什么是MVC?
MVC(Model-View-Controller):它是一种软件架构设计模式,分为三个部分:
- Model(模型):业务的数据模型;
- View(视图):数据模型的可视化;
- Controller(控制器):模式和视图的连接控制器。
它的主要目的就是将代码分层模块化,降低各层之间的耦合性,每个模块符合单一职责原则。
很多应用的Web框架都是基于MVC模式去设计的,这里Spring也不例外,同样提供了基于MVC的web框架Spring Web MVC ,通常我们称为SpringMVC。
准备工作
实际开发中,相信我们对SpringMVC的使用已经非常熟悉了,那么在接下来的源码解析之前,我们先介绍在SpringMVC的一些基础知识。
支持的功能
作为Web框架,SpringMVC也提供了很多丰富的功能:
- 类型转换:默认支持各种数字和日期类型的数据格式化,也支持自定义格式化转化。
- 验证:对请求参数的全局或局部验证,支持JSR-303、HibernateValidator验证。
- 拦截器:注册拦截器对传入的请求进行拦截处理。
- 内容类型:自定义请求的内容类型解析,像json、xml等。
- 消息转换器:自定义消息转换器对不同类型的消息进行序列化和反序列化,默认是Jackson。
- 视图控制器:初始化一些默认的url请求路径对应的页面,像首页、404、500等。
- 视图解析器:配置视图的解析器,像Thymeleaf、Freemarker、velocity等,默认使用的是JSP、Jackson。
- 静态资源:提供一些静态资源的url配置。
- Servlet配置:SpringMVC提供了DispatcherServlet来覆盖默认的DefaultServletHttpRequestHandler处理,特支持自定义的Servlet配置。
- 路径匹配:自定义与路径匹配和URL处理相关的选项。
DispatcherServlet
我们先看它的类图,
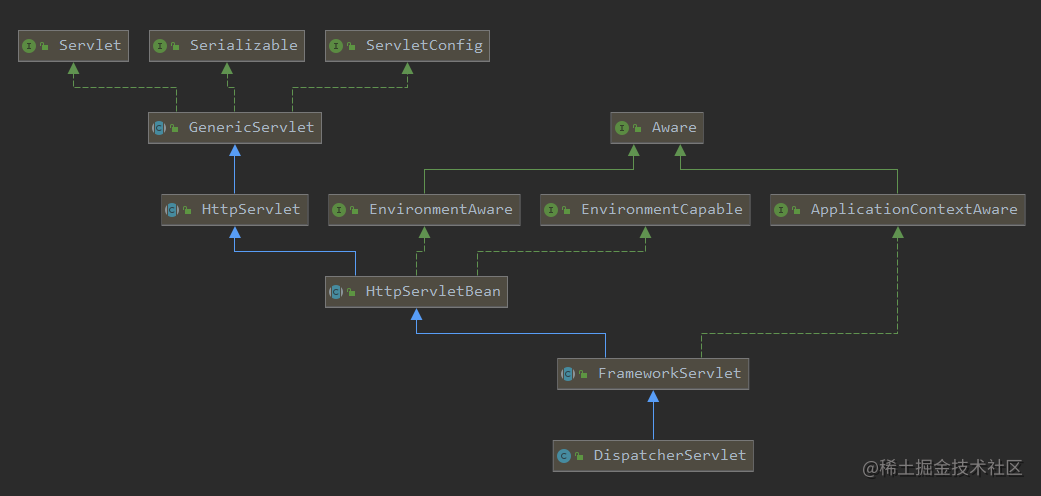
它是前端控制器,是SpringMVC的核心,也是Servlet的实现子类,它的主要作用就是处理请求,通过可配置的组件执行请求映射,视图解析,异常处理等功能;而我们可以把它当作是SpringMVC中真正的Servlet。
Servlet配置
跟IOC、AOP等一样,SpringMVC的Servlet配置同样支持两种配置方式,分别是:
- XML配置:在Servlet3.0之前,我们通常通过web.xml去配置Servlet,
<web-app>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/app-context.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>app</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value></param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>app</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/app/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
来完成前端控制器DispatcherServlet的初始化,以及请求映射、视图解析等其它功能;包括所有的url映射路径、拦截器等都配置在xml中,虽然方便统一管理维护,但是配置相对繁琐,不同功能之间高耦合,也不够灵活。
- Java代码配置:在Servlet3.0之后的新特性,支持基于注解的配置方式来替代web.xml了,所以在SpringMVC中我们可以通过Java代码来配置,
public class MyWebApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
//注册配置类
context.register(AppConfig.class);
//创建DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet servlet = new DispatcherServlet(context);
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet("app", servlet);
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping("/app/*");
}
}
同时也支持与web.xml的结合使用。目前开发中最常用的SprongBoot就是依赖于Java配置来配置SpringMVC的。
关键Bean
SpringMVC定义了九种特殊的Bean来完成负责处理请求和不同策略的返回渲染,它们分工明确互不干涉,分别是:
- MultipartResolver:文件解析器,用于解析包括文件上传在内的多部分请求的策略。
- LocaleResolver:国际化语言环境解析器,用于自动解析设置客户端的语言环境,包括时区、请求头、cookoe、session、区域的解析。
- ThemeResolver:主题解析器,用于解析自定义静态资源的样式。
- HandlerMapping:请求映射器,负责实际请求的处理器,像配置@RequestMapping注解的类或方法。
- HandlerAdapter:请求处理适配器,用于请求的解析处理,像参数适配、反射调用等。
- HandlerExceptionResolver:请求异常解析器,用于解析对请求处理时发生的异常解决策略,像错误响应等,
- RequestToViewNameTranslator:视图预处理转换器,用于获取Request中的viewName,将提供的请求转换为默认视图名称。
- ViewResolver:视图解析器,将视图名称解析为View类型的视图。
- FlashMapManager:用于存储、检索和管理
FlashMap实例,其中FlashMap适用于保存Flash属性,而Flash属性用于解决重定向时无法传递的参数的存储。
初始化流程
相比较之前解析Spring中IOC、AOP等初始化流程的复杂,MVC则更加容易,可能也是Spring源码解析中最轻松的一个环节了,接下来就让我们开始吧。
