不管是工作还是面试 深入了解SpringBoot源码 都将给你带来非常实实在在的收获 so 今天我们来揭开SpringBoot的第一个面纱(run方法)。
1.初始化.搭建阅读环境 springboot版本为 2.1.x
github fork或者下载: github.com/spring-proj…
下载后 idea打开 由于springboo默认没将其写到父pom的modles中 所以我们将spring-boot-samples导入,执行 SampleTestApplication执行run方法(这里我选的是这个启动类)。
启动项目
-
报错 Kotlin: Language version 1.1 is no longer supported; please, use version 1.2 or greater.
-
解决方式
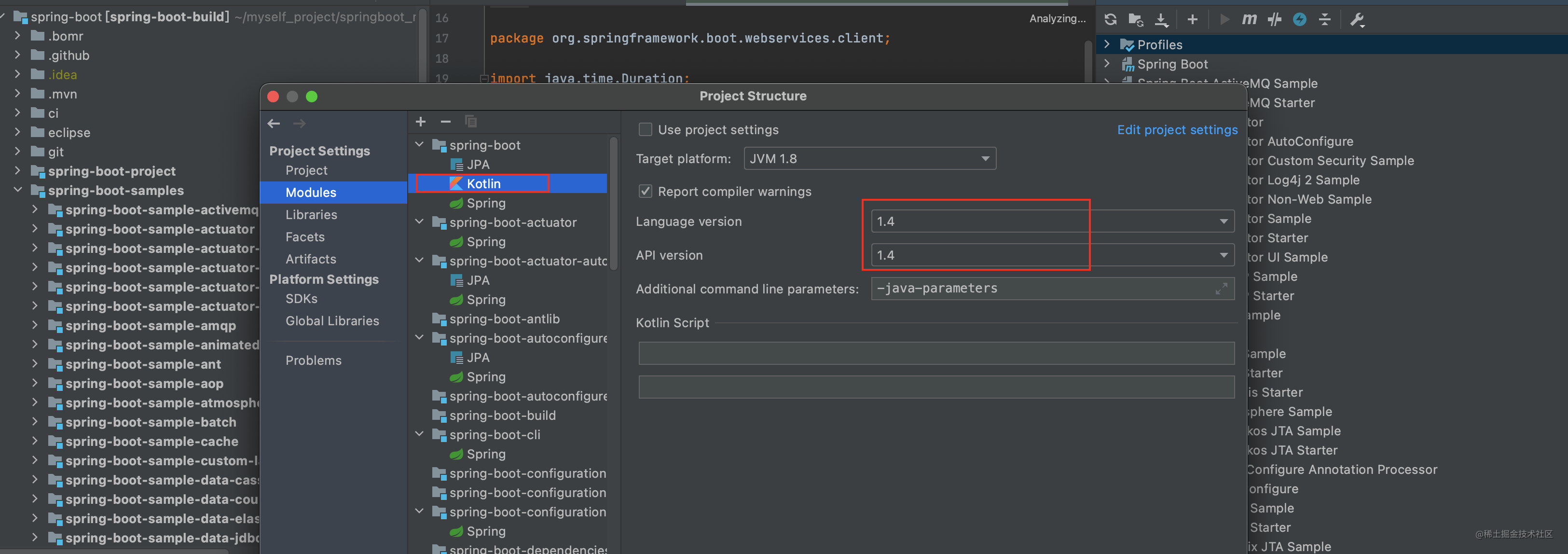
-
可能和idea版本有关系 我报了这个错 然后勾选idea这个选项就好了
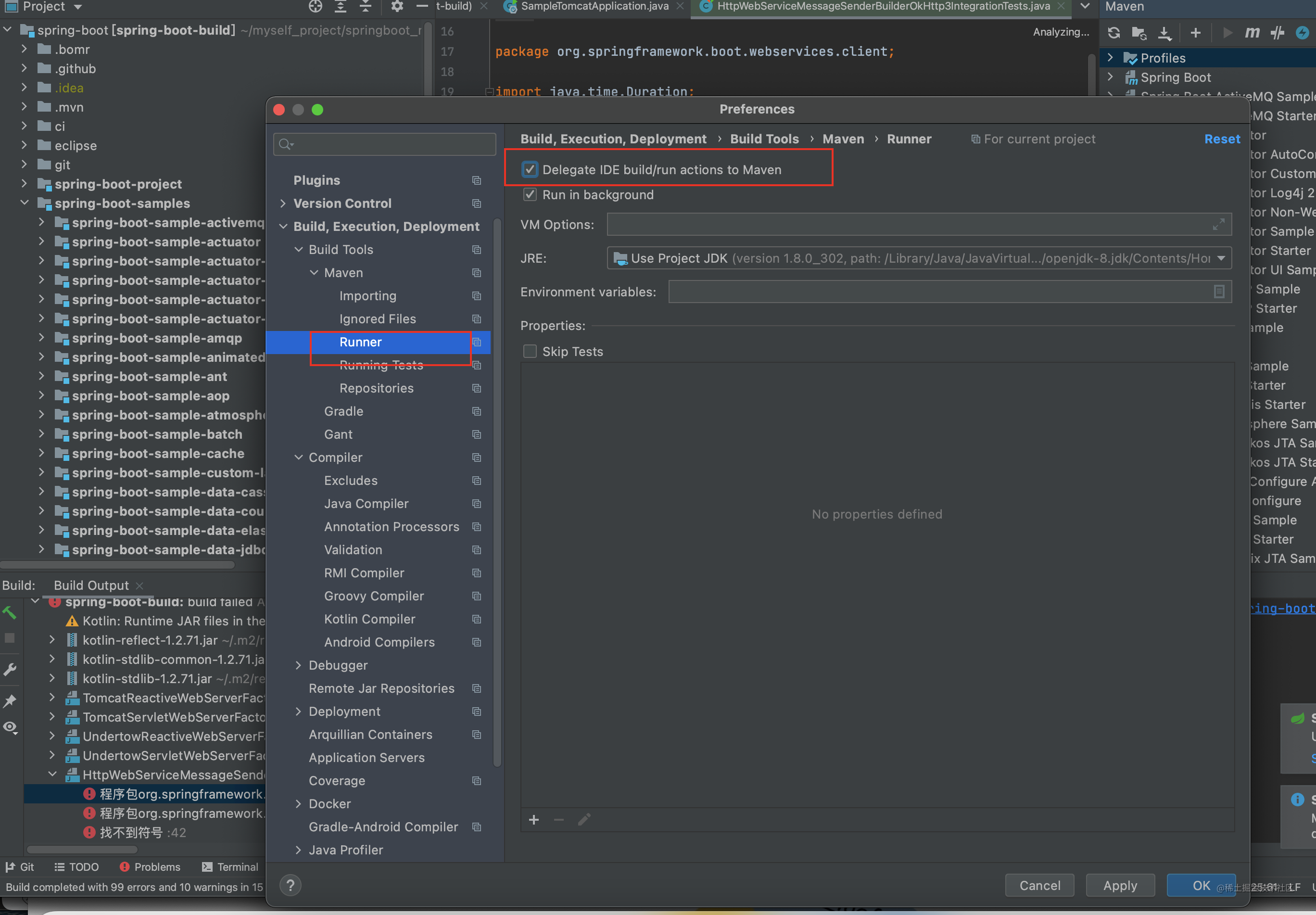
- 注意其会有代码格式检查 需要关掉 在properties标签中加入<disable.checks>true</disable.checks>
- 或者格式化下代码 mvn spring-javaformat:apply
-
2. SpringBoot main方法执行过程详解
注意:(由于一边调试一边写注释的话 debug会错位 造成调试不便 所以我在另一个项目中调试的源码版本都一样)
1. 启动run();方法
@SpringBootApplication
public class SampleTestApplication {
// NOTE: this application will intentionally not start without MySQL, the test will
// still run.
// 启动入口
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SampleTestApplication.class, args);
}
}
2. 进入SpringApplication的构造方法
主要包含两个 1.上下文初始化对象 2.监听器对象
/**
* 创建一个新的 {@link SpringApplication} 实例。该应用程序上下文将从指定的primarySources加载 bean
* (有关详细信息,请参阅 {@link SpringApplication class-level} 文档。可以在调用之前自定义实例
* {@link #run(String...)}.
