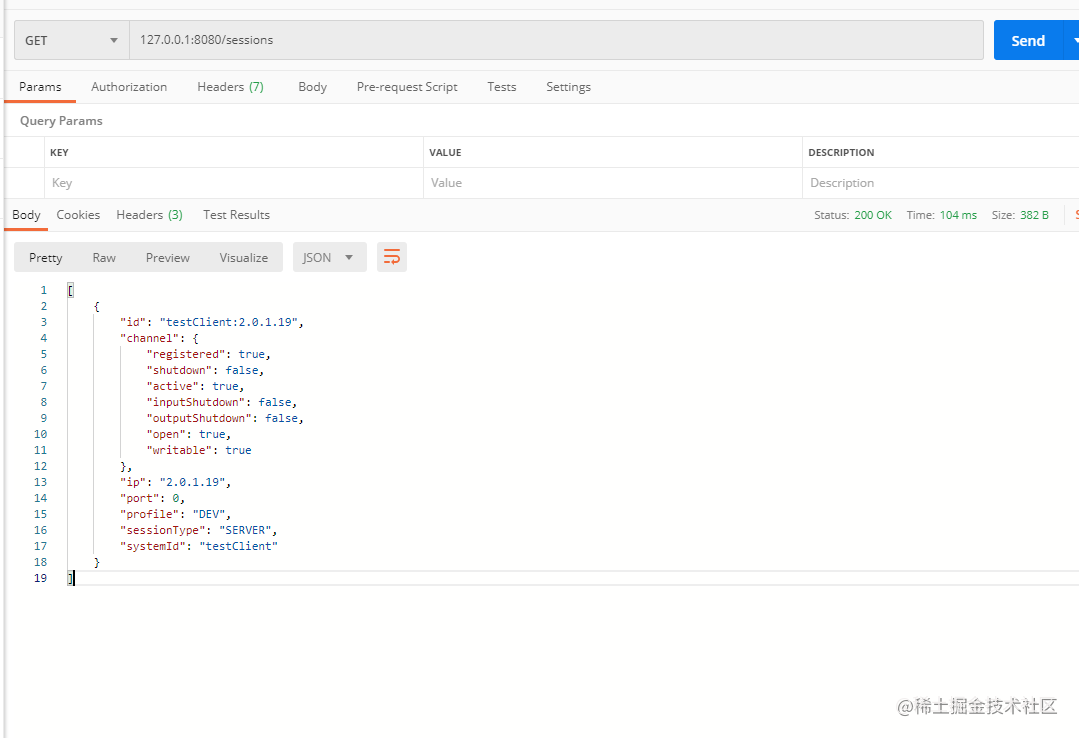
需要注意的是,服务端向客户端发送请求的时候,需要systemId与ip去确定是哪个客户端,这里可以使用sessionManager的findAll去找到所有的session,然后 挑一个客户端的信息去发送即可。
以上~
只是介绍了大概的实现思路以及部分代码,需要更详细的了解的,请移步github。 如果有好的建议以及写的不好的的放的话还请指教~