刚才已经介绍完SpringMVC中的九种特殊Bean,我们大概知道它们各自的作用,而SpringMVC的初始化流程其实就和它们一一对应相关,所以与其说MVC的初始化,不如说是九种Bean的初始化。
从0到1,我们还是需要找到初始化流程的入口。前面Servlet配置中已经介绍了Servlet的初始化方式了,其中xml的配置是基于XmlWebApplicationContext容器,代码的配置是基于AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext容器来加载完成的;这里我们主要来解析基于代码的配置方式的初始化流程。
先写个非常简单的测试Demo,
public class MyWebApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
context.scan("com.test.spring.mvc");
// context.register(MvcConfig.class);
DispatcherServlet servlet = new DispatcherServlet(context);
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet("dispatcherServlet", servlet);
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping("/");
}
}
@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test(){
return "test";
}
}
通过idea配置好Tomcat容器,启动之后访问http://localhost:8080/test,看到页面上成功返回test展示。
接下来我们就开始一步步去探究它的初始化流程了。
注册DispatcherServlet
首先我们需要需要创建IOC容器AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext,它是之前的IOC解析中的AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的Web版本;然后我们设置IOC的包扫描路径,主要用来扫描我们编写的Controller类。
我们知道DispatcherServlet是Servlet的实现子类,那在了解它之前,我们先了解下Servlet。
Servlet是运行在Web服务器中的Java程序,而它的生命周期如下,
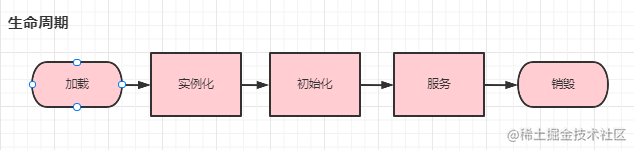
- Web容器在加载时或者第一次使用Servlet时,先创建Servlet实例;
- 实例化之后,容器会调用init()方法进行初始化,而对于每一个Servlet实例,init()方法只能被调用一次;
- 初始化之后,Servlet一直保存在Web容器中,通过service()方法来处理响应客户端请求;
- 销毁时,先调用destroy()方法(仅执行一次),等service()方法中正在执行的请求全部完成或超时时,通过垃圾回收器来销毁被Web容器释放的Servlet对象。
接下来这里创建DispatcherServlet对象,并把IOC容器注册进去,然后再把DispatcherServlet注册到容器的Servlet中去,并设置两个属性:
- setLoadOnStartup:设置DispatcherServlet的加载顺序,当值大于等于0时,表示容器在启动时就加载并初始化这个Servlet,正数值越小则加载优先级越高;小于0或者不设置时,则表示该容器在Servlet被选择时才会去加载。
- addMapping:添加url路径映射,在这里可以配置项目接口的url路径前缀,默认必须要添加
/。
可以发现这几个方法都是调用Servlet的原生API,而真正的处理代码都是由Web容器中根据Servlet的规范接口去实现的。而我们最重要还是去关注Servlet原生API的在SpringMVC中的实现,也就是DispatcherServlet这个类,它也是SpringMVC的核心。
初始化Servlet
我们已经知道Servlet实例化之后首先会调用init()方法,然而我们去查看DispatcherServlet源码,并没有发现这个方法,那么这个方法的具体实现肯定是在其某个父类当中,通过它的类图,我们先查看顶层父类接口Servlet的源码,
public interface Servlet {
void init(ServletConfig var1) throws ServletException;
ServletConfig getServletConfig();
void service(ServletRequest var1, ServletResponse var2) throws ServletException, IOException;
String getServletInfo();
void destroy();
}
发现init()的方法是由子类GenericServlet实现,
public abstract class GenericServlet implements Servlet, ServletConfig, Serializable {
...
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
this.config = config;
this.init();
}
public void init() throws ServletException {
}
...
}
而这里又调用了自定义的一个init()方法,而它的具体实现实际是委托了子类HttpServletBean来完成,我们看下实现源码,
public final void init() throws ServletException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "'");
}
//init-param设置的Bean属性