* @param resourceLoader the resource loader to use
* @param primarySources the primary bean sources
* @see #run(Class, String[])
* @see #setSources(Set)
*
* -- 在该构造中 将创建上下文对象
*
*/
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
//初始化资源加载器,默认为null
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
//校验
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
//初始化 primarySources 类并去重 一般我们就是一个即启动类
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
//推断当前 WEB 应用类型,一共有三种:NONE,SERVLET,REACTIVE 默认SERVLET
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
// <2.1> 设置应用上下文初始化器,从META-INF/spring.factories读取 ApplicationContextInitializer类对应的实例名称集合并去重(一共6个) 随后 利用反射工具进行对象的创建
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// <2.2> 设置监听器,从META-INF/spring.factories 读取ApplicationListener类的实例名称集合并去重。然后反射创建对象 其实和2.1过程很相似 唯一区别是 传入的参数 不同
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
//推断主入口应用类,通过当前调用栈,获取Main方法所在类,并赋值给mainApplicationClass
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
紧接着我们看下 <2.1> 处做了什么
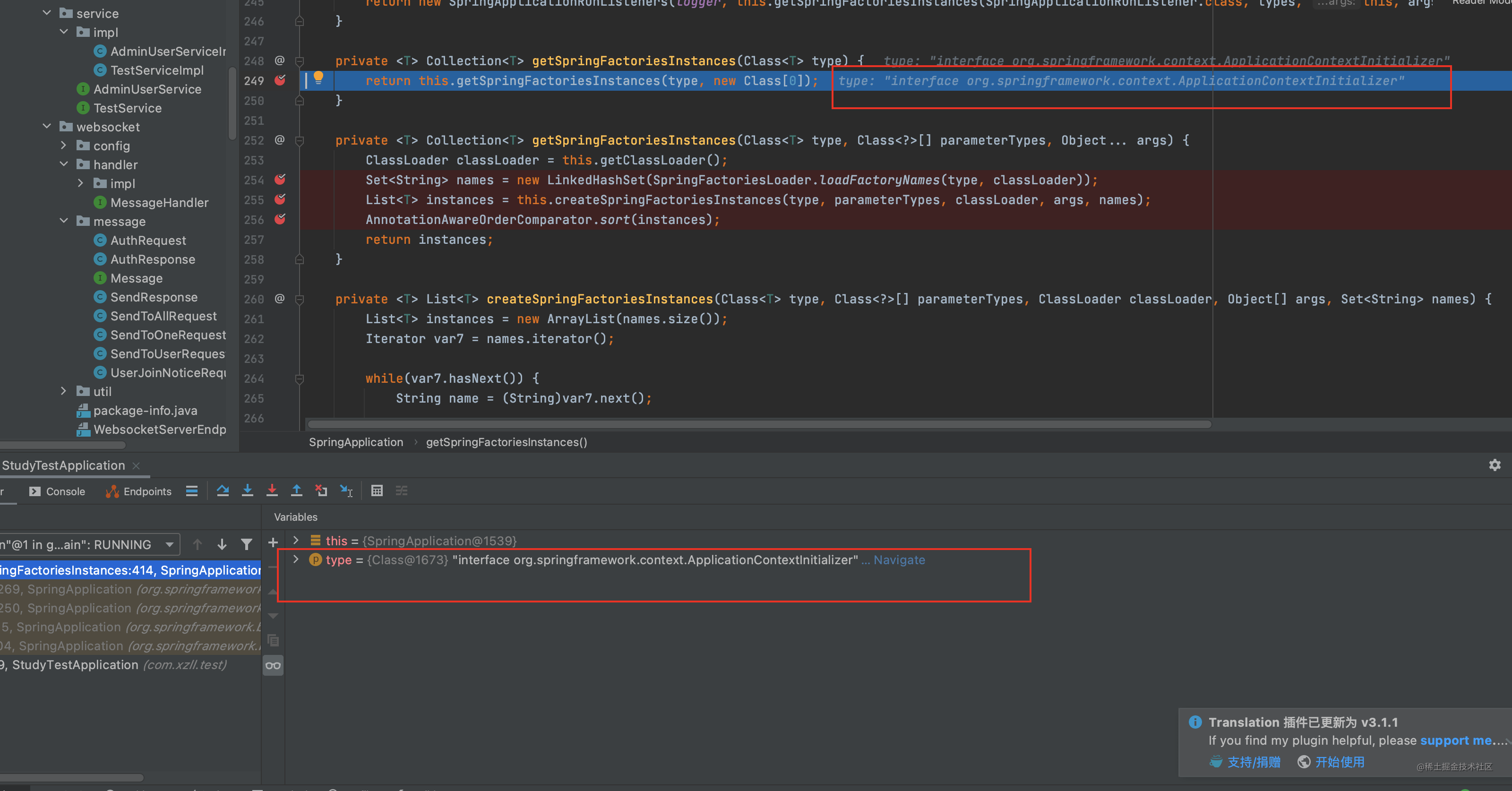
可以看到其用的系统类加载器 关于类加载器 可聊得就太多了 这里不做展开了
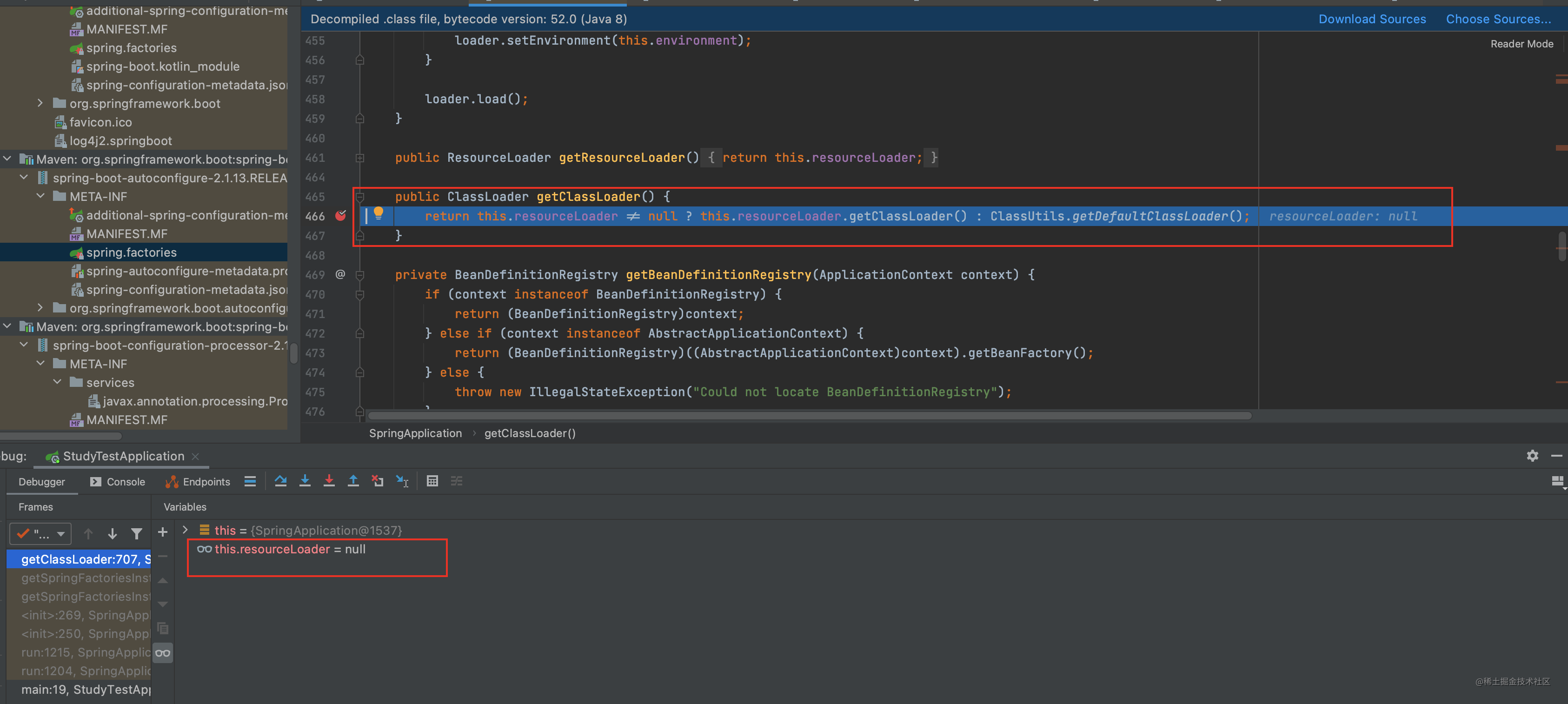
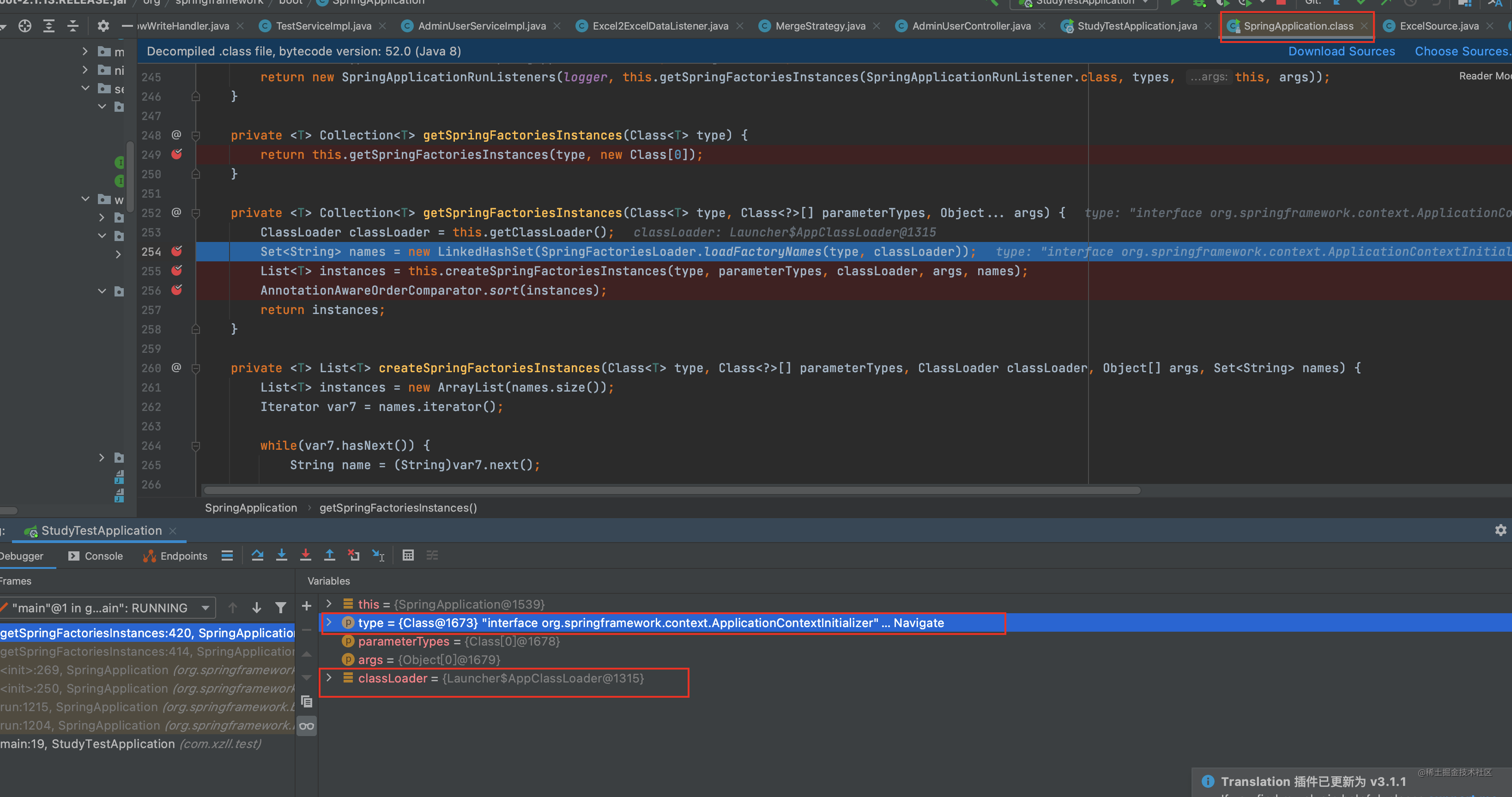
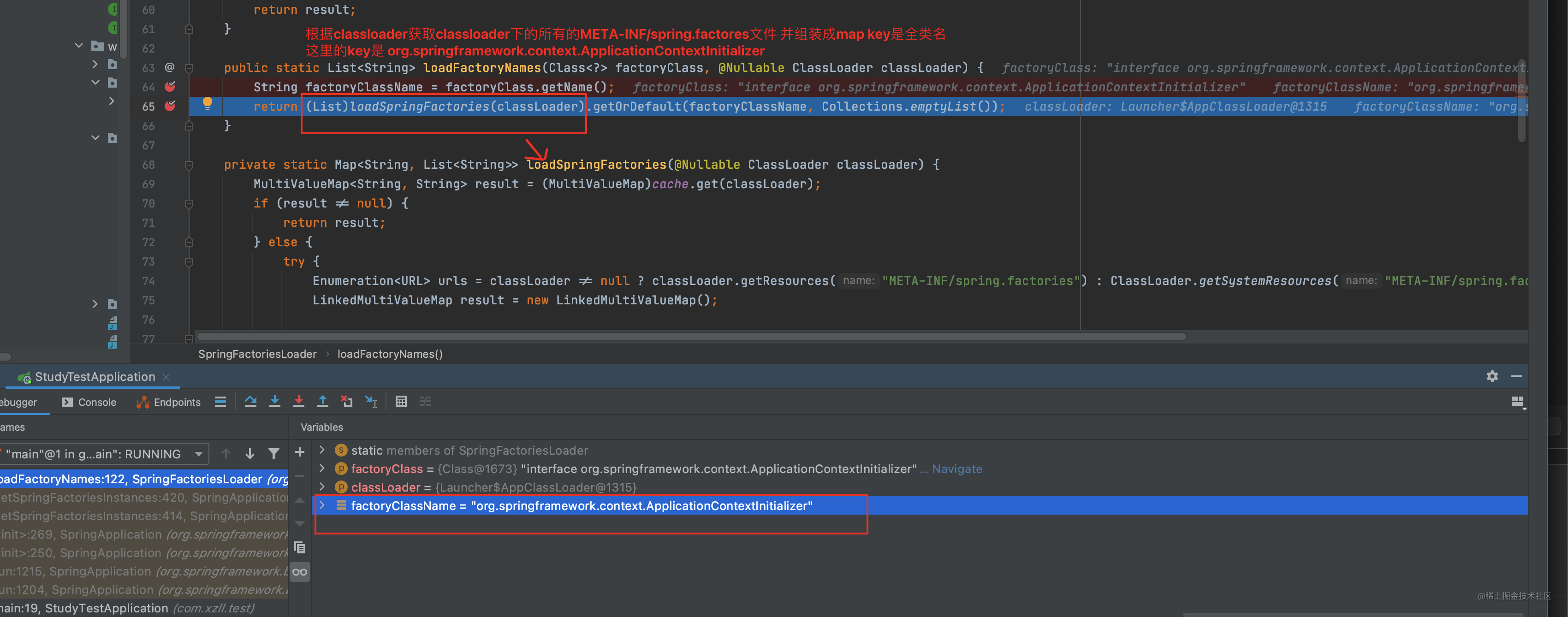
接着使用 private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader)方法获取该类加载器下的所有spring.factories文件 名称 注意是名称还没到创建对象呢
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
//根据类加载器先看看有没有 有直接返回 其实大部分情况都有 只有第一次调用该方法 也就是 构造SpringApplication上下文时候 需要加载当前包以及子包下的spring.factories文件
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = (MultiValueMap)cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} else {
try {
//获取当前类加载器下的所有META-INF/spring.factories文件
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories") : ClassLoader.getSystemResources("META-INF/spring.factories");
LinkedMultiValueMap result = new LinkedMultiValueMap();
//遍历properties 取出对饮的value 文件
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
//这里的url我理解就是 文spring.factoies文件的全路径 事实也是这样的
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
//根据文件的全路径 加载文件中的数据
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
//遍历某个spring.factory.properties文件
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next();
//获取key并去空格 key的形式是啥? 比如像这样: org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer
String factoryClassName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim();
//value就是其对饮的值啦 可能会有很多 具体看某个 spring.factories文件就知道了 commaDelimitedListToStringArray 该方法会将value切分 使用 ,号
String[] var9 = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue());
int var10 = var9.length;
//遍历value数组 填充进LinkedMultiValueMap中
for(int var11 = 0; var11 < var10; ++var11) {
String factoryName = var9[var11];
result.add(factoryClassName, factoryName.trim());
}
}
}
//将类加载器下的所有spring.factores文件都加载到后 填充进 cache中
//cache是个 ConcurrentReferenceHashMap key是 ClassLoader value是 MultiValueMap<String, String> 第一个string是spring.factories的某个key value是某个值(逗号切分后的)
cache.put(classLoader, result);//看看人家多重注性能 哈哈
return result;
} catch (IOException var13) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var13);
}
}
}
-
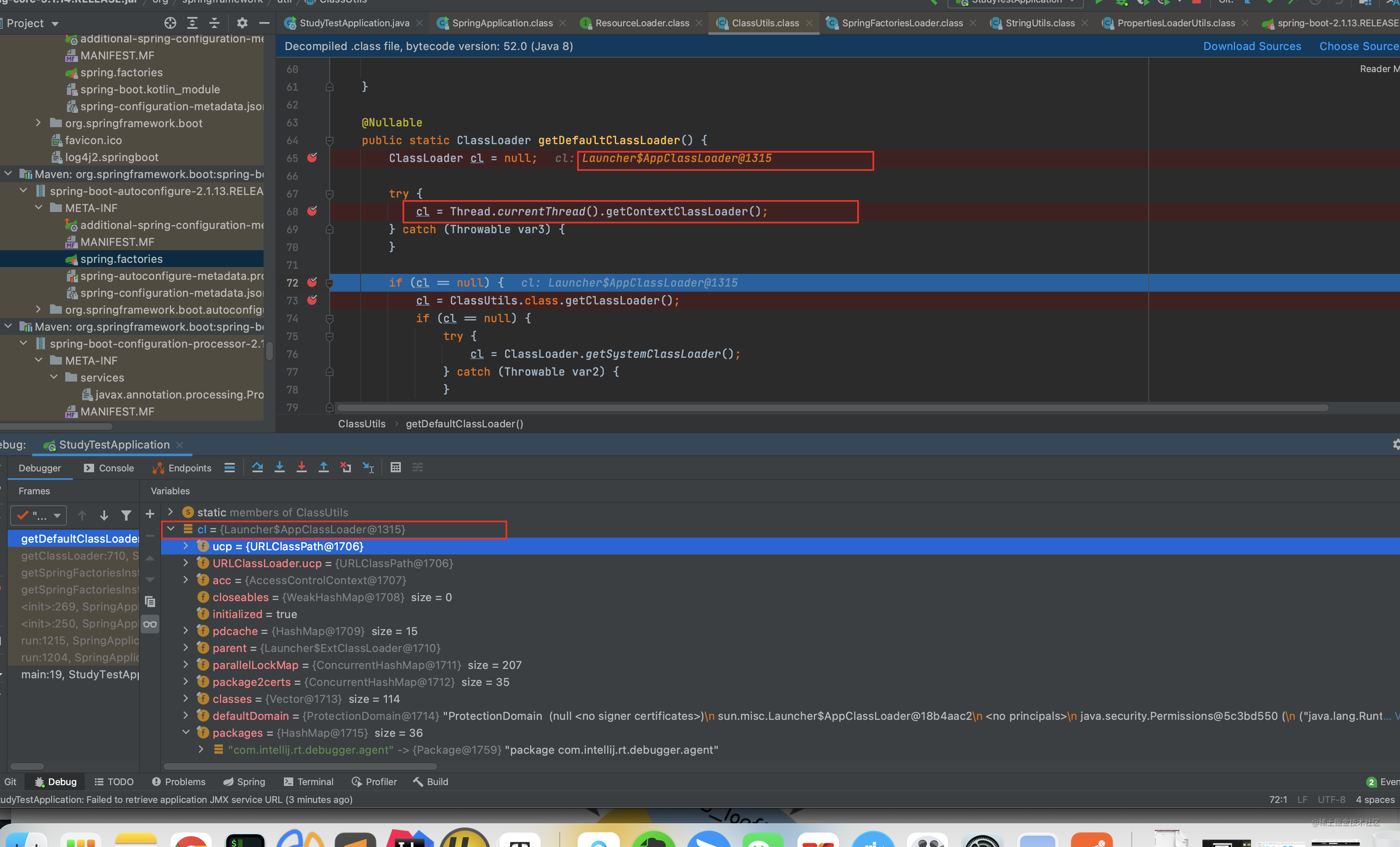
搞几张截图具体看看
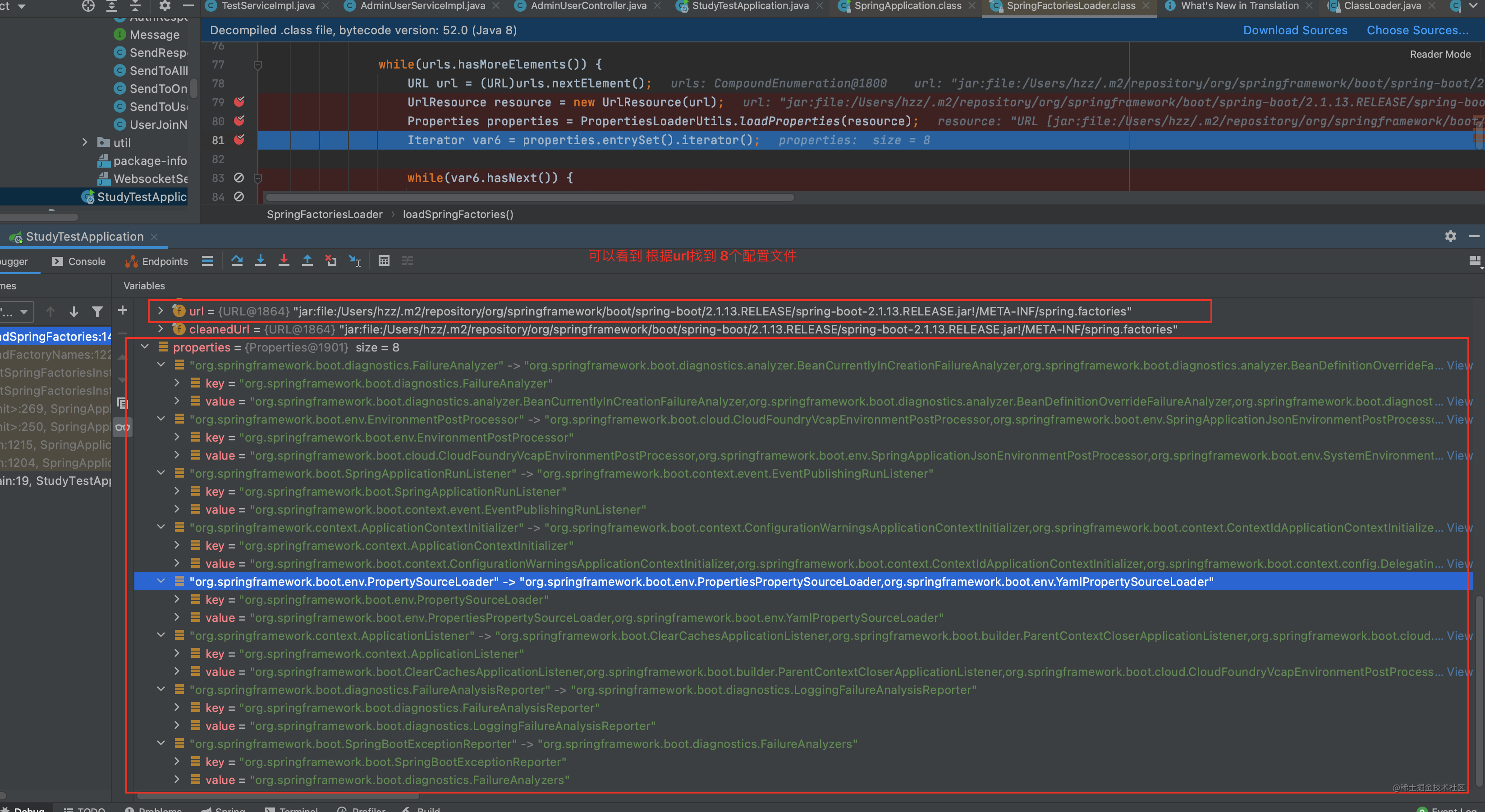
可以看到 根据 org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer这个key找到6个对应的值 注意 spring会把当前主类所在的包以及所有子包下的spring.factories都扫描出来 并存放到 cache中
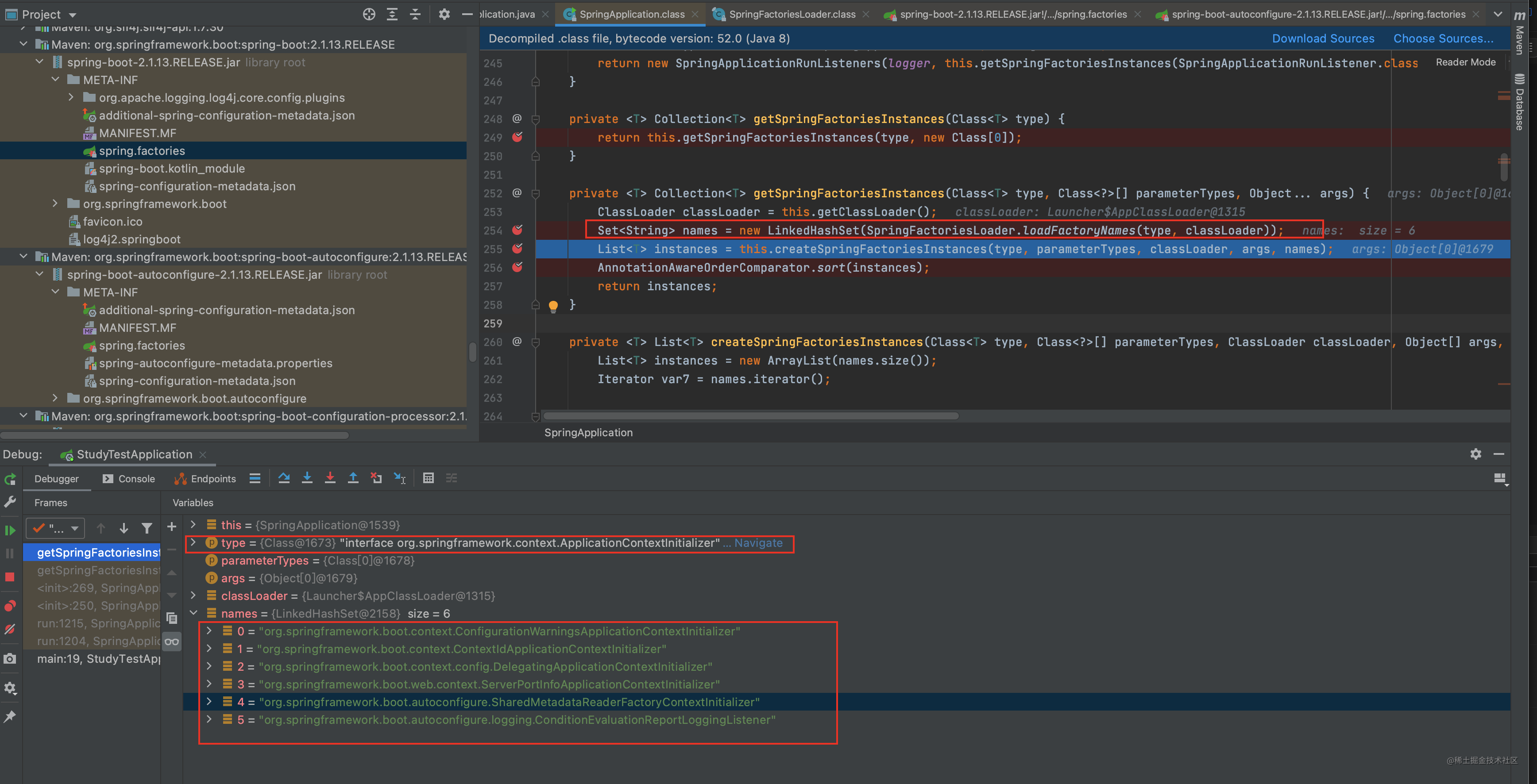 这6大对象是在哪配置的呢?
这6大对象是在哪配置的呢?
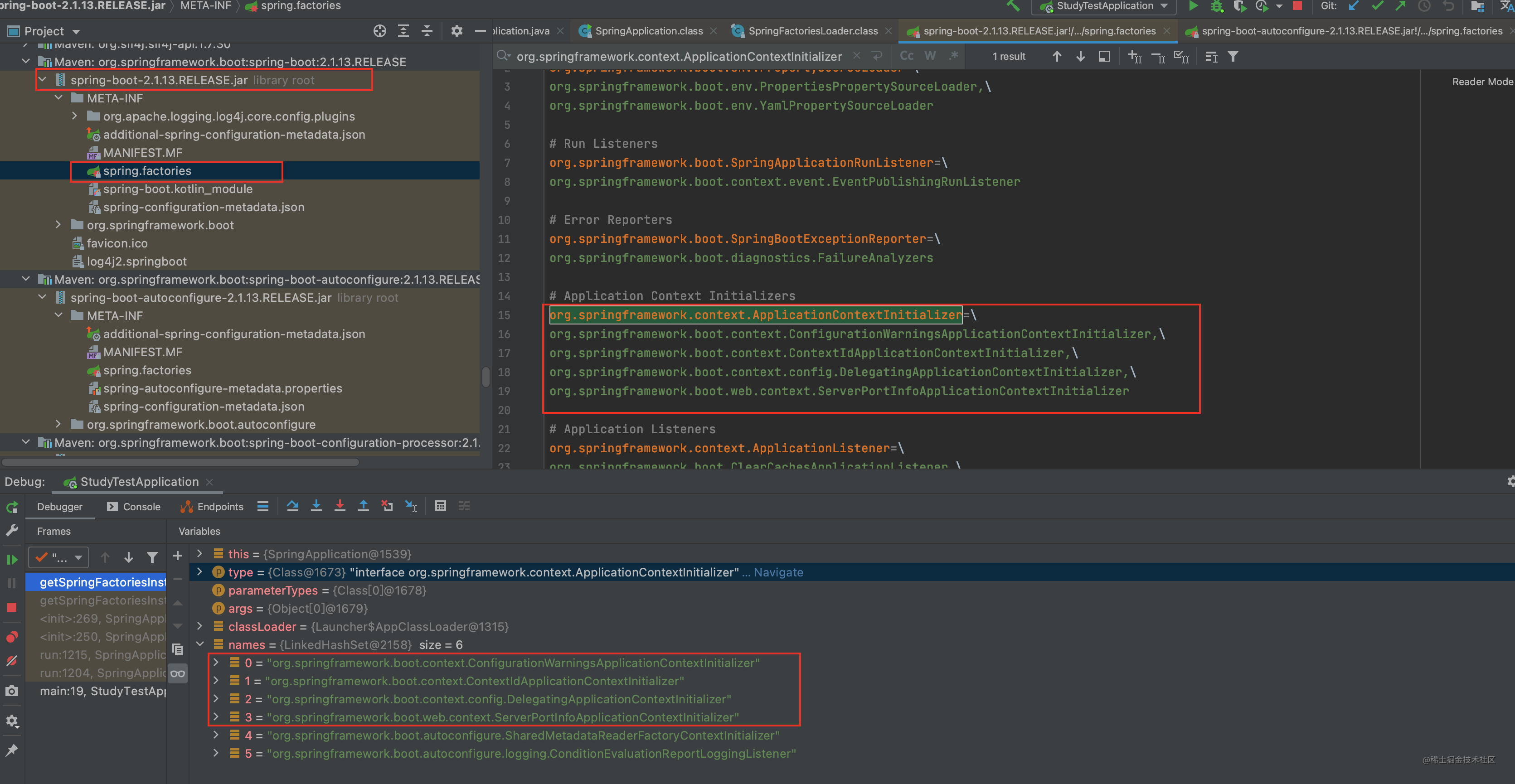
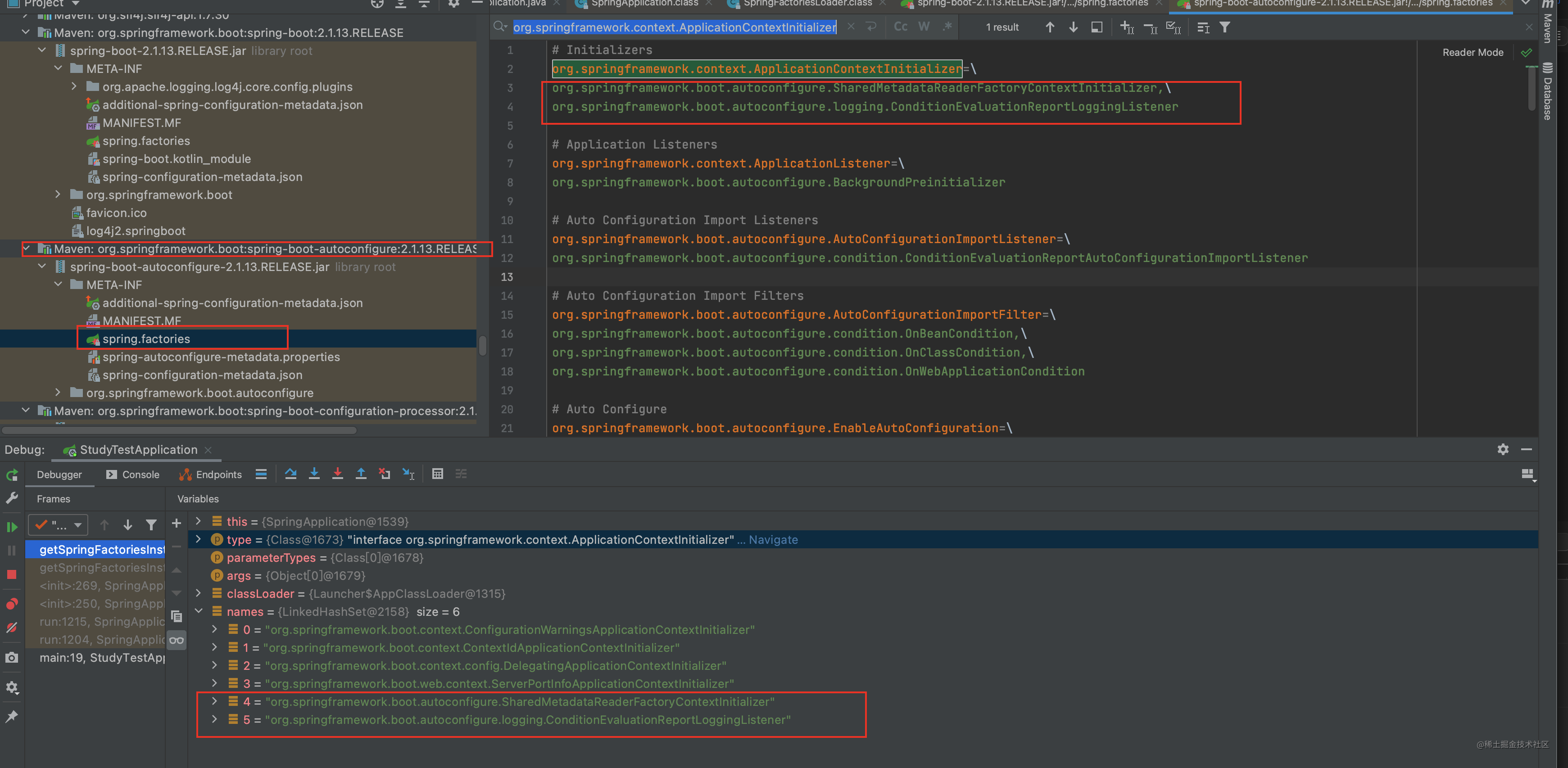
根据上边两张图片 可以看到其配置的位置
加载完所有的spring.factories后 调用 createSpringFactoriesInstances方法 使用反射创建对象 这步简单没啥好说的
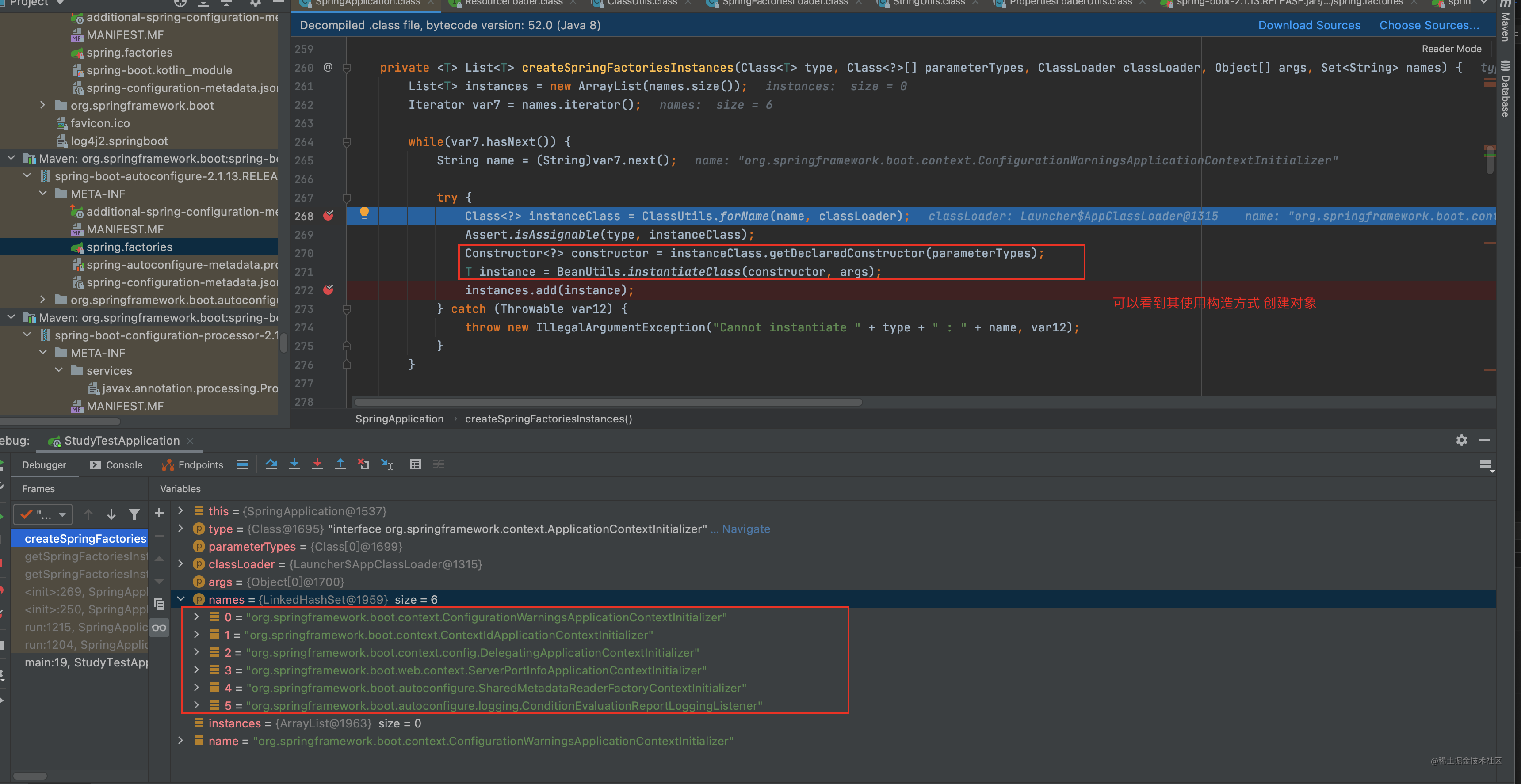
- 最后 给其排个序 注意 这里的排序是根据类注解@Order上的值来排的 不要错误以为其可以对springbean的加载顺序有影响
<2.2> 基本和<2.1>一样 只不过<2.2>是初始化的监听器组件 所以这里不在过多描述
3. SpringApplication初始化完毕后 进入其run方法
这个方法很长也很重要
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
//1. 初始化应用上下文和异常报告集合 在构造SpringApplicaiton时候已经创建过对象了
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList();
//2. 设置系统属性“java.awt.headless”的值,默认为true,用于运行headless服务器,进行简单的图像处理,多用于在缺少显示屏、键盘或者鼠标时的系统配置
this.configureHeadlessProperty();
/**
* 从spring.factories配置文件中加载到EventPublishingRunListener对象并赋值给SpringApplicationRunListeners
* 其作用是准备运行时监听器 用于监听运行时候一切的事件
*
* 在spring-boot的spring.factories文件中
*
* # Run Listeners
* org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\
* org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener
*/
//3. 创建所有springboot运行监听器并发布应用启动事件
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args);
//启动监听器
listeners.starting();
Collection exceptionReporters;
try {
//初始化默认应用参数类
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
//4. 根据监听器(SpringApplicationRunListeners)和应用参数(命令行 ,application.properties文件 等)来准备spring环境
