工厂类
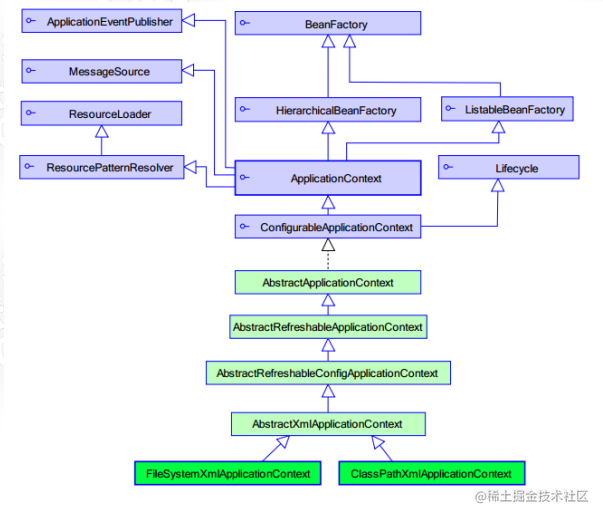
- BeanFactory和ApplicationContext创建实例的时机不同:前者是在工厂实例化完以后,在调用getBean的时候,才会来创建类的实例,而后者是一加载配置文件的时候就会将配置文件中所有单例模式生成的类全都实例化。
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:类路径下的配置文件
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext: 加载文件系统中的配置文件
- 更多时候使用的是ApplicationContext接口以及他的实现类ClassPathXmlApplicationContext和FileSystemXmlApplicationContext来完成Spring工厂类的创建
Bean管理XML方式
三种实列化Bean的方式
- 使用构造器实列化(默认无参数)
========Bean2========
public class Bean1 {
public Bean1(){
System.out.println("Bsne1被实列化了.....");
}
}
========Test========
public void demo1(){
//创建工厂
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//通过工厂获得类的实列
Bean1 bean1 = (Bean1)applicationContext.getBean("bean1");
}
========XMLBean========
<bean id="bean1" class="demo2.Bean1"></bean>
- 使用静态工厂方法实列化(简单工厂模式)
========Bean2========
public class Bean2 {
public Bean2(){
System.out.println("Bsne2被实列化了.....");
}
}
========Bean2Factory========
public class Bean2Factory {
public static Bean2 createBean2(){
System.out.println("Bean2Factory开始工作了");
return new Bean2();
}
}
========Test========
public void demo2(){
//创建工厂
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//通过工厂获得类的实列
Bean2 bean2 = (Bean2)applicationContext.getBean("bean2");
}
========XMLBean========
<bean id="bean2" class="demo2.Bean2Factory" factory-method="createBean2"></bean>
- 使用实列工厂方式实列化(工厂方式模式)
========Bean3========
public class Bean3 {
public void Bean3(){
System.out.println("Bean3被实列化了....");
}
}
========Bean3Factory========
public class Bean3Factory {
public Bean3 createBean3(){
System.out.println("Bean3Factory开始工作了");
return new Bean3();
}
}
========Test========
public void demo3(){
//创建工厂
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//通过工厂获得类的实列
Bean3 bean3 = (Bean3)applicationContext.getBean("bean3");
}
========XMLBean========
<bean id="bean3Factory" class="demo2.Bean3Factory"></bean>
<bean id="bean3" factory-bean="bean3Factory" factory-method="createBean3"></bean>
Bean的配置
- id和name
- 一般情况下,装配一个Bean时,指定一个id属性作为Bean的名称
- id属性咋IOC容器中必须是唯一的
- 如果Bean的名称中含有特殊字符,就需要使用name属性
- class
- 用于设置一个类的完全路径名称,主要作用是IOC容器生成类的实列
Bean的作用域
| 类别 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| singleton | 在SpringIOC容器中仅存在一个Bean实列,Bean以单实列的方式存在 |
| prototype | 每次调用getBean()时都会返回一个新实列 |
| request | 每次HTTP请求都会创建一个新的Bean,该作用域仅适用于WenApplicationContext环境 |
| session | 同一个HTTPSession共享一个Bean,不同的HTTPSession适用不同的Bean。该作用域仅适用WenApplicationContext环境 |
Bean的生命周期
-
Spring初始化bean或销毁bean时,有时需要做一些处理工作,因此Spring可以在创建和销毁bean的时候调用bean的两个生命周期方法。
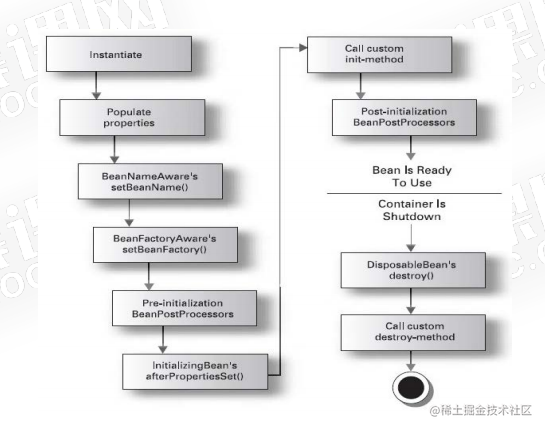
过程
- instantiate bean对象实例化
- 对象实列化
- populate properties 封装属性
- 设置属性
- 如果Bean是吸纳BeanNameAware执行 setBeanName
- 设置Bean的名称
- 如果Bean实现BeanFactoryaware或者ApplicationcontextAware设置工厂 setBeanFactory 或者上下文对象 setApplicationContext
- 了解工厂信息
- 如果存在类实现BeanPostProcessor(后处理Bean),执行 postProcessBefpreInitialization