PropertyValues pvs = new HttpServletBean.ServletConfigPropertyValues(this.getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
//封装成IOC容器中的BeanWrapper
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(this.getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, this.getEnvironment()));
this.initBeanWrapper(bw);
//属性注入
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
} catch (BeansException var4) {
if (this.logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
this.logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "'", var4);
}
throw var4;
}
}
//初始化
this.initServletBean();
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "' configured successfully");
}
}
我们主要关注调用initServletBean()方法来进行Servlet的初始化,而具体的方法实现是由FrameworkServlet来完成的,
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
this.getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + this.getServletName() + "'");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + this.getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = this.initWebApplicationContext();
//空实现,子类扩展接口
this.initFrameworkServlet();
} catch (ServletException var5) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", var5);
throw var5;
} catch (RuntimeException var6) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", var6);
throw var6;
}
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + this.getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}
通过源码,我们看到它的作用主要就是为了调用initWebApplicationContext()方法来初始化WebApplicationContext,而我们知道WebApplicationContext实例在注册DispatcherServlet前已经完成创建了,
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(this.getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
//配置和刷新ApplicationContext
this.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
//加载ApplicationContext
wac = this.findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
//创建ApplicationContext
wac = this.createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
this.onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
//缓存到属性
String attrName = this.getServletContextAttributeName();
this.getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}
通过源码能看到这里初始化WebApplicationContext的流程逻辑如下:
- webApplicationContext存在,由于已经通过构造函数注入,则建立父子容器关系,调用configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext()初始化容器(最终调用refresh()方法来完成);
- webApplicationContext不存在,先尝试从ServletContext的属性缓存中加载,如果加载不到,则调用createWebApplicationContext()来默认创建WebApplicationContext实例,并建立父子容器关系,调用configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext()初始化容器;
- 调用onRefresh()方法初始化MVC组件;
- 将webApplicationContext缓存到ServletContext的属性中。
到这里的方法执行完,也就完成了Servlet,也就是DispatcherServlet的初始化了,也代表着Web容器已经启动完成了。
初始化相关组件
我们知道DispatcherServlet是SpringMVC的核心,其中封装了MVC中的各种组件,那接下来我们就具体地看看上面调用onRefresh()方法中是怎么完成对MVC组件的初始化的?