//项目中可以使用@Autowired private Environment environment;来获取一些你需要的属性 很方便哦
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
//配置要忽略的bean
this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
//5. 打印bannner
Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment);
//6. 根据不同的类型创建不同的 ApplicationContext 类型有三种 SERVLET,REACTIVE 普通web
context = this.createApplicationContext();
//7. 获取异常报告器 通过getSpringFactoriesInstances方法 用来报告启动时的错误 ps : 这个方法用的地方这的是太多了
exceptionReporters = this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[]{ConfigurableApplicationContext.class}, context);
//8. 准备应用上下文 调用各个(8个在SpringApplication时候初始化的你忘了吗)ApplicationContextInitializer的initialize方法 和触发SpringApplicationRunListeners的contextPrepared及contextLoaded方法等
this.prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//9. 刷新应用上下文 这一步 灰常重要 这里关于bean的东西不在展开 我将写一篇文章专门解释bean相关的内容
this.refreshContext(context);
//10. 应用上下文后置处理,做一些扩展功能 具体怎么扩展我会写个文章专门介绍Springboot的扩展点以及方式
this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
//11.停止stopWatch 并打印耗时日志
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
(new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
//12. 发布应用上下文启动完成事件:触发所有SpringapplicationRunListener监听器的started事件方法
listeners.started(context);
//13. 执行所有Runner执行器:执行ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner
this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable var10) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var10, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(var10);
}
try {
//14. 发布应用上下文就绪事件:触发SpringapplicationRunnListener 监听器的running事件方法
listeners.running(context);
//15. 返回应用上下文
return context;
} catch (Throwable var9) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var9, exceptionReporters, (SpringApplicationRunListeners)null);
throw new IllegalStateException(var9);
}
}
4.下边详细分析以上步骤
1、初始化应用上下文和异常报告集合 在构造SpringApplicaiton时候已经创建过对象了
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collecton<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
2、设置系统属性java.awt.headless的值:
/*
java.awt.headless模式是在缺少显示屏、键盘或者鼠标的系统配置
当配置了如下属性之后,应用程序可以执行如下操作:
1、创建轻量级组件
2、收集关于可用的字体、字体指标和字体设置的信息
3、设置颜色来渲染准备图片
4、创造和获取图像,为渲染准备图片
5、使用java.awt.PrintJob,java.awt.print.*和javax.print.*类里的方法进行打印
*/
private void configureHeadlessProperty() {
System.setProperty(SYSTEM_PROPERTY_JAVA_AWT_HEADLESS,