- 如果Bean实现InitializingBean执行afterPropertiesSet
- 调用< bean init-method= "init">指定初始化方法init
- 如果存在类实现BeanPostProcessor (处理Bean),执行postProcessAfterInitialization
- 执行业务处理
- 如果Bean实现DisposableBean执行destroy
- 调用< bean destroy-method= "customerDestroy">指定销毁方法customerDestroy
Spring属性注入
- 对类成员变量注入方式
- 构造函数注入
- 属性setter方法注入
- 接口注入(Spring不支持)
Bean的构造方法的属性注入
- 通过构造方法注入Bean的属性值或依赖的对象,它保证了Bean实例在实例化后就可以使用构造器中注入在元素里声明的属性
========User========
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public User(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
========Test========
public void demo1(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
User user = (User) applicationContext.getBean("user");
System.out.println(user);
}
========BeanXML=======
<bean id="user" class="demo4.User">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="张三"/>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="20"/>
</bean>
set方法的属性注入
- 使用set方法注入,在Spring配置文件中,通过设置注入的属性
=========Person========
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Cat cat;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Cat getCat() {
return cat;
}
public void setCat(Cat cat) {
this.cat = cat;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", cat=" + cat +
'}';
}
}
========Cat========
public class Cat {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
=========Test========
public void demo2(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Person person = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("person");
System.out.println(person);
}
========BeanXML========
<bean id="person" class="demo4.Person">
<property name="name" value="张三"/>
<property name="age" value="19"/>
<property name="cat" ref="cat"/>
</bean>
<bean id="cat" class="demo4.Cat">
<property name="name" value="ketty"/>
</bean>
p名称空间注入
- 未来简化XML文件配置,Spring从2.5开始引入一个新的p名称空间
- 引入常值:<属性名>="xxx"
- 引用其他Bean对象:<属性名>-ref="xxx"
=========引入xmlbs=========
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
=========BeanXML==========
<bean id="person" class="demo4.Person" p:name="张三" p:age="18" p:cat-ref="cat"></bean>
<bean id="cat" class="demo4.Cat" p:name="xiaoxiao"></bean>
SpEL注入
-
SpELl:Spring Expression Language,Spring表达式语言,对依赖注入进行简化。
-
语法:#{表达式}
<bean id = "" value = "#{表达式}">
简单类型
<bean id="productInfo" class="demo4.PorductInfo"></bean>
<bean id="product" class="demo4.Product">
<property name="name" value="#{'afterglow'}"/>
<property name="price" value="#{productInfo.calculatePrice()}"/>
<property name="category" value="#{category}"/>
</bean>
复杂类型
- 数组类型的属性注入
- List集合类型的属性注入
- Set集合类型的属性注入
- Map集合类型的属性注入
- Properties类型的属性注入
========CollectionBean========
public class CollectionBean {
private String[] arrs; //数组类型
private List<String> list; //List集合类型
private Set<String> set; //Set集合类型
private Map<String, Integer> map; //Map集合类型
private Properties properties; //属性类型
public String[] getArrs() {