首先注意到onRefresh()方法是FrameworkServlet委托子类DispatcherServlet来实现的,看下源码,
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
this.initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
this.initMultipartResolver(context);
this.initLocaleResolver(context);
this.initThemeResolver(context);
this.initHandlerMappings(context);
this.initHandlerAdapters(context);
this.initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
this.initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
this.initViewResolvers(context);
this.initFlashMapManager(context);
}
这里的实现代码分别封装了各组件的初始化方法,按顺序分别是:
- 多文件上传初始化
- 语言环境解析初始化
- 主题解析器初始化
- 请求映射初始化
- 请求适配器初始化
- 请求异常解析初始化
- 视图预处理器初始化
- 视图解析器器初始化
- FlashMap管理初始化
如果点进去查看它们各自的初始化逻辑会发现很简单,其实就是对九种关键Bean的实例化,其中一些组件在没有配置的情况下,会使用默认的配置去解析处理,而它们各自的作用前面也已经介绍过了,这里就不在一一分析各组件初始化方法的源码了。
调用流程
经过上面的初始化流程已经成功完成Web容器的启动了,那么接下来我们思考下,当服务端接收到客户端的请求时,SpringMVC是怎么对请求进行解析处理的呢?
首先,回到Servlet的生命周期,我们知道Servlet会一直存在Web容器中,然后通过service()方法来处理响应客户端请求,那我们就从这个入口开始分析。
1.开始解析
通过DispatcherServlet的类图,查看顶层父类接口Servlet的service()方法,发现被子类FrameworkServlet覆写,
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());
if (HttpMethod.PATCH != httpMethod && httpMethod != null) {
super.service(request, response);
} else {
this.processRequest(request, response);
}
}
当请求不为空同时方式不为PATCH时,会调用父类HttpServlet的service()方法,
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String method = req.getMethod();
long lastModified;
if (method.equals("GET")) {
lastModified = this.getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1L) {
this.doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader("If-Modified-Since");
if (ifModifiedSince < lastModified) {
this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
this.doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(304);
}
}
} else if (method.equals("HEAD")) {
lastModified = this.getLastModified(req);
this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
this.doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("POST")) {
this.doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("PUT")) {
this.doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("DELETE")) {
this.doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("OPTIONS")) {
this.doOptions(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("TRACE")) {
this.doTrace(req, resp);
} else {
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[]{method};
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(501, errMsg);
}
}
发现这是其实就是对不同请求方式的处理方法进行路由,而doGet()、doPost()、doPut()等处理方法实际还是交给FrameworkServlet来实现,而最终所有的请求处理都是交给processRequest()来完成的,
...
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.processRequest(request, response);
}
protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.processRequest(request, response);
}
protected final void doPut(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.processRequest(request, response);
}
...