System.getProperty(SYSTEM_PROPERTY_JAVA_AWT_HEADLESS, Boolean.toString(this.headless)));
}
3、创建所有spring运行监听器并发布应用启动事件
//创建spring监听器
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
//new创建监听器 SpringApplicationRunListeners
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger,
//又是调用这个方法 去获取监听器(SpringApplicationRunListener)相关的对象
getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));
}
//构造方法 初始化log以及用 getSpringFactoriesInstances方法获取到的对象赋值给 listeners变量
SpringApplicationRunListeners(Log log, Collection<? extends SpringApplicationRunListener> listeners) {
this.log = log;
this.listeners = new ArrayList<>(listeners);
}
//循环遍历获取监听器 并挨个启动
void starting() {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.starting();
}
}
//启动监听器
@Override
public void starting() {
//这里创建ApplicationStartingEvent对象 并将其设置为广播类型
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args));
}
//applicationStartingEvent是springboot框架最早执行的监听器,在该监听器执行started方法时,会继续发布事件,主要是基于spring的事件机制
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
//获取线程池,如果为空则同步处理。这里线程池为空,还未初始化
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
if (executor != null) {
//异步发送事件
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
//同步发送事件
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
4、 根据监听器(SpringApplicationRunListeners)和应用参数(命令行 ,application.properties文件 等)来准备spring环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
//详细环境的准备
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// 获取或者创建应用环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 配置应用环境,配置propertySource和activeProfiles
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
//listeners环境准备,广播ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
//将环境绑定到当前应用程序
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
// 获取或者创建应用环境,根据应用程序的类型可以分为servlet环境、标准环境(特殊的非web环境)和响应式环境
private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() {
//存在则直接返回
if (this.environment != null) {
return this.environment;
}
//根据webApplicationType创建对应的Environment
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
return new StandardServletEnvironment();
case REACTIVE:
return new StandardReactiveWebEnvironment();
default:
return new StandardEnvironment();
}
}
//配置应用环境
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
if (this.addConversionService) {