return arrs;
}
public void setArrs(String[] arrs) {
this.arrs = arrs;
}
public List<String> getList() {
return list;
}
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public Set<String> getSet() {
return set;
}
public void setSet(Set<String> set) {
this.set = set;
}
public Map<String, Integer> getMap() {
return map;
}
public void setMap(Map<String, Integer> map) {
this.map = map;
}
public Properties getProperties() {
return properties;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CollectionBean{" +
"arrs=" + Arrays.toString(arrs) +
", list=" + list +
", set=" + set +
", map=" + map +
", properties=" + properties +
'}';
}
}
========Test========
public void demo1(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
CollectionBean collectionBean = (CollectionBean)applicationContext.getBean("collectionBean");
System.out.println(collectionBean);
}
========BeanXML========
<bean id="collectionBean" class="Demo5.CollectionBean">
<!--数组集合属性注入-->
<property name="arrs">
<list>
<value>1</value>
<value>2</value>
<value>3</value>
<value>4</value>
<value>5</value>
<value>6</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="list">
<!--List集合属性注入-->
<list>
<!--
对象属性使用ref
简单属性使用value
-->
<value>11</value>
<value>12</value>
<value>13</value>
<value>14</value>
<value>15</value>
<value>16</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--Set集合属性注入-->
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>121</value>
<value>122</value>
<value>123</value>
<value>124</value>
<value>125</value>
<value>126</value>
</set>
</property>
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="222" value="4555"/>
<entry key="333" value="5666"/>
</map>
</property>
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="usrname">root</prop>
<prop key="passwd">123456</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
Bean管理-注解方式
注解定义Bean
- @Component 描述Spring框架中Bean
- @Repository 用于对DAO实现类进行标注
- @Service 用于对Service实现类进行标注
- @Controller 用于对Controller实现类进行标注 这三个注解是为了让标注类本身的用途清晰,Spring在后续版本会对其增强 @Repository用于对DAO层;@Service用于Service层;@Controller用于Controller的声明。@Component则在DAO层、Service层和Controller都可以使用
属性注入-注解方式
普通类型
@Value("xxx")
对象类型:
- 使用@Autowired进行自动注入
- @Autowired 默认按照类型进行注入
- 如果存在两个相同Bean类型相同,则按照名称注入
- Autowired注入时可以针对成员变量或者set方法
- 通过@Autowired的required属性,设置一定要找到匹配的Bean
- 使用@Qualifier指定注入Bean的名称(统一注入名字)
- 使用Qualifier指定Bean名称后,注解Bean必须指定相同名称
- @Resource可代替@Autowired和Qualifier的组合形式
Spring的其他注解:
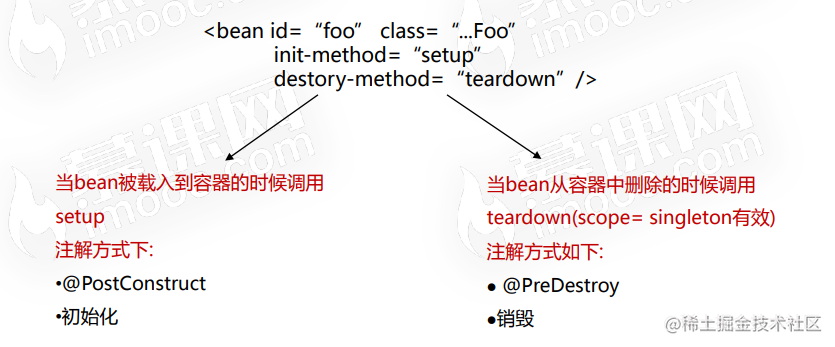
-
Spring初始化bean或者销毁bean时,有时需要做一些处理,因此spring可以在创建和拆卸bean的时候调用bean的两个生命周期方法。
XML配置和注解配置混合使用
- XML方式优点
- 结构清晰,易于阅读
- 注解方式的优点
- 开发边界属性注入方便
- XML与注解的整合开发
- 1.引入context命名空间
- 2.在配资文件中天街context:annotation- config标签
<context:annotation-config/>
<bean id="productService" class="Demo2.ProductService"></bean>
<bean id="categoryDao" class="Demo2.CategoryDao"></bean>
<bean id="productDao" class="Demo2.ProductDao"></bean>