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//用于统计请求的处理时间
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
//保留请求的快照,语言环境、属性等
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = this.buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = this.buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new FrameworkServlet.RequestBindingInterceptor());
this.initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
//请求处理
this.doService(request, response);
} catch (IOException | ServletException var16) {
failureCause = var16;
throw var16;
} catch (Throwable var17) {
failureCause = var17;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", var17);
} finally {
//恢复原始属性
this.resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (failureCause != null) {
this.logger.debug("Could not complete request", (Throwable)failureCause);
} else if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
this.logger.debug("Leaving response open for concurrent processing");
} else {
this.logger.debug("Successfully completed request");
}
}
//发布请求处理事件
this.publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, (Throwable)failureCause);
}
}
分析源码知道,这里主要是对请求前后的准备和事件处理工作,为了保证请求前后的原始属性不变;而具体的细节处理都是委托子类DispatcherServlet的doService()方法来完成的,
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : "";
this.logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + this.getServletName() + "'" + resumed + " processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]");
}
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap();
Enumeration attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
label112:
while(true) {
String attrName;
do {
if (!attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
break label112;
}
attrName = (String)attrNames.nextElement();
} while(!this.cleanupAfterInclude && !attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet"));
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, this.getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
try {
this.doDispatch(request, response);
} finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted() && attributesSnapshot != null) {
this.restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
实现逻辑比较简单,主要作用还是为了请求的处理而做准备,将MVC中初始化的相关组件配置保存中请求的属性中,以便后面的解析工作;更详细的解析处理还是通过封装的doDispatch()方法完成的,
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Object dispatchException = null;
try {
//多部分请求检查转换
processedRequest = this.checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = processedRequest != request;
//获取请求对应的Handler
mappedHandler = this.getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
this.noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
//获取HandlerAdapter
HandlerAdapter ha = this.getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
//Last-Modified缓存机制
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if ((new ServletWebRequest(request, response)).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
//前置处理
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
//处理请求
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
//应用默认视图名称
this.applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
//后置处理
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
} catch (Exception var20) {
dispatchException = var20;
} catch (Throwable var21) {
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", var21);
}
//结果处理
this.processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, (Exception)dispatchException);
} catch (Exception var22) {
this.triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, var22);
} catch (Throwable var23) {
this.triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", var23));
}
} finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
} else if (multipartRequestParsed) {
this.cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
经过层层的准备,具体的请求的解析处理逻辑终于展现出来了,而之前初始化的相关组件的作用也在这里得到了体现。接下来会分别解析源码的具体处理逻辑。
2.多部分请求转换
开始会先调用checkMultipart()方法来检查当前request是否需要转换为包含文件上传在内的多部分请求MultipartHttpServletRequest,进去看下源码,
protected HttpServletRequest checkMultipart(HttpServletRequest request) throws MultipartException {
if (this.multipartResolver != null && this.multipartResolver.isMultipart(request)) {
if (WebUtils.getNativeRequest(request, MultipartHttpServletRequest.class) != null) {