ConversionService conversionService = ApplicationConversionService.getSharedInstance();
environment.setConversionService((ConfigurableConversionService) conversionService);
}
//配置property sources 即application.properties 文件
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
//配置profiles 如dev test prod
configureProfiles(environment, args);
}
5、打印banner略
6、 根据不同的类型创建不同的 ApplicationContext 类型有三种 SERVLET,REACTIVE 普通web
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch(this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName("org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext");
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName("org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext");
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName("org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext");
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var3) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", var3);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext)BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
7、获取异常报告器 通过 getSpringFactoriesInstances方法 ps : 这个方法用的地方这的是太多了
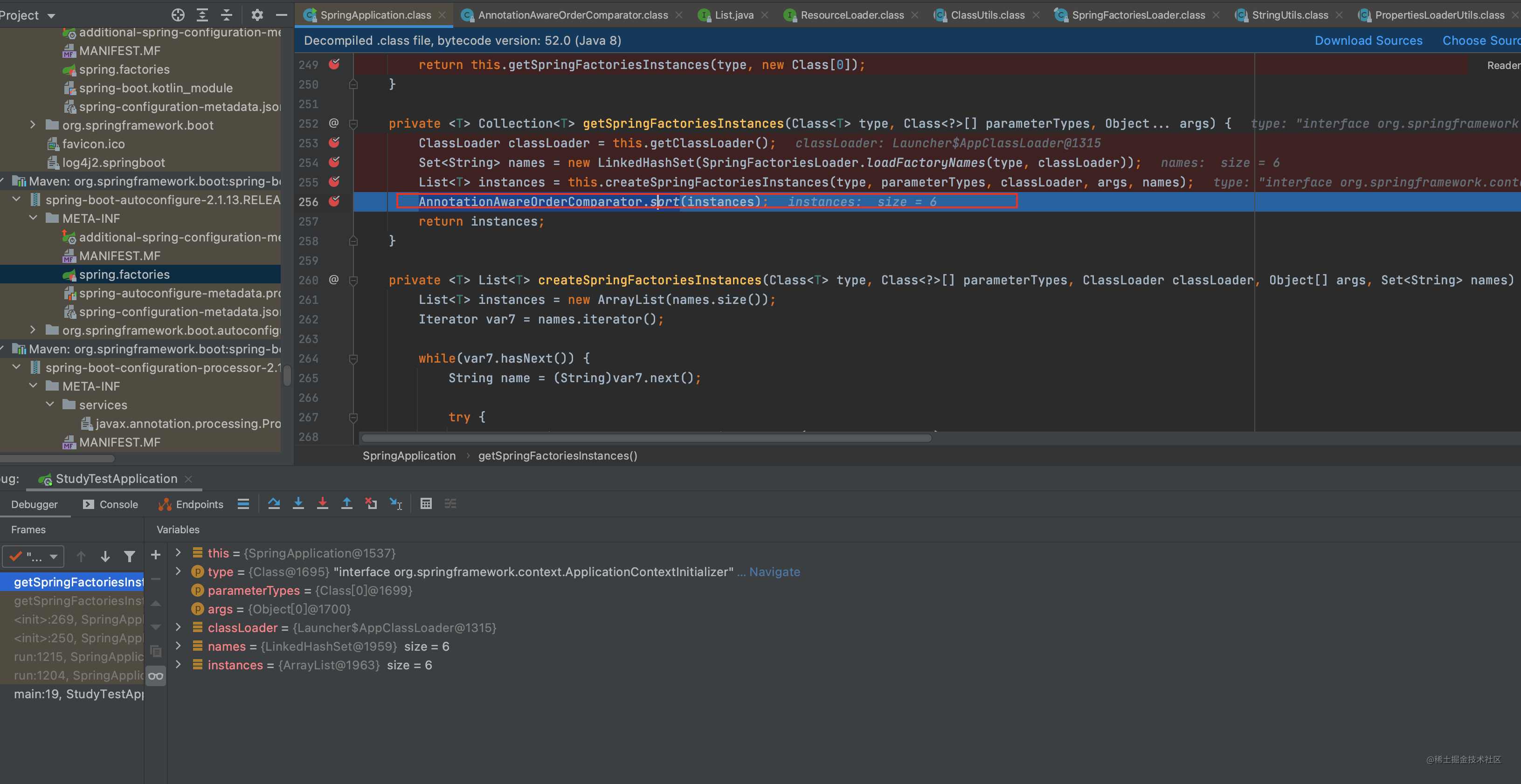
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = this.getClassLoader();
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
List<T> instances = this.createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
可以看下有这些异常收集器
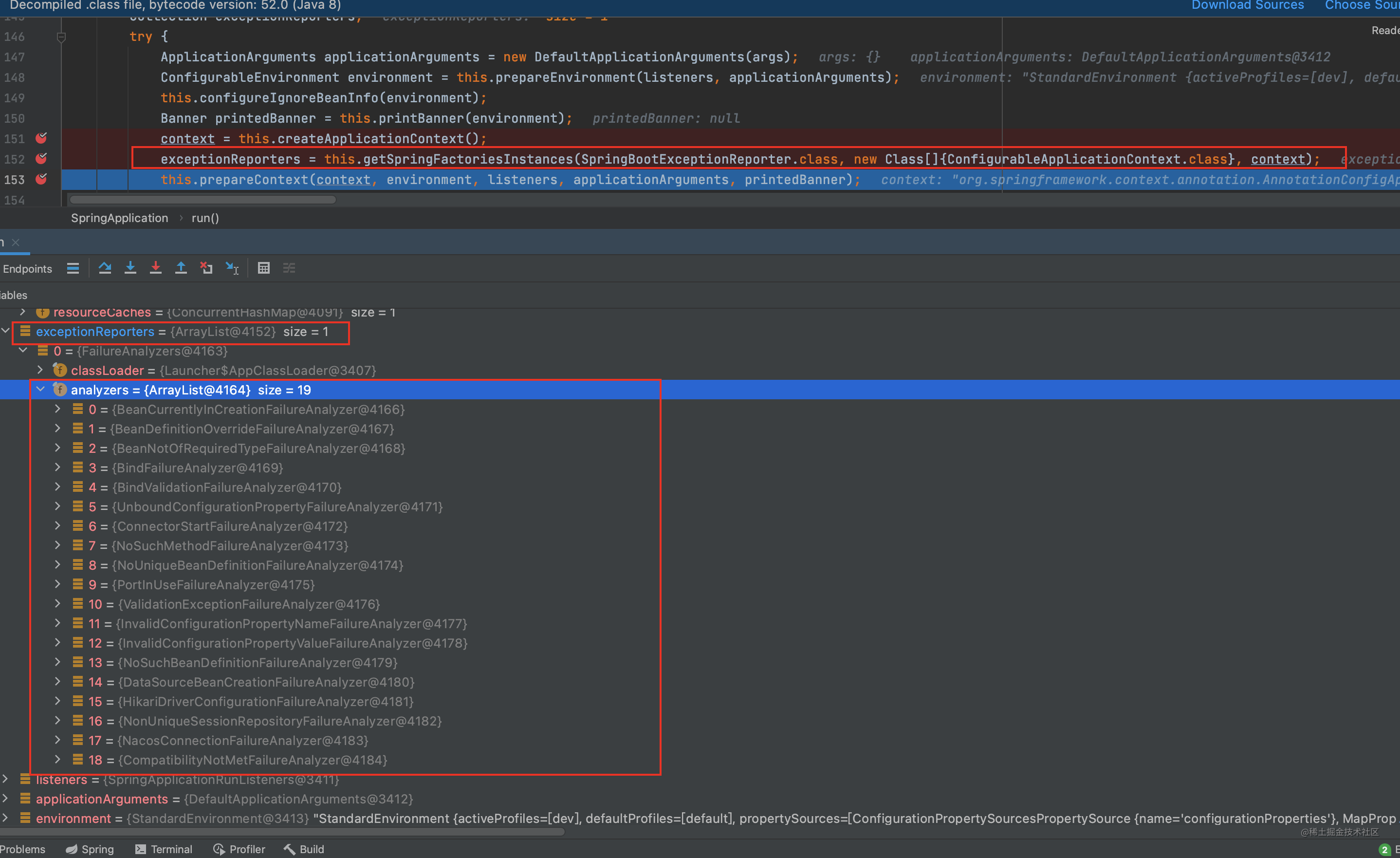
8、准备应用上下文
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
//设置上下文的环境配置
context.setEnvironment(environment);
//上下文后置处理 beanNameGenerator和resourceLoader默认为空,可以方便后续做扩展处理
this.postProcessApplicationContext(context);
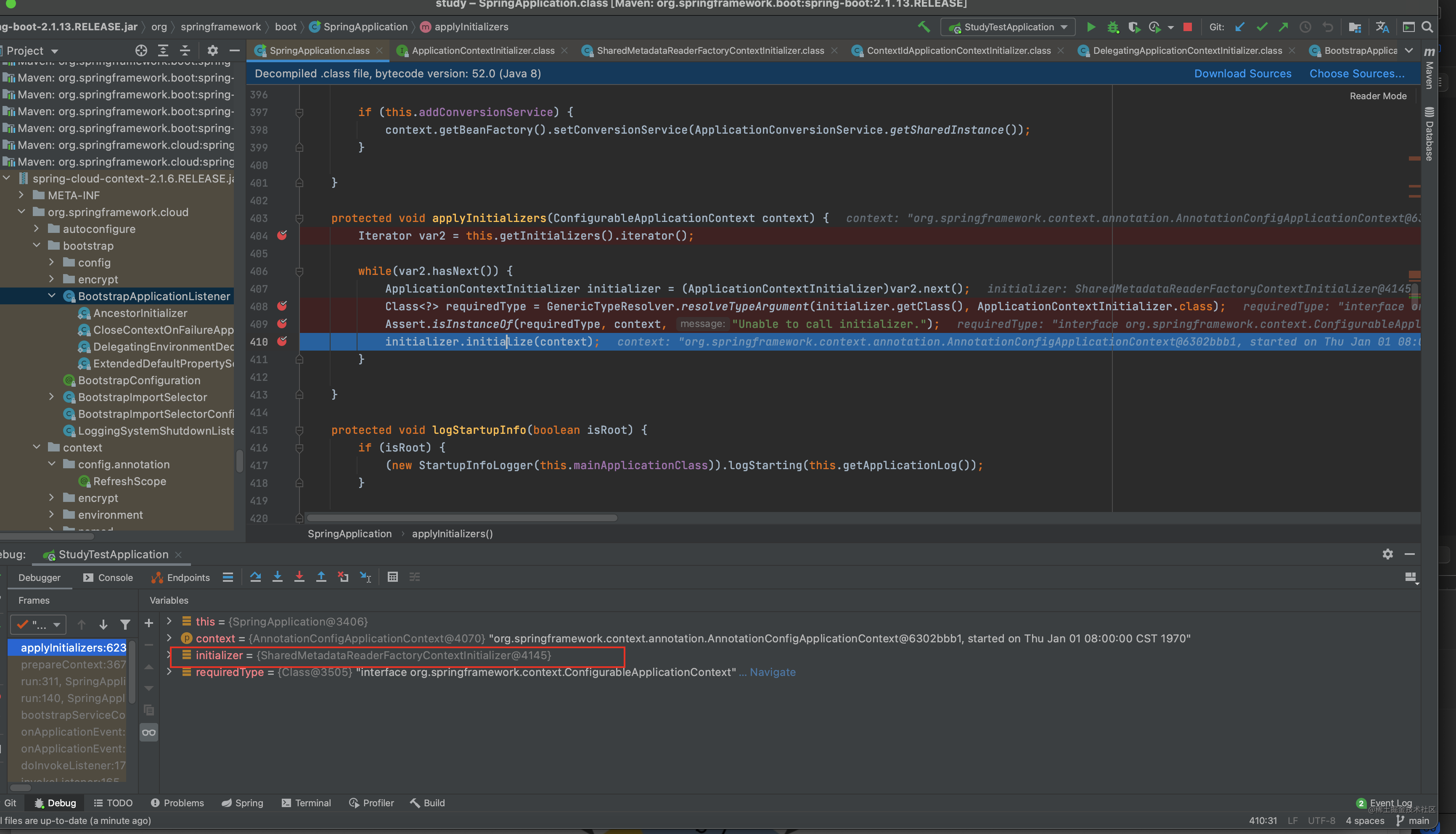
//调用ApplicationContextInitializer的初始化方法初始化context
this.applyInitializers(context);
//调用SpringApplicationRunListener监听器的ContextPrepared方法。添加事件监听器
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
//记录启动日志
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
this.logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
this.logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// 注册启动参数bean,将容器指定的参数封装成bean,注入容器
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory)beanFactory).setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
Set<Object> sources = this.getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
//将bean 的定义信息 (如xml scan扫描到的) 加载到上下文中