this.logger.debug("Request is already a MultipartHttpServletRequest - if not in a forward, this typically results from an additional MultipartFilter in web.xml");
} else if (this.hasMultipartException(request)) {
this.logger.debug("Multipart resolution failed for current request before - skipping re-resolution for undisturbed error rendering");
} else {
try {
return this.multipartResolver.resolveMultipart(request);
} catch (MultipartException var3) {
if (request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.exception") == null) {
throw var3;
}
}
this.logger.debug("Multipart resolution failed for error dispatch", var3);
}
}
return request;
}
这里如果之前没有配置multipartResolver解析器,则这里会跳过检查;反之则会调用isMultipart()判断当前请求是否多部分请求,如果是,则最后会通过MultipartResolver解析器调用resolveMultipart()将当前request转换为MultipartHttpServletRequest,查看它的类图,会发现它其实是HttpServletRequest的扩展子类;而resolveMultipart()中转换处理的源码也很复杂,感兴趣可以深究。
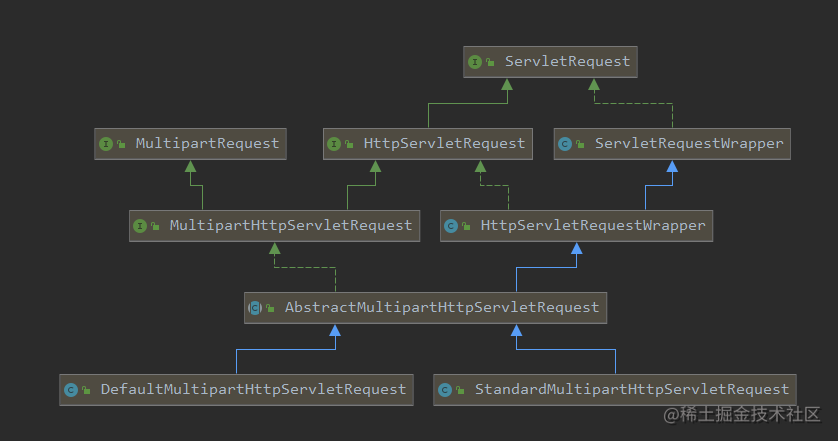
3.获取请求对应的Handler
检查完request之后,然后会调用getHandler()方法获取当前request对应的处理器,也就是请求路径对应的controller,我们来看下是怎么去寻找获取到的,
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
Iterator var2 = this.handlerMappings.iterator();
while(var2.hasNext()) {
HandlerMapping hm = (HandlerMapping)var2.next();
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + this.getServletName() + "'");
}
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
这里handlerMappings是个List集合,在初始化的时候会加载两种Url映射器:
- BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping:匹配BeanName为路径的Controller,比如BeanName="/test";虽然这样的url配置在SpringMVC中是支持的,但是实际开发中是不会出现的。
- RequestMappingHandlerMapping:匹配@RequestMapping,包括@GetMapping、@PostMapping等注解设置的路径。
这里我们还是以正常的设置方式RequestMappingHandlerMapping去解析url是怎么匹配到Controller的,我们看下getHandler()源码,
@Nullable
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//获取对应的HandlerMethod
Object handler = this.getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = this.getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
} else {
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String)handler;
handler = this.obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
//封装到执行链中
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = this.getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
//跨域处理
if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.globalCorsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = this.getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
CorsConfiguration config = globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig;
executionChain = this.getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
}
它的实现是在HandlerMapping的实现子类AbstractHandlerMapping中,这里会先调用getHandlerInternal()匹配对应的Controller,并封装成HandlerMethod返回;然后调用getHandlerExecutionChain(),将当前request和HandlerMethod封装到执行链HandlerExecutionChain中,并将匹配的拦截器HandlerInterceptor添加到执行链里;最后判断当前request是否为跨域请求,是则再次处理封装执行链HandlerExecutionChain。
这里利用责任链的处理模式,降低请求对象与处理器的耦合,可以方便的对请求解析进行扩展和拦截。
我们来看子类AbstractHandlerMethodMapping中getHandlerInternal()的具体实现,
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//截取有效的url路径
String lookupPath = this.getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Looking up handler method for path " + lookupPath);
}
//获取读锁
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
HandlerMethod var4;
try {
//通过路径查找HandlerMethod
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = this.lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (handlerMethod != null) {
this.logger.debug("Returning handler method [" + handlerMethod + "]");
} else {
this.logger.debug("Did not find handler method for [" + lookupPath + "]");
}
}
//从容器中获取Controller对象并封装成HandlerMethod
var4 = handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null;
} finally {
//释放读锁
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
return var4;
}
通过上面代码,可以看到这里的url匹配查找会先加上读锁,我们知道读锁是共享的,而写锁是独占的,主要用来保证容器中注册的映射发生改变时,不会影响与对应的Controller的一致性。我们看下匹配方法lookupHandlerMethod()的源码,
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T>.Match> matches = new ArrayList();
//获取已注册的路径
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
//匹配Controller并添加到matches中
this.addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
this.addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
//对HandlerMethodMapping排序
Comparator<AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T>.Match> comparator = new AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.MatchComparator(this.getMappingComparator(request));
Collections.sort(matches, comparator);
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Found " + matches.size() + " matching mapping(s) for [" + lookupPath + "] : " + matches);
}
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T>.Match bestMatch = (AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.Match)matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T>.Match secondBestMatch = (AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.Match)matches.get(1);
//匹配多个相同handler则抛出异常
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous handler methods mapped for HTTP path '" + request.getRequestURL() + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
this.handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
} else {
return this.handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
private void addMatchingMappings(Collection<T> mappings, List<AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T>.Match> matches, HttpServletRequest request) {
Iterator var4 = mappings.iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
T mapping = var4.next();
//匹配Mapping
T match = this.getMatchingMapping(mapping, request);
if (match != null) {
matches.add(new AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.Match(match, (HandlerMethod)this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().get(mapping)));
}
}
}
到这里基本就完成url路径匹配了,在这些方法中做了很多准备及匹配处理,看起来实现很复杂,但是慢慢Debug下去,会发现整个逻辑的主要流程还是比较简单的,更详细的匹配逻辑这里就不再深入了。
如果加载当前请求对应的Handler不存在的话,服务端则会响应404错误返回。
4.获取HandlerAdapter
找到对应的Handler之后,需要通过调用getHandlerAdapter()拿到Handler对应的HandlerAdapter,而它的作用前面我们也已经知道了,
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
Iterator var2 = this.handlerAdapters.iterator();
while(var2.hasNext()) {
HandlerAdapter ha = (HandlerAdapter)var2.next();
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Testing handler adapter [" + ha + "]");
}
if (ha.supports(handler)) {
return ha;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler + "]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
代码比较简单,初始化时handlerAdapters会加载以下三种HandlerAdapter:
- HttpRequestHandlerAdapter:适配实现HttpRequestHandler接口的Handler,需要重写handleRequest方法 。
- SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter:适配实现Controller接口的Handler,需要重写handleRequest方法,并返回ModelAndView。
- RequestMappingHandlerAdapter:和RequestMappingHandlerMapping配对使用,适配@RequestMapping等注解的Handler。
这里通过supports()方法进行instanceof类型判断,来选择相应的HandlerAdapter进行后续的处理。
5.LastModified缓存机制
接下来针对GET或HEAD的请求方式,这里做了一个叫LastModified的缓存机制,它的作用及实现逻辑也很好理解,首先第一次请求成功时,服务端会在响应头中添加Last-Modified属性,值为服务端最后的更新时间;当请求第二次访问时,会去调用getLastModified()方法获取请求头中If-Modified-Since属性,然后调用checkNotModified()方法检查服务端的内容在属性值的时间之后是否发生改变,如果未发生变化则响应304状态码(只返回响应头,不然会响应内容)。
6.拦截器的前后置处理
和Spring中的BeanPostProcessor中相似,SpringMVC在这里提供了HandlerInterceptor拦截器,针对在Handler真正处理请求的逻辑前后,可以方便扩展对请求的一些处理,我们看下HandlerInterceptor源码,
public interface HandlerInterceptor {
//处置处理
default boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
return true;
}
//后置处理
default void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, @Nullable ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
}
//完成后处理
default void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, @Nullable Exception ex) throws Exception {
}
}
它提供了三种方法的接口实现,开发中我们可以通过实现此接口来对Request做一些拦截处理。
7.处理请求
前面我们已经获取了当前请求对应的Handler及做了一些处理前的准备工作,而真正处理请求是通过handle()方法来完成的,这里会调用AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter中的源码,
@Nullable
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
return this.handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod)handler);
}
发现具体实现还是在子类RequestMappingHandlerAdapter的handleInternal()中,
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
this.checkRequest(request);
ModelAndView mav;
//会话同步
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized(mutex) {
//处理逻辑
mav = this.invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
} else {
//处理逻辑
mav = this.invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
} else {
//处理逻辑