this.load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
//调用springapplicationRunListener监听器的contextLoaded事件方法,
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
看看怎么applyInitializers的 具体流程不在展开 有点复杂
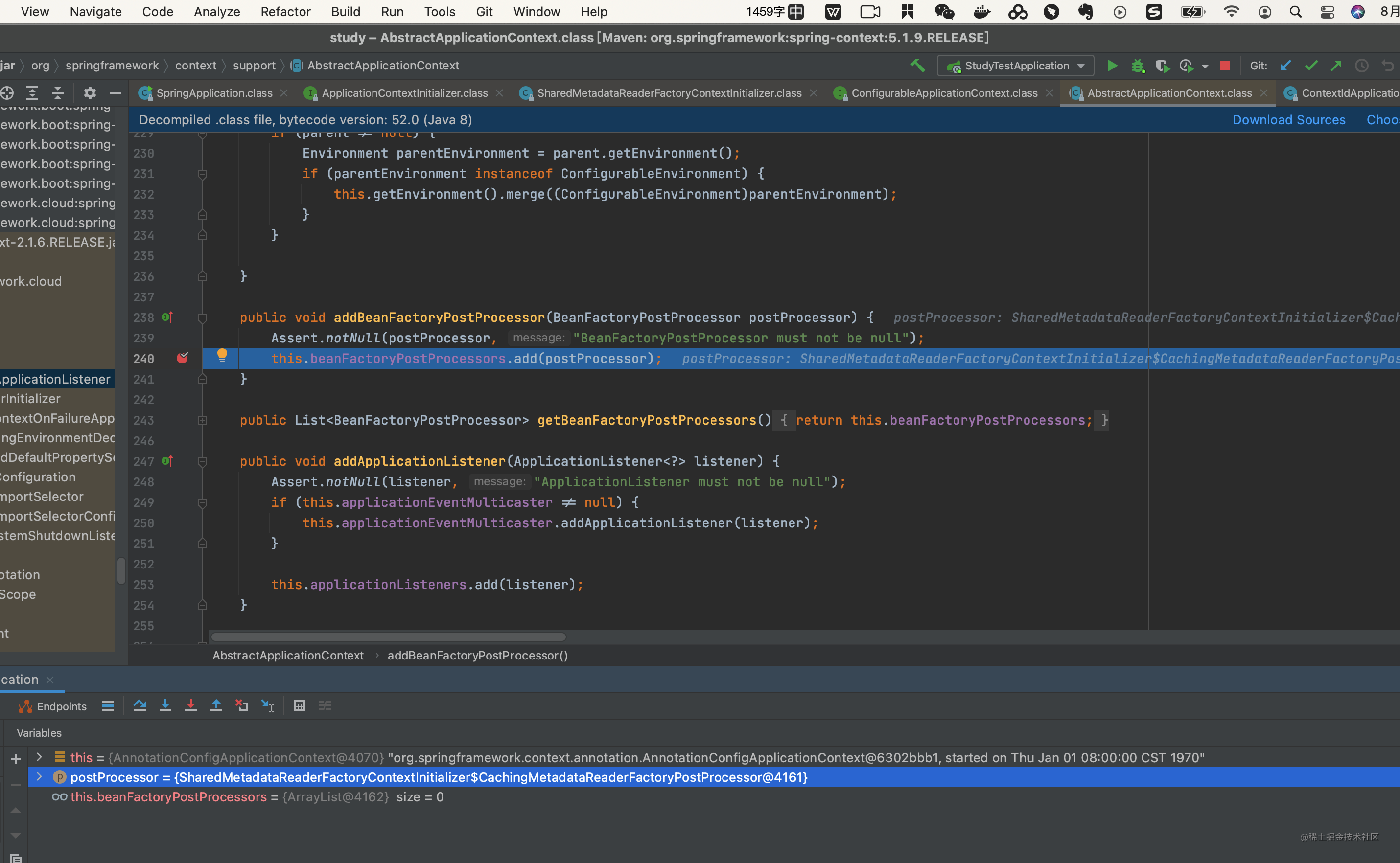
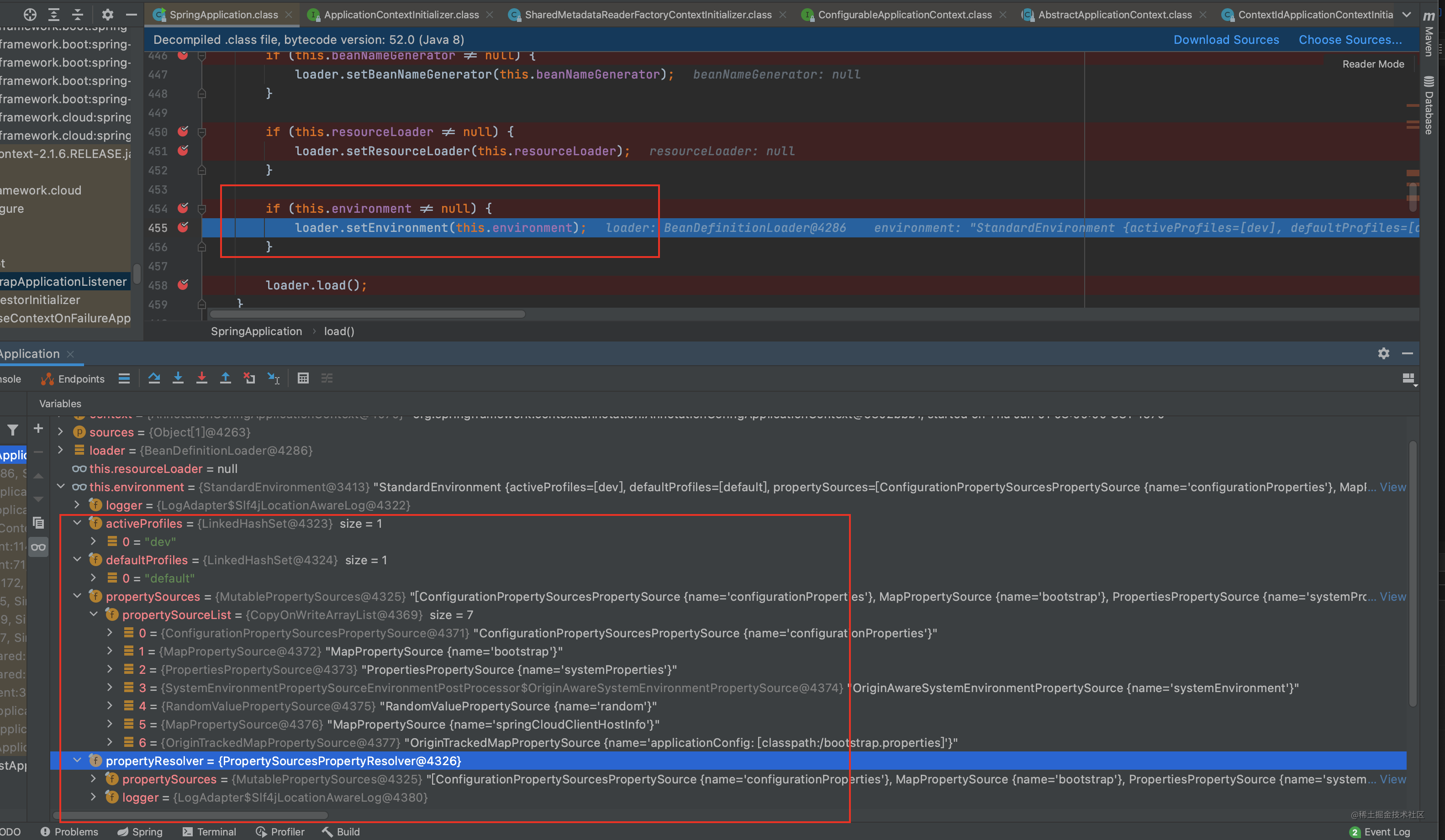
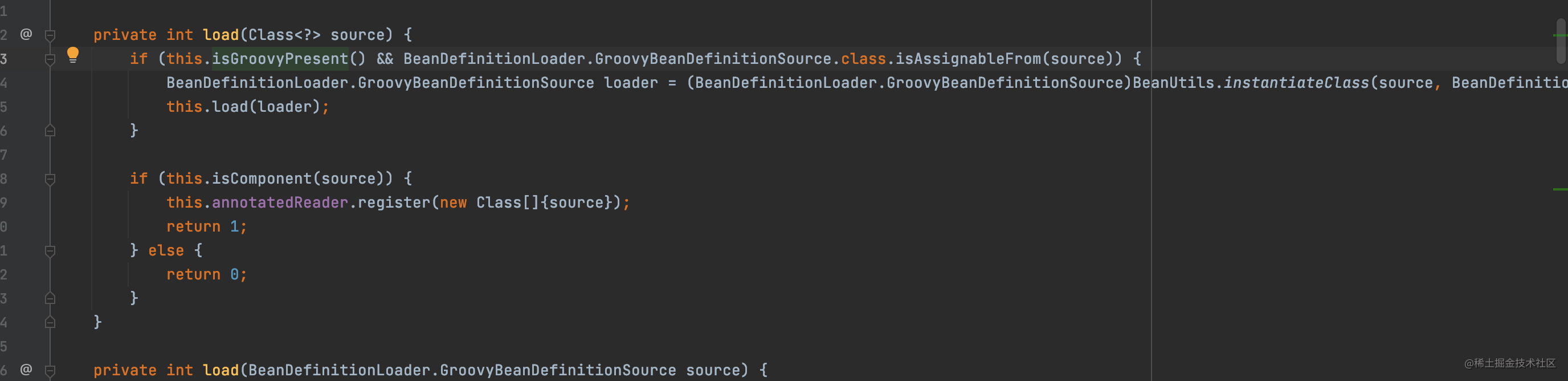
我们看下load干了啥
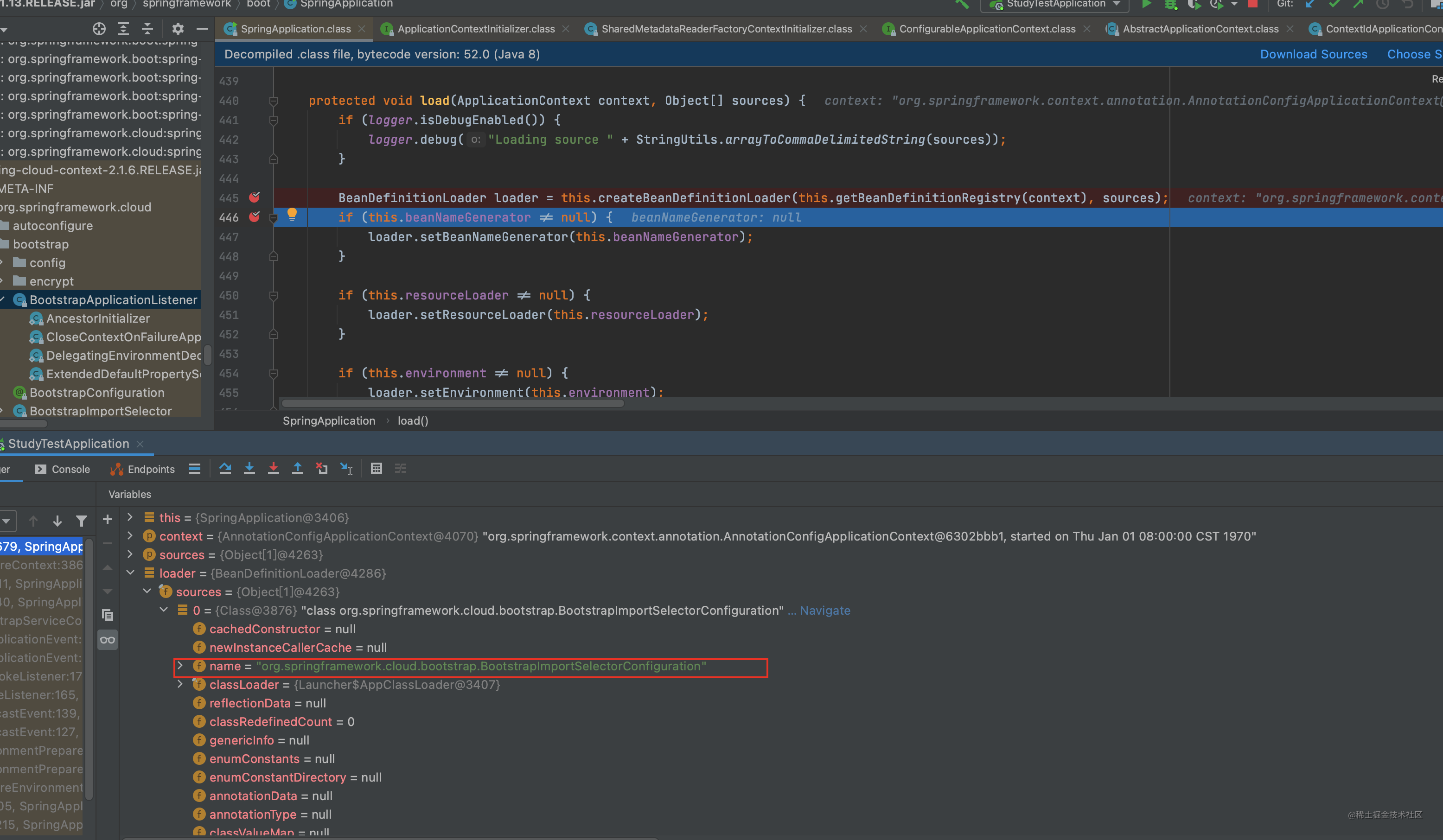
加载 env信息
springboot会优先选择groovy加载方式,找不到在选择java方式
9、刷新应用上下文 这一步 灰常重要 这里关于bean的东西不在展开 我将写一篇文章专门解释bean相关的内容
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
refresh(context);
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
//注册销毁钩子
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
}
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
//刷新上下文环境,初始化上下文环境,对系统的环境变量或者系统属性进行准备和校验
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
//初始化beanfactory,解析xml,相当于之前的xmlBeanfactory操作
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
//为上下文准备beanfactory,对beanFactory的各种功能进行填充,如@autowired,设置spel表达式解析器,设置编辑注册器,添加applicationContextAwareprocessor处理器等等
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
//提供子类覆盖的额外处理,即子类处理自定义的beanfactorypostProcess
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
//激活各种beanfactory处理器
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
//注册beanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
//初始化上下文中的资源文件如国际化文件的处理
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
//初始化上下文事件广播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
//给子类扩展初始化其他bean
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
//在所有的bean中查找listener bean,然后 注册到广播器中
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//初始化剩余的非懒惰的bean,即初始化非延迟加载的bean
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
//发完成刷新过程,通知声明周期处理器刷新过程,同时发出ContextRefreshEvent通知别人
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
10、 应用上下文刷新后置处理
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
//当前方法的代码是空的,可以做一些自定义的后置处理操作
protected void afterRefresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
}
11、 停止stopWatch 并打印耗时日志
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
(new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
12、 发布应用上下文启动完成事件:触发所有SpringapplicationRunListener监听器的started事件方法
listeners.started(context);
void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.started(context);
}
}