mav = this.invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
if (!response.containsHeader("Cache-Control")) {
//会话缓存
if (this.getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
this.applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
} else {
this.prepareResponse(response);
}
}
return mav;
}
我们能看到这里做了关于Session会话的同步及缓存,但是我们主要关注的是调用invokeHandlerMethod()来真正处理请求的,如果继续深入了解该方法的源码,能够知道会先对方法带有的参数进行解析适配等工作,最后底层还是通过反射来调用我们之前拿到的Handler中保存的Controller类及方法,也就是我们的自己实现的业务逻辑代码了。
8.异常处理
上面的处理调用完成会返回一个ModelAndView,如果我们服务响应的是json、xml等非页面视图模型这样的格式,这个的mv就等于null;最后会通过调用processDispatchResult()方法对ModelAndView进行处理,
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv, @Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
this.logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException)exception).getModelAndView();
} else {
Object handler = mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null;
mv = this.processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = mv != null;
}
}
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
this.render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
} else if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name '" + this.getServletName() + "': assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling");
}
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, (Exception)null);
}
}
}
这里的结果处理会分为两个步骤,第一个就是调用processHandlerException()方法对处理请求的逻辑中发生的异常进行处理,
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView processHandlerException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
ModelAndView exMv = null;
if (this.handlerExceptionResolvers != null) {
Iterator var6 = this.handlerExceptionResolvers.iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
HandlerExceptionResolver handlerExceptionResolver = (HandlerExceptionResolver)var6.next();
exMv = handlerExceptionResolver.resolveException(request, response, handler, ex);
if (exMv != null) {
break;
}
}
}
if (exMv != null) {
if (exMv.isEmpty()) {
request.setAttribute(EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
return null;
} else {
if (!exMv.hasView()) {
String defaultViewName = this.getDefaultViewName(request);
if (defaultViewName != null) {
exMv.setViewName(defaultViewName);
}
}
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Handler execution resulted in exception - forwarding to resolved error view: " + exMv, ex);
}
WebUtils.exposeErrorRequestAttributes(request, ex, this.getServletName());
return exMv;
}
} else {
throw ex;
}
}
@Nullable
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) {
if (this.shouldApplyTo(request, handler)) {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Resolving exception from handler [" + handler + "]: " + ex);
}
this.prepareResponse(ex, response);
ModelAndView result = this.doResolveException(request, response, handler, ex);
if (result != null) {
this.logException(ex, request);
}
return result;
} else {
return null;
}
}
我们能看到,最后将发生的异常信息、状态码等写到Response中返回给客户端。
9.视图渲染
如果当前请求处理结果返回的ModelAndView存在,则会调用render()方法进行页面渲染,
protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
Locale locale = this.localeResolver != null ? this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request) : request.getLocale();
response.setLocale(locale);
//获取视图名称
String viewName = mv.getViewName();
View view;
if (viewName != null) {
//视图解析
view = this.resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name '" + mv.getViewName() + "' in servlet with name '" + this.getServletName() + "'");
}
} else {
view = mv.getView();
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a View object in servlet with name '" + this.getServletName() + "'");
}
}
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + this.getServletName() + "'");
}
try {
if (mv.getStatus() != null) {
response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value());
}
//视图渲染
view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);
} catch (Exception var8) {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + this.getServletName() + "'", var8);
}
throw var8;
}
}
我们先会按到返回的视图名称,然后通过ViewResolver视图解析器去解析获取对应的View,最后再调用render()对页面进行渲染返回,向页面中的JSTL语法、EL表达式或者原始的Request的属性等都会进行解析。
最后到这一步,SpringMVC中的调用流程处理就已经全部完成了。
把一件事做到极致就是天分!