13、执行所有Runner执行器:执行ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);
}
}
}
14、发布应用上下文就绪事件:触发SpringapplicationRunnListener 监听器的running事件方法
listeners.running(context);
void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.running(context);
}
}
SpringApplicationRunListener说明:
注意: 由于在启动过程中多次调用了SpringApplicationRunListener的方法 我觉得有必要说明一下这个接口的方法都是干嘛的. 如下:
public interface SpringApplicationRunListener {
// 在run()方法开始执行时,该方法就立即被调用,可用于在初始化最早期时做一些工作
void starting();
// 当environment构建完成,ApplicationContext创建之前,该方法被调用
void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment);
// 当ApplicationContext构建完成时,该方法被调用
void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context);
// 在ApplicationContext完成加载,但没有被刷新前,该方法被调用
void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context);
// 在ApplicationContext刷新并启动后,CommandLineRunners和ApplicationRunner未被调用前,该方法被调用
void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context);
// 在run()方法执行完成前该方法被调用
void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context);
// 当应用运行出错时该方法被调用
void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception);
}
5. 最后我们来总结下整个流程 (文字+图),一图胜千言万字。
run方法启动总结(文字版)
1. 构造SpringApplication对象
1.1 推断是哪种应用 通过是否包含包路径进行判断(具体看代码即可)
1.2 设置应用上下文初始化器,从META-INF/spring.factories读取ApplicationContextInitializer类的实例名称集合并去重后 创建对象
1.3 设置监听器,从META-INF/spring.factories读取ApplicationListener类的实例名称集合并去重,并创建对象
1.4 推断主入口应用类,通过当前调用栈,获取Main方法所在类,并赋值给mainApplicationClass
2.调用SpringApplication的run方法 (非重要方法这里直接略过)
2.1 加载SpringApplicationRunListeners监听器 并发送ApplicationStartingEvent事件
(这个事件的内容其实简单来说就是 "我要启动啦" )
2.2 配置环境模块 Environment (我们可以在项目中通过他获取配置)
2.3 打印bannner (你也可以自定义你的banner)
2.4 根据不同的类型创建不同的 ApplicationContext(也叫上下文/容器) (类型有三种 SERVLET,REACTIVE 普通web)
2.5 获取异常报告器 (用来报告启动时的错误)
2.6 准备应用上下文 并调用 ApplicationContextInitializer的initialize进行初始化
2.7 刷新上下文 (如@Autoware BeanFactory初始化 等等关于bean的操作都在这里)
2.8 刷新后的操作 (由子类去扩展)
2.9 发送事件(时间内容是"我已经启动"),标志spring容器已经刷新,此时所有的bean实例都已经加载完毕
3.0 查找容器中注册有CommandLineRunner或者ApplicationRunner的bean,遍历并执行run方法
3.1 发送ApplicationReadyEvent事件(事件内容为 “启动成功我现在可以接受请求了!”)
3.2 返回应用上下文
run方法启动总结(图片版更详细些)
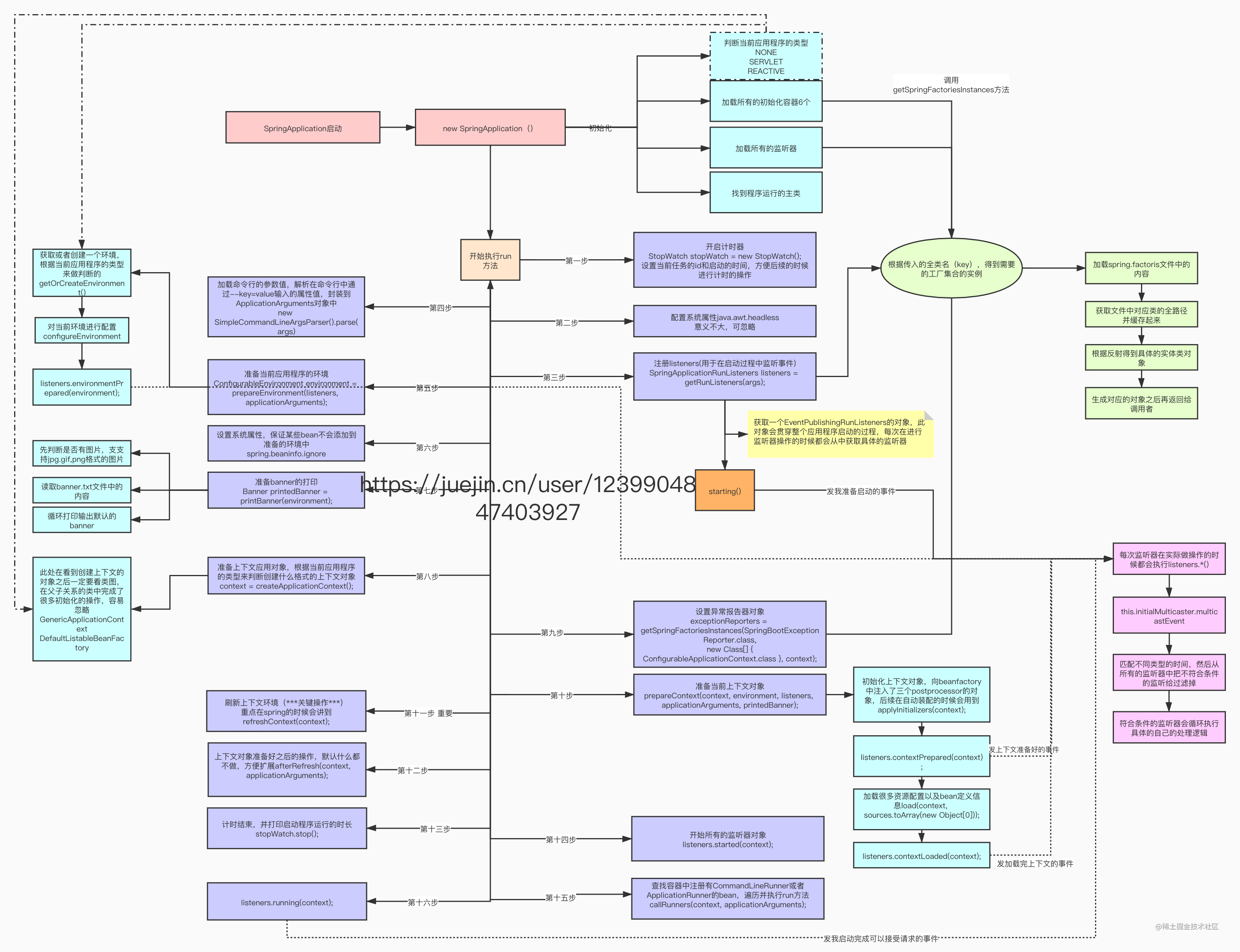
6. 总结
- 一入源码深似海 看源码时候我们不需要过于深入专进去 要把握好一个度 如果把每个方法的内部的内部的内部的内部都看一遍 那样反而会使我们绕进去 也比较耗时费力。我个人觉得 主流程首先你一定是要看的,并且在每个阶段做了什么事情 你也一定要知道,另外就是像刷新容器这种操作 一定一定一定要多看几遍并且可以深入去研究下他到底是如何做得 ,另外 一定要有自己的注释 总结 思考。否则过几天真的很容易忘。
完。
